What Is a Washer Head Screw?
A washer head screw is a screw with an integrated washer in its design. These screws are designed to securely join parts together, providing a strong bond. The incorporation of washers improves the stability of the joint, helping to withstand vibration and shock, and reducing the likelihood of loosening.
Washer head screws are also convenient for assembly work, as the built-in washer part simplifies the process and enhances work efficiency by reducing the need for re-tightening.
Applications of Washer Head Screws
Washer head screws are used in various industries and applications:
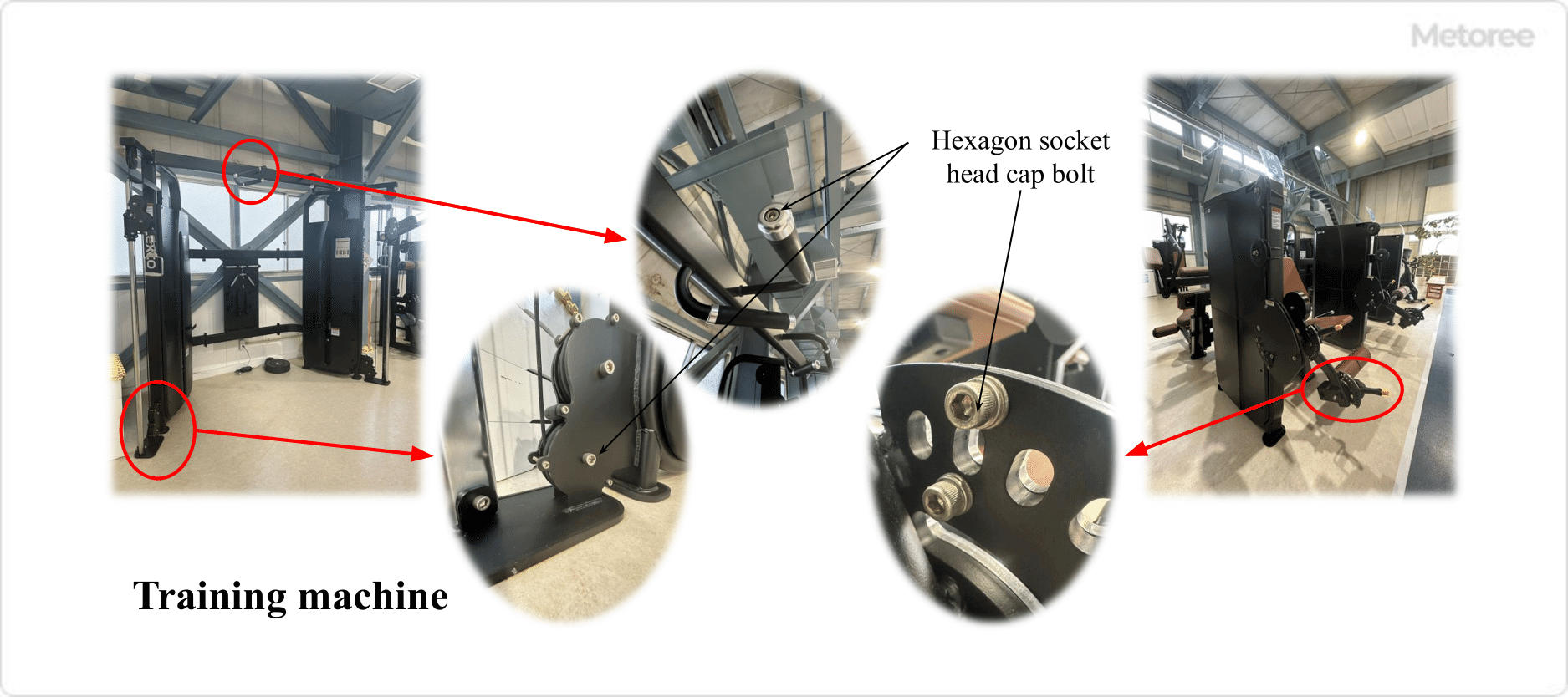
1. Automotive
In automotive assembly and repair, these screws are used in engine assembly, chassis, body panel assembly, and interior panel installation, providing stable joints capable of withstanding vibrations and impacts.
2. Electronic Equipment
Used in assembling circuit boards and enclosures in electronic equipment, these screws help in securely joining enclosure parts, preventing shifting or loosening due to vibration and shock.
3. Furniture Manufacturing
In the furniture manufacturing industry, washer head screws are used to attach metal parts to wood, ensuring stability and durability. They are also user-friendly for furniture that requires assembly by the consumer.
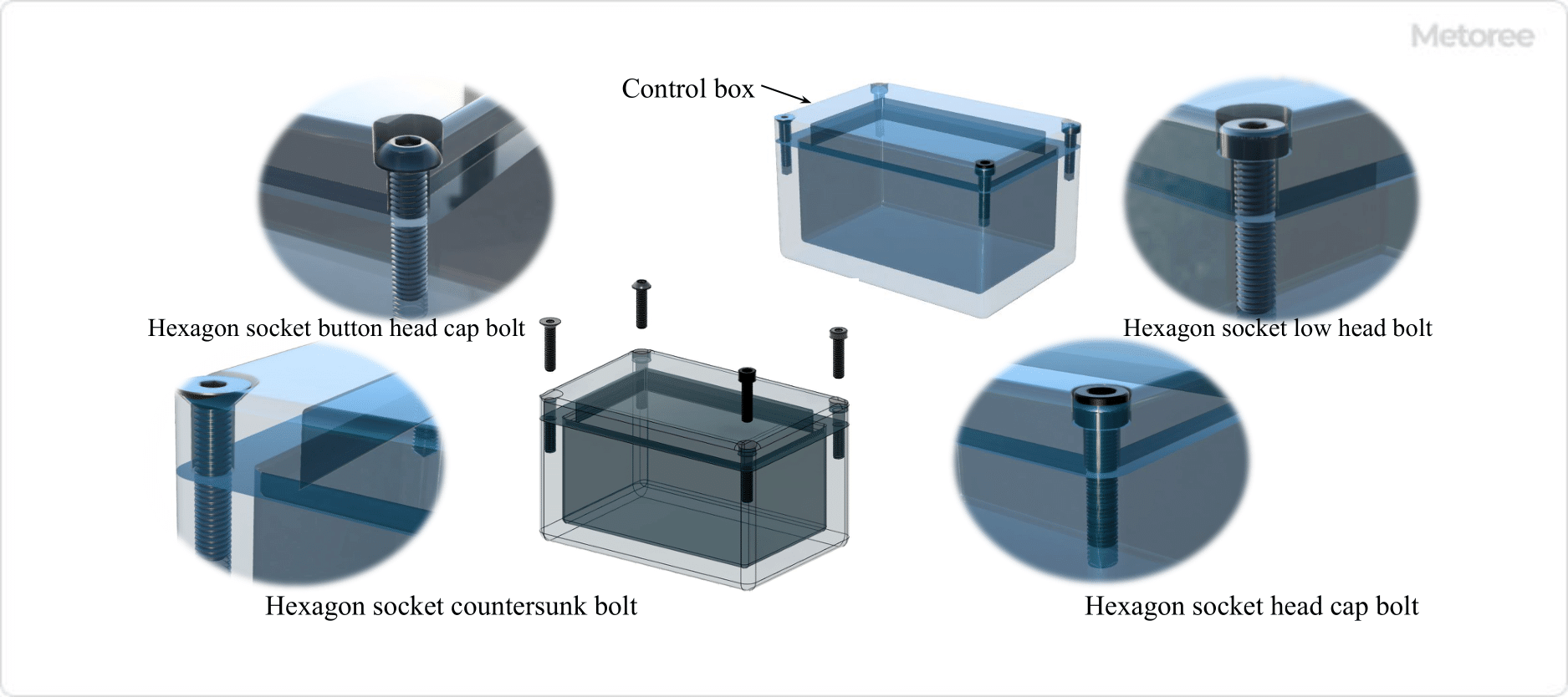
Principle of Washer Head Screws
These screws are typically made by first manufacturing the screw head and then pressing the washer through the head side, making the washer a permanent part of the screw. The manufacturing process usually leaves an unthreaded area near the base of the washer, known as the imperfectly threaded area, which must be considered when fixing thin plates.
How to Select Washer Head Screws
When choosing washer head screws, consider the following:
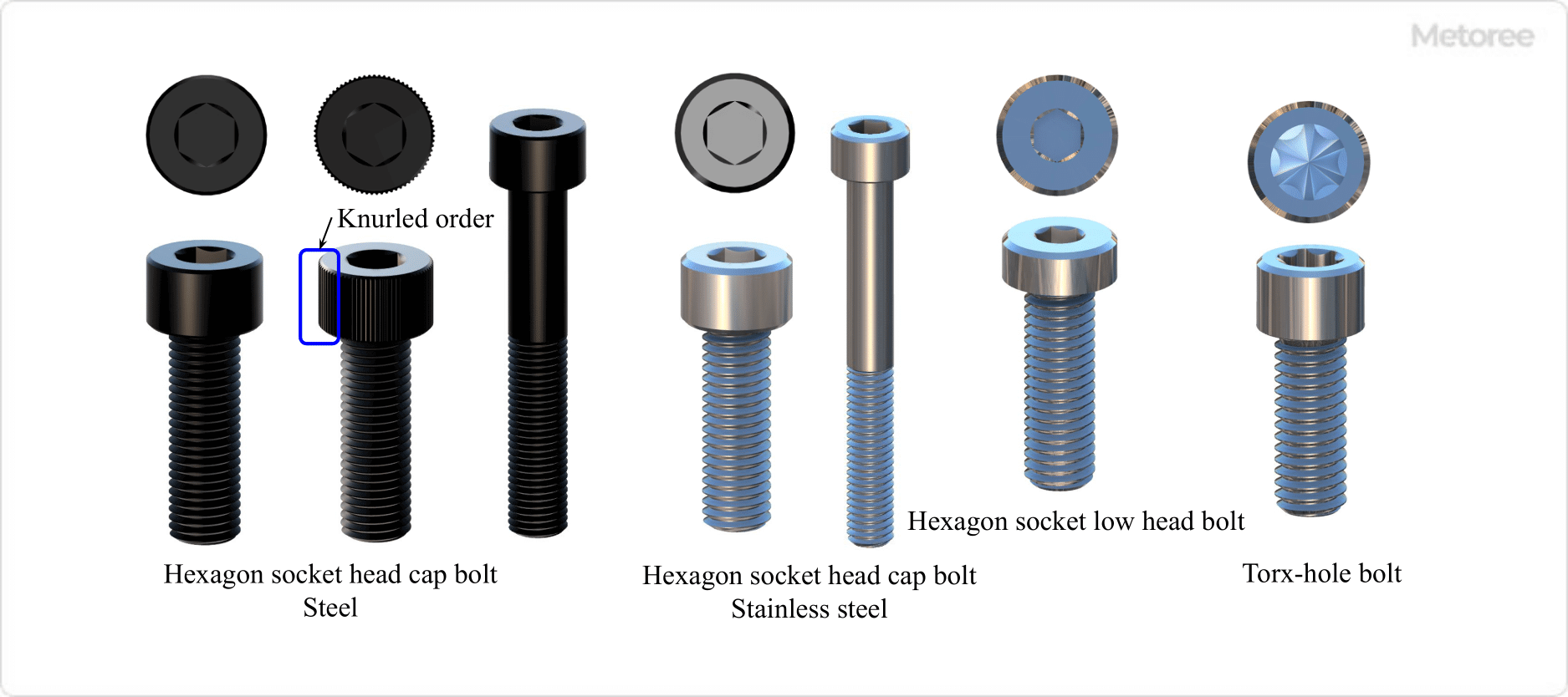
1. Head Shape
Select the head shape based on the tool used and the space available. Hexagonal heads are useful in tight spaces, while aesthetically pleasing head shapes are preferable for visible areas.
2. Material
Choose materials based on the operating environment and application. Options include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and carbon steel for strength.
3. Length
Select the correct length to ensure a secure connection without causing internal collisions or failing to bond adequately.
4. Screw Pitch
Choose the right thread pitch, which is the distance a screw travels in one turn, to ensure the effective joining of parts. Pitch is typically expressed in metric or inch measurements.