What Is a Network Analyzer?
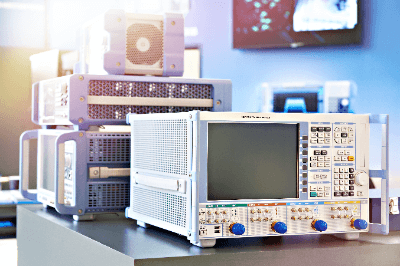
A network analyzer is a test instrument that evaluates the network characteristics of a device under test (DUT). This is done by measuring certain key S-parameters on multi-port networks.
Specifically, it can measure the attenuation and impedance of the input signal to the DUT. In particular, it can evaluate the high-frequency characteristics of electronic components, etc., and has a wide range of applications, including the ability to perform measurements on transmission devices. Such measurements can be conducted on microwave systems, common WIFI networks, corporate networks, basic computer-to-computer connections, and even on large-scale cell phone networks.
The output of a network analyzer is represented by the S-parameter (scattering parameter), which defines the physical quantities known as forward reflection (S11), forward transmission (S21), reverse transmission (S12), and reverse reflection (S22). This is typically the case with a 2-port network, but the devices or connections being tested may have more than 2 ports. Whatever the network situation, the correct Network Analyzer must be chosen to match the number of ports present. This is a basic premise but an important one if the reflection and loss parameters are to be accurately calculated.
Uses of Network Analyzers
Network analyzers are broadly classified into scalar network analyzers and vector network analyzers (VNA), of which vector network analyzers (VNA), which provide not only amplitude information but also phase information, have a wider range of uses.
The advantages of network analyzers for high-frequency applications are used in the development of matching circuits for high-frequency amplifiers. Here, the design is based on accurate S-parameters for each amplifier, antenna, and/or filter.
In many cases, a network analyzer is also used to evaluate impedance matching. This is because impedance mismatch in the transmission lines of each device or cable in a high-frequency handling circuit network can cause power loss or signal distortion.
Principles of Network Analyzers
A network analyzer is equipped with a signal source, a signal separator, a directional coupler, and at least three receivers.
- Signal Source
The signal source provides the signal to the system and is supplied by a synthesizer module.
- Signal Separator
The signal separator uses a resistor splitter to split the input signal into circuit signals and receivers (reference signal R).
- Directional Coupler
The directional coupler separates the input wave from the reflected wave, which is measured at the receiver (reference signal A).
The output of the DUT is measured at a third receiver (transmission signal B). Evaluation is performed by comparing the signals (e.g., S11 is defined by A/R and S21 by B/R).
Accurate measurement of the network analyzer is ensured by precise calibration. For calibration, a standard device with known characteristics is used. A commonly used calibration method is the SOLT method, in which a short-circuit, open-circuit, and load-capable standard are coupled to a reference plane in a direct connection (thru).
Since this is a very precise measurement, care must be taken to avoid measurement errors in various aspects such as connector tightening torque, ambient temperature, input signal, cable stability, etc.
Other Information on Network Analyzers
1. Basic Knowledge of Network Analyzers
There are two types of network analyzers: vector network analyzers (VNA) and scalar network analyzers. Vector network analyzers are widely used these days.
Network analyzers have a method of measuring amplitude changes in transmission and reflection measurements called S-parameters. S-parameters are also called S-matrices, and there is a numbering system for their definition. The numbering scheme is “Sij i=output port, j=input port,” where S11 represents the coefficient of a signal incident at port 1 that has been transmitted to port 1, S12 represents the coefficient of a signal incident at port 2 that is transmitted to port 1.
The S parameter can be measured by using a VNA measuring instrument. However, the VNA must be calibrated using several calibration methods before measurement.
The basic method of VNA calibration is to use three standard instruments. Widely known calibration methods include the SOLT calibration method, the UnKnown Thru calibration method, and the TRL calibration method described above.
2. About Impedance Measurement
Impedance is an important parameter used to characterize electronic circuits, electronic components, and electronic materials. It is the amount of opposition to an alternating current (AC) that interrupts a circuit or other device at a certain frequency. There are various types of impedance measurement methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
The measurement method must be selected in consideration of the frequency range required for the measurement and the resistance and reactance conditions of the impedance measurement range. Measurement methods include the bridge method, resonance method, I-V method, network analysis method, time domain network analysis method, and automatic balanced bridge method.
The bridge method is explained as an example. The advantages of the bridge method are its high accuracy (around 0.1%), its ability to cover a wide frequency range with multiple measuring instruments, and its low cost. On the other hand, one demerit of the bridge method is that it requires a balance operation, and a single unit can cover only a narrow range of frequencies. The bridge method’s measurement frequency range is approximately 300-MHz DC.
3. Trends in Frequency Extension
The maximum frequency extension of network analyzers now extends into the sub-THz band (220 GHz). This is because it is predicted that the next generation communication standard, 6G, will most likely use the 140 GHz band, known as the D-band.
However, because of its high frequency, the sub-THz band is susceptible to electrical length errors, parasitic elements, and other measurement discontinuities, making total calibration accuracy, including that of the RF probe tips and cables, extremely important.
In reality, the frequency range that can be calibrated at one time is often limited, and manufacturers are competing to develop easy-to-use measuring instruments, including the handling of data between calibrations and the addition of frequency extenders dedicated to the millimeter wave band.
4. Addition of Modulated Power Evaluation Function, Etc.
Generally speaking, Network analyzers are used to evaluate the impedance of DUTs and S-parameters, which are small signals. Therefore, models that enable network analyzers to perform modulation analysis, which is mainly handled by conventional spectrum analyzers, are gradually being released. With wireless technologies on the increase, the ability to examine complex RF (Radio Frequency) bands is an essential feature, one worth integrating into a Network Analyzer.
In the future, network analyzers will be used not only for impedance and S-parameter evaluation but also for evaluating switches, filters, high-frequency (RF) amplifiers, low-noise amplifiers (LNA), and other RF front ends, including large-signal analysis and modulation analysis.


 A high-voltage power supply unit is a
A high-voltage power supply unit is a 

