What Is a Separator?
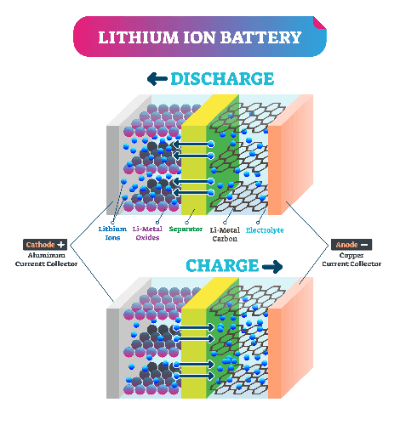
A separator is a component that separates the positive (anode) and negative (cathode) electrodes of a secondary battery to prevent electrical contact between the positive and negative electrodes and ensure ion conductivity. The types of batteries include nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries, fuel cells, and more.
Although specifications differ depending on the battery type, such as nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and fuel cells, the common feature is that it is a component that facilitates the fundamental electrochemical reaction between the positive and negative electrodes.
For example, in a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions (Li+) and electrons move in and out between the positive (anode) and negative (cathode) electrodes to charge and discharge the battery.
This is achieved by creating a small hole in the separator to allow lithium ions to pass through.
Application of Separators
In this section, we will describe an example of the application of separators used in lithium-ion batteries. With the proliferation of tablet PCs and electric vehicles, there is a growing demand for lithium-ion batteries with higher capacity and energy density.
Separators are used to insulate the positive (anode) and negative (cathode) electrodes, prevent abnormal heat generation due to short circuits, and facilitate the charge and discharge of the battery through proper ionic conduction between the positive (anode) and negative (cathode) electrodes.
Here are some examples of separators used in lithium-ion batteries:
- Separators for automotive laminated lithium-ion batteries
- Separators for automotive rectangular lithium-ion batteries
- Separator for a laminated lithium-ion battery for smartphones
Principle of Separators
This section explains the principle of separators used in lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are charged and discharged by the conduction of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes, and an electrolyte is injected to facilitate the conduction of lithium ions. During this process, if electrons are conducted through the electrolyte, electricity cannot be transmitted to the external circuit. Therefore, a separator is placed between the positive and negative electrodes to allow only lithium ions to pass through and prevent internal short circuits caused by contact between the positive and negative electrodes.
As a result, the separator must possess ion conductivity and electrical insulation properties. Additionally, it requires materials that are electrically, chemically, and mechanically robust to ensure stable battery operation. For this reason, separator materials and shapes are modified in various ways depending on the application to enhance the efficiency of the electrochemical reaction of lithium ions from the positive electrode (anode) to the negative electrode (cathode).
Examples of Technological Innovations in Separators
Fluoroplastic Coating
- Objective: To enhance adhesion in the production of laminated cells
- Summary: The use of fluoropolymer coating enables strong adhesion between electrodes (positive and negative electrodes). Separators are gaining attention as a technology that can prevent cell deformation, improve the C-rate, and develop structures that lead to higher capacity.
 A Raised Access Floor is a floor with a fixed height space under the floor. The purpose is to pass network wiring, etc., which tend to become cluttered, through the space under the floor. It is also known as free-access floor or a double-layered floor.
A Raised Access Floor is a floor with a fixed height space under the floor. The purpose is to pass network wiring, etc., which tend to become cluttered, through the space under the floor. It is also known as free-access floor or a double-layered floor. A
A 



 Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Grating is a
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Grating is a 
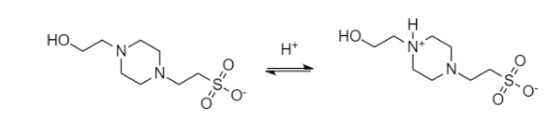
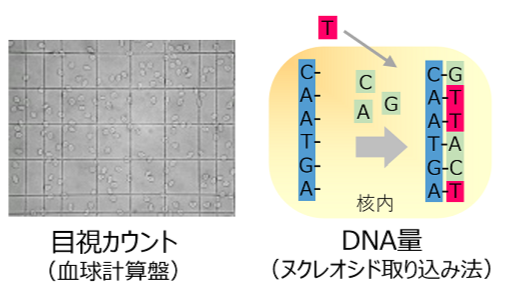
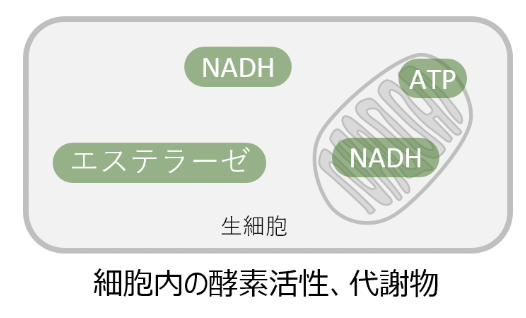 細胞毒性 / Cytotoxicity
細胞毒性 / Cytotoxicity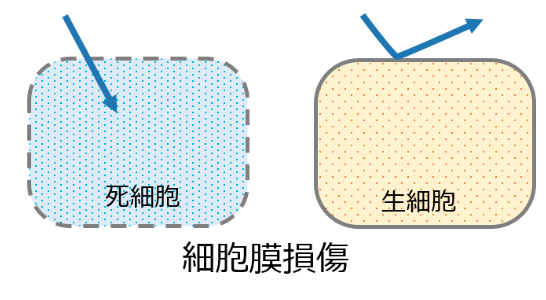
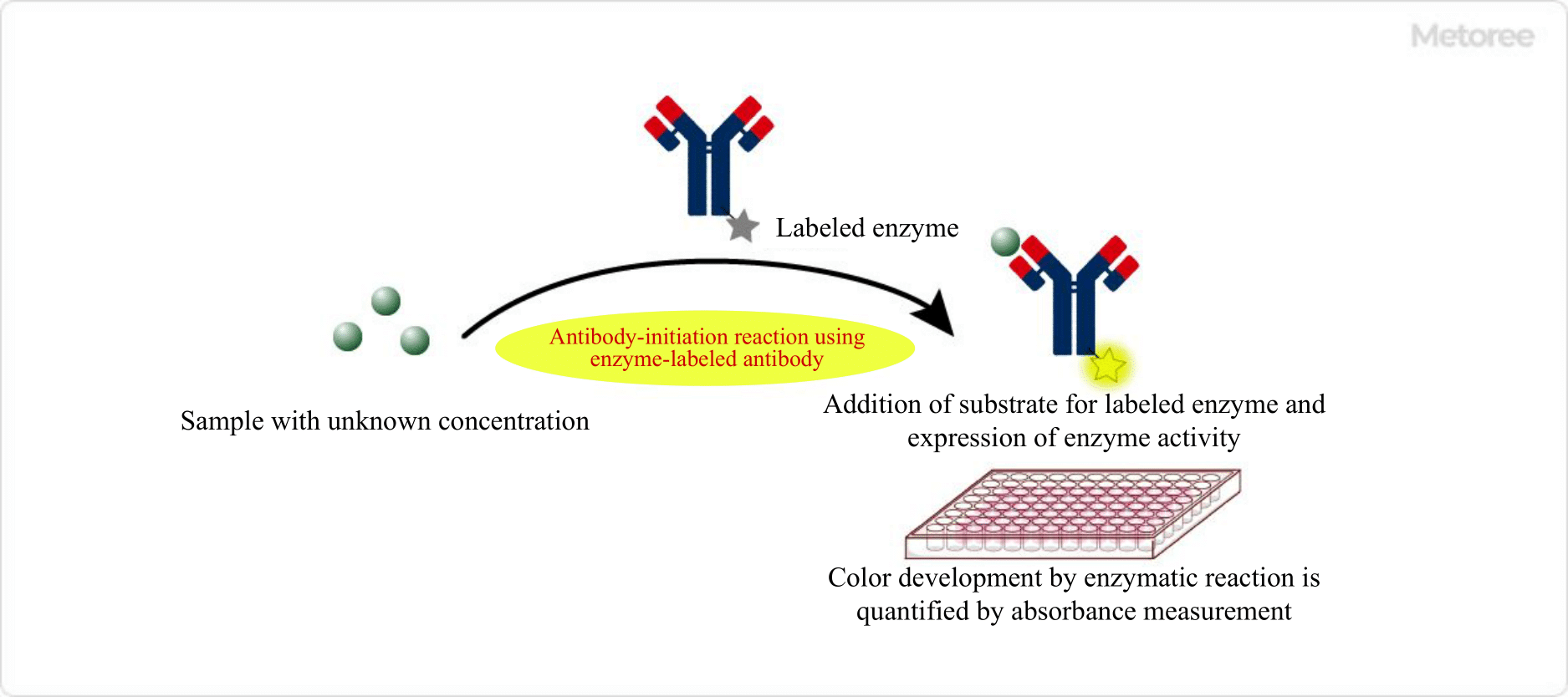
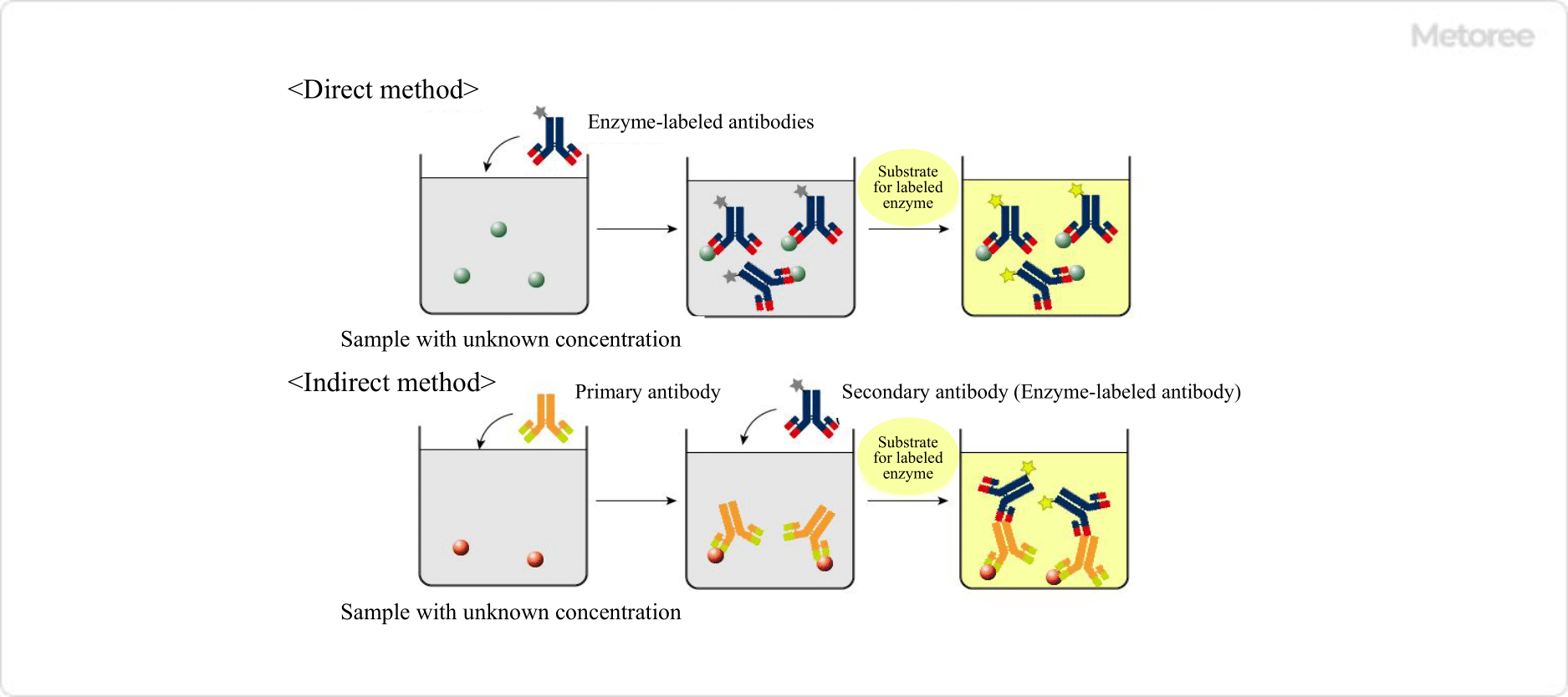
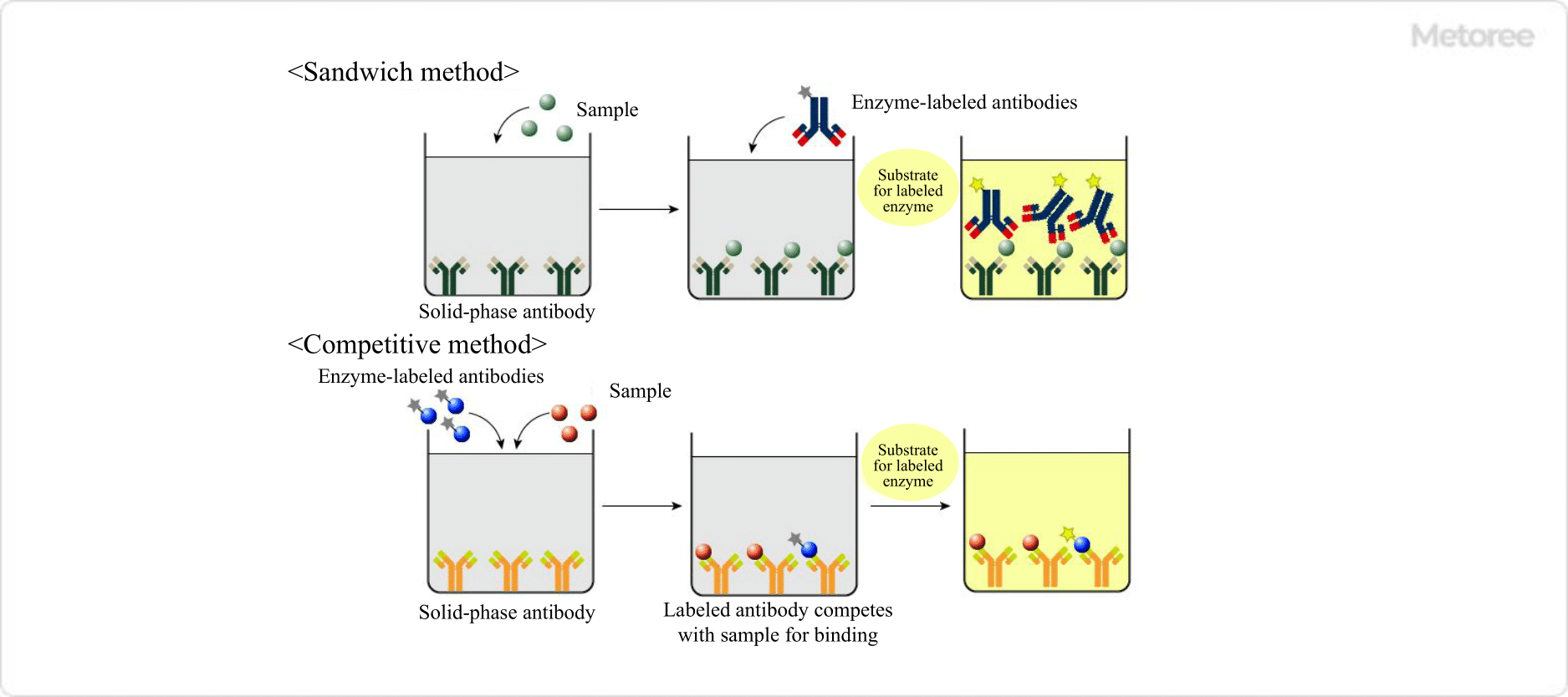
 A CT (Computed Tomography) Scanner is a scanner used for inspection.
A CT (Computed Tomography) Scanner is a scanner used for inspection.
