What Is an ELISA Kit?
An ELISA Kit is one of the immunoassay method using antibodies for quantification by ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay).
ELISA is a method for quantifying trace amounts of biological substances using an antigen-antibody reaction.
Uses of ELISA Kits
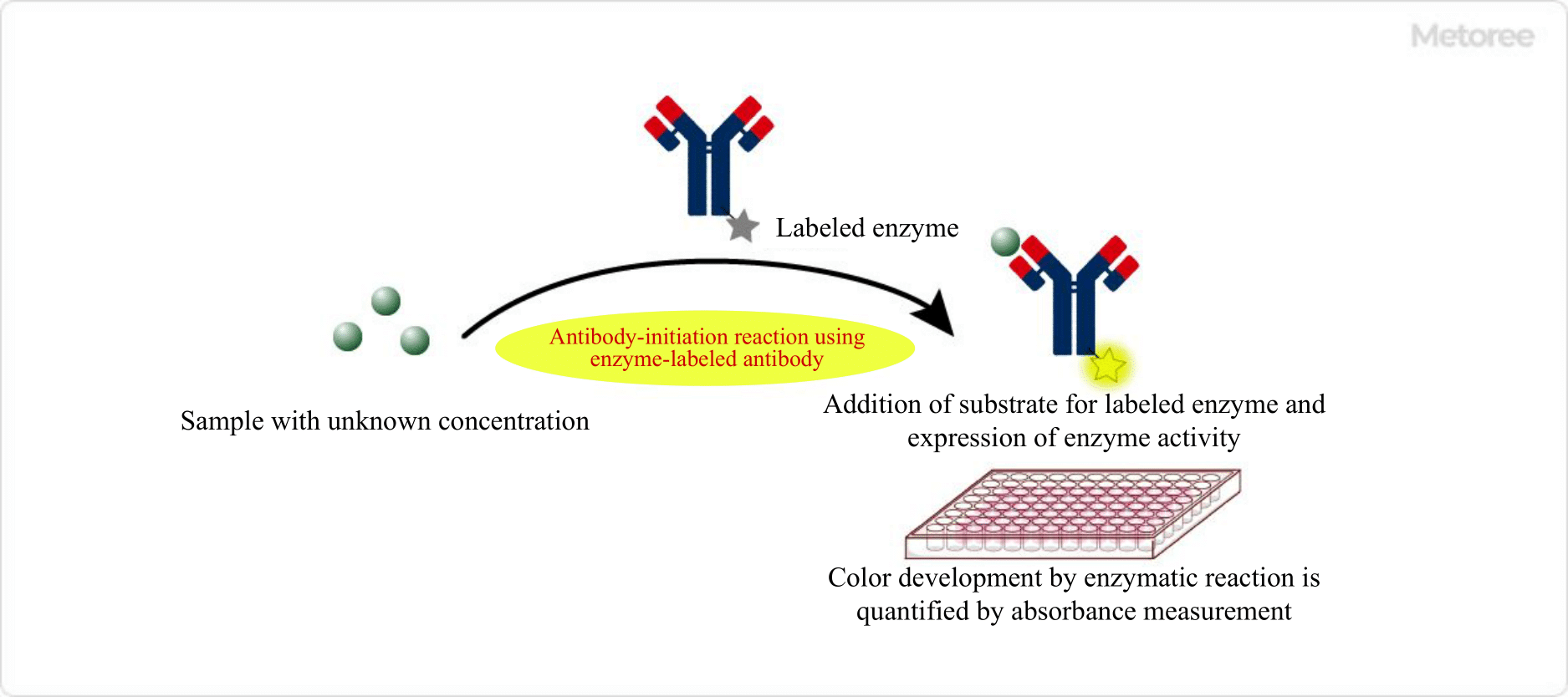
Figure 1. Overview of ELIS
ELISA kits are often used in the field of biology from the viewpoint that trace amounts of biological substances can be detected with high accuracy by antigen-antibody reaction. For example, they are used to measure blood proteins such as cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, or in immuno-oncology to measure soluble immune checkpoint molecules to elucidate the status of cancer immunity.
In neurobiology, they is used to quantify Aβ, tau, and α-synuclein proteins that are known to cause neuropathy.
Other ELISA kits, such as phosphorylation-specific kits and immunoglobulin kits, are available, allowing you to select the ELISA kit that best suits your research and objectives.
Competitive ELISA analysis is also appropriate when measuring histamine, pesticides, dioxin, etc.
Principle of ELISA Kits
ELISA uses an antibody or an antigen that binds specifically to the substance to be measured (antigen-antibody reaction). Finally, an enzyme-labeled antibody (or antigen) is used to detect and evaluate enzyme activity by absorbance measurement.
By measuring the enzyme activity, the concentration of the enzyme in solution, the substances in the reagents involved in the antigen-antibody reaction, and the target substance can be quantified.
There are four main methods: direct method, indirect method, sandwich method, and competitive method.
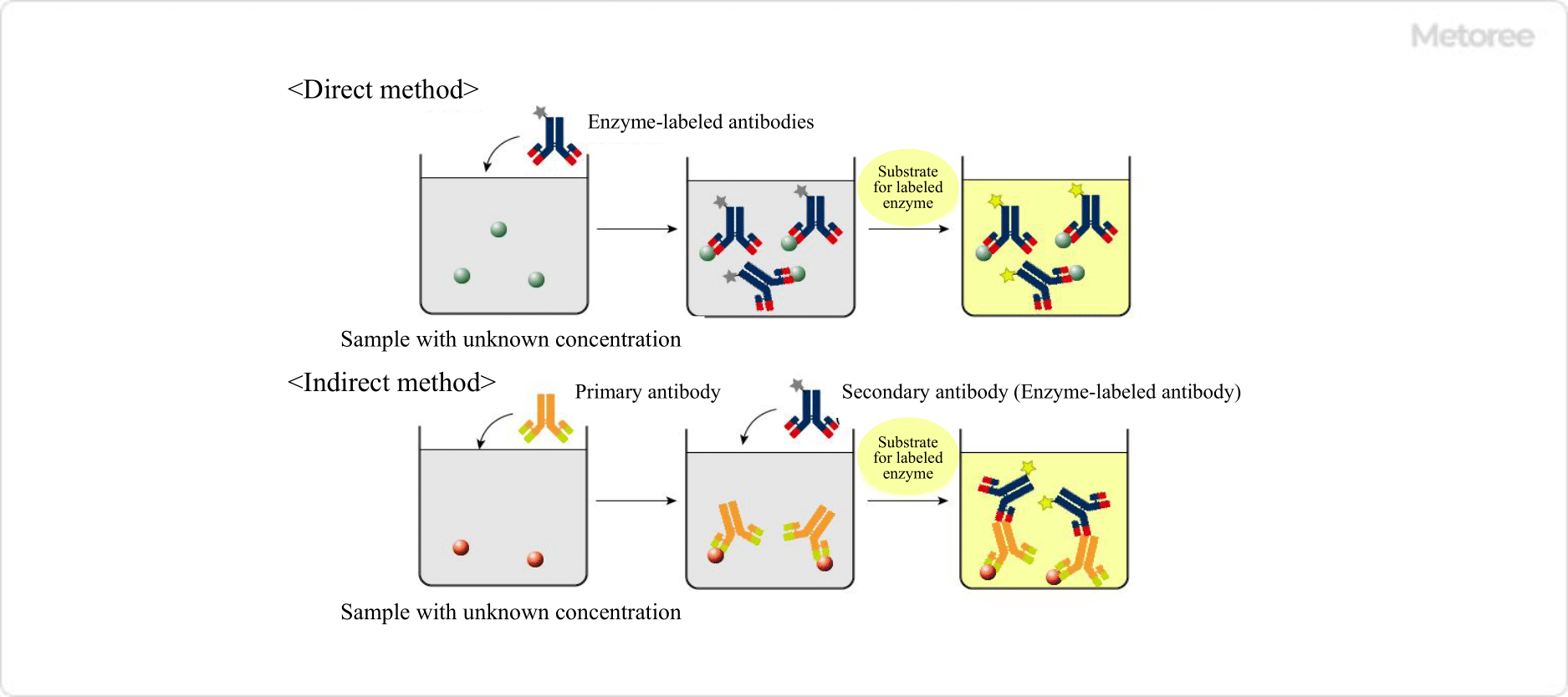
Figure 2. Direct and indirect methods
1. Direct Method
In this method, the target antigen or antibody is solid-phased on a microplate, and the labeled antigen or antibody directly interacts with it. After the antigen or antibody is applied, the plate is washed and the enzyme activity on the microplate is detected. Since no secondary antibody is required, this method can be performed in a single step and in a short time.
2. Indirect Method
First, an antibody specific for the target antigen is applied to the solid-phase microplate. Then, the enzyme activity of the enzyme on the labeled secondary antibody is detected. This method is characterized by increased sensitivity, but requires more time than the direct method.
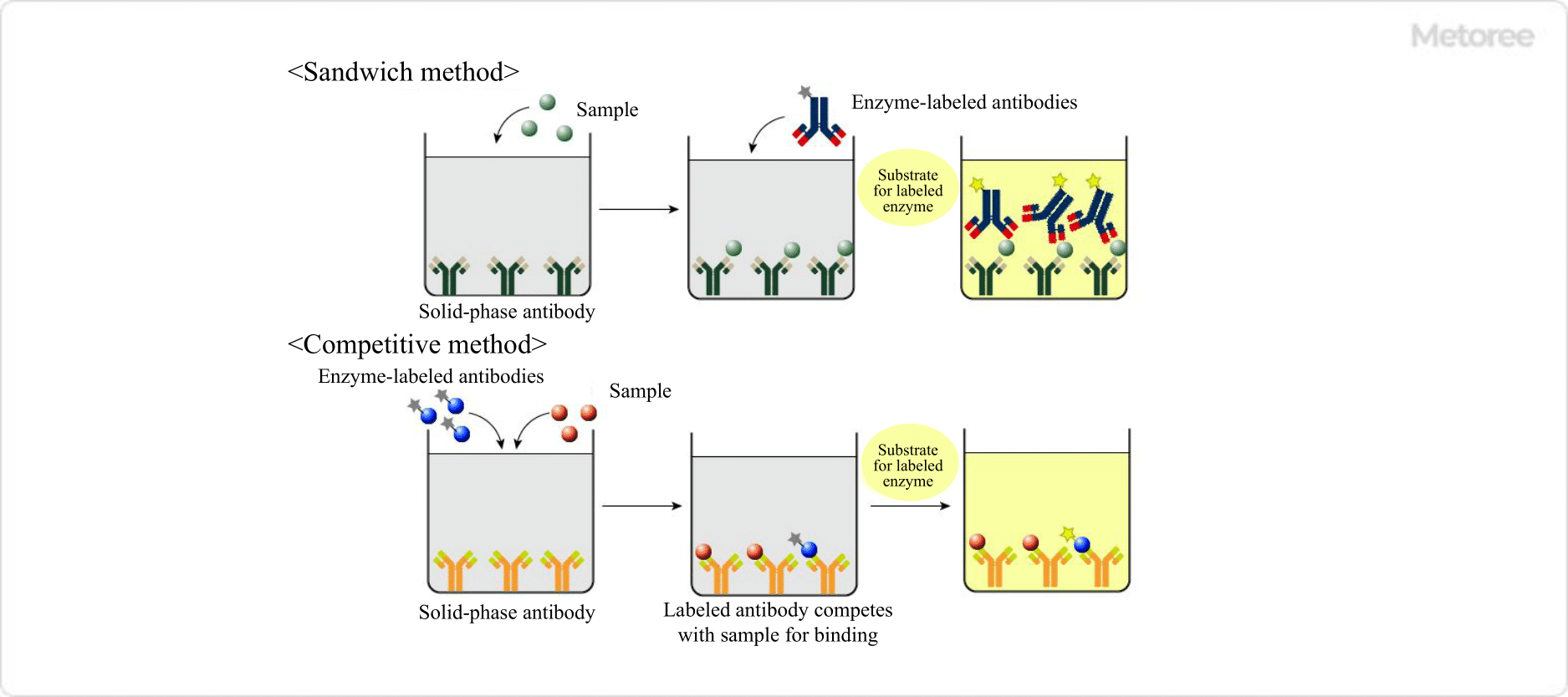
Figure 3. Sandwich and competitive methods
3. Sandwich Method
A microplate coated with an antibody that binds to the target substance in the sample is used to react with the sample as an antigen. Subsequently, the sample is reacted with another antibody labeled with an enzyme, and the excess antibody is washed off before the enzyme activity on the microplate is measured.
It is necessary to select an antibody that has a different antigen recognition site from the antibody used for solid phase and the enzyme-labeled antibody.
The advantage of the sandwich method is that the specificity of the reaction is higher than that of the direct method, resulting in higher detection accuracy.
4. Competitive Method
The competitive method can be used to measure small molecules that are difficult to detect with the sandwich method, or when there is only one binding site for the antibody.
An antibody that binds to the target substance is coated on a solid phase, and the sample is simultaneously reacted with a labeled antigen of known concentration. If the sample contains a large amount of the target substance, the absorbance decreases because there is little enzyme-labeled antigen that can bind to the antibody.
Conversely, if the sample contains less of the target substance, more of the enzyme-labeled antigen is available to bind to the antibody, resulting in an increase in absorbance.
How to Select an ELISA Kit
As mentioned above, since detection is performed using specific antigen-antibody reactions, the first prerequisite is to use a product that uses the correct combination of reagents for the sample. In addition, whether using direct, indirect, sandwich, or competitive methods, each method has their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to select the most preferable one according to the purpose of the measurement.
Solid-phase attachment to a microplate is generally by hydrophobic interaction or covalent bonding, and it is important to select the correct microplate according to the binding mode. In addition to hydrophobic and hydrophilic types, many types are available, including those processed with amino and carboxyl groups for covalent binding applications.