What Is an Engine Lathe?
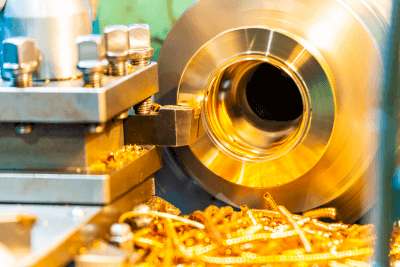
A lathe is a type of machine tool for metalworking. The workpiece is fixed to a rotating base called a chuck. A cutting tool called a bite is applied to the workpiece to cut it into the desired shape.
There are various types of lathes, of which the most basic is the engine lathe. Generally, the word “lathe” means an ordinary engine lathe.
An engine lathe consists of parts including a spindle head, bed, tailstock, feeder, and reciprocating table. The shaving process, which involves applying a tool to the workpiece, can be done by hand. By changing the type of byte, various types of machining can be performed with a single machine.
Uses of Engine Lathes
Lathes are used for processing cylindrical or bar materials, as they rotate and sharpen the workpiece. In lathe turning, the workpiece is made symmetrical to the axis of rotation, so lathes are used for machining to create cylindrical or conical shapes, threading, and other operations.
In factories and other workplaces, numerically controlled (NC) lathes are most widely used, as they perform machining automatically by numerical control. However, engine lathes are suitable for complex and difficult processing that NC lathes cannot handle, as well as for small-lot processing such as prototypes and custom-made products.
In addition, since the use of an engine lathe enables a good understanding of lathe principles, they are widely used for educational and practical training purposes at technical high schools and vocational schools.
Features of Engine Lathes
Engine lathes consist of a spindle head, bed, tailstock, feeder, and reciprocating table.
The spindle head is equipped with a spindle and motor that rotates the workpiece, a spindle speed converter, and a start lever. The spindle is equipped with a chuck that holds the workpiece. The chuck grips the workpiece in a mechanical, magnetic, or vacuum type. However, the most common type is the mechanical type.
The tailstock is a movable stand installed on the opposite side of the spindle head and can be fixed in position according to the length of the workpiece. A support center can be set on the axis of the tailstock to support the workpiece or a drill can be set for drilling.
The reciprocating table is located between the spindle head and the tailstock and consists of a saddle, an apron, and a tool rest to mount a tool. The feed unit is located on top of the reciprocating table and feeds the tool post vertically or horizontally.
The bed is the main body of the lathe and supports the spindle head, tailstock, reciprocating table, and other devices. Since large cutting resistance is generated during cutting, the bed must be rigid enough to withstand such resistance. In addition, vibration caused by the motor must be suppressed in order to improve machining quality.
Machining operations that can be performed with engine lathes include external rounding to cut the outside of a workpiece into a cylindrical shape, tapering to make the workpiece conical, plunge cutting to separate the material, boring to machine the inside of a cylinder and thread cutting.