What Is a Pillow Block?
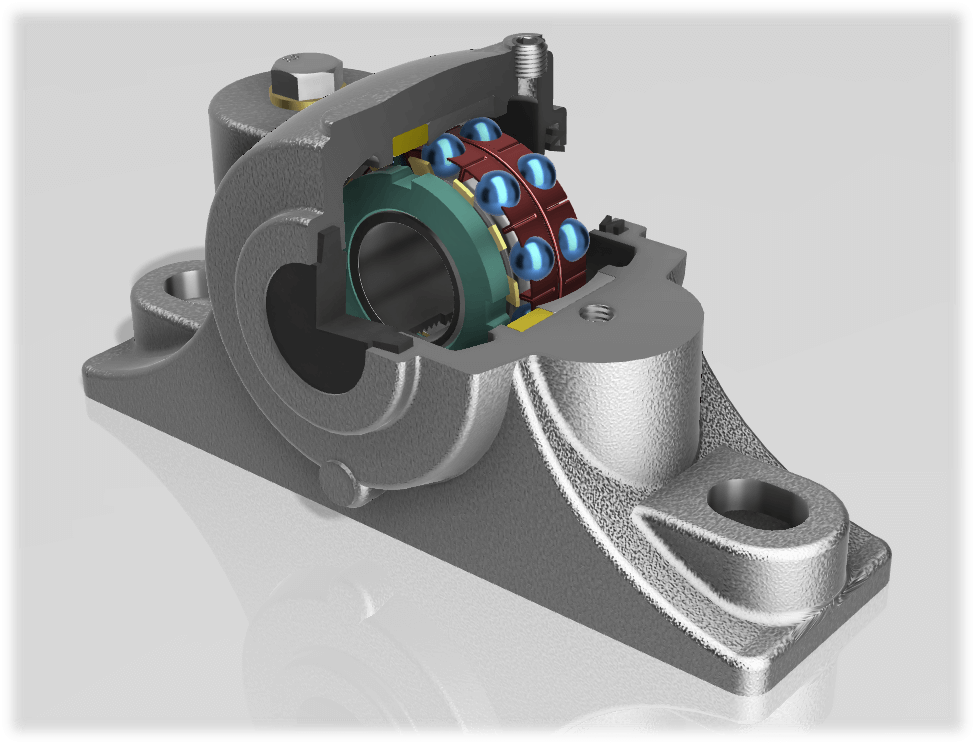
A pillow block is a bearing assembly that includes a housing with a mounting seat and bolt holes for mounting on a support surface parallel to the bearing center axis, along with a radial bearing.
The choice between spherical ball bearings and spherical roller bearings depends on the shaft diameter, with the bearing housing and bearings being interchangeable across different manufacturers.
Uses of Pillow Blocks
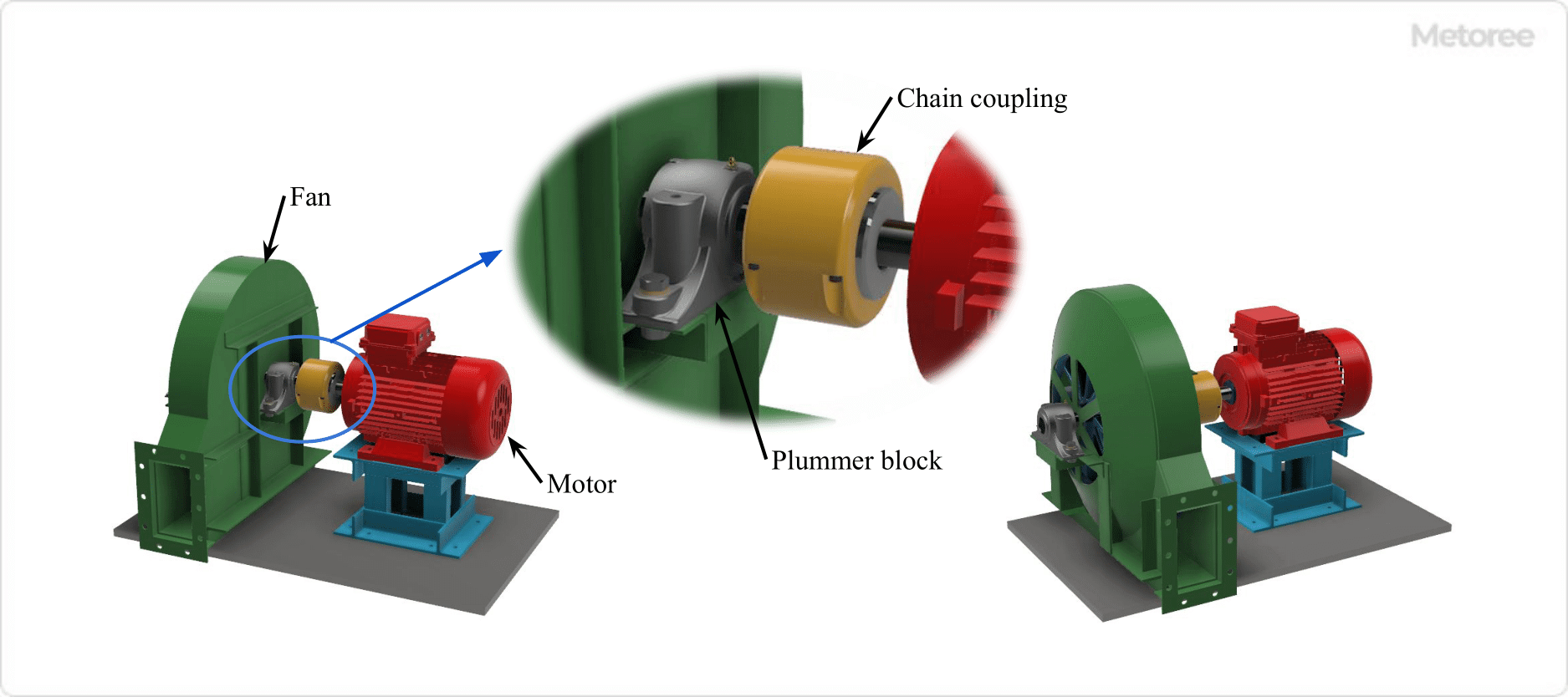
Figure 1. Example of Plummer Block Application (Turbofan Bearing)
Pillow blocks support rotating shafts with bearings in situations where the machine or equipment cannot directly accommodate the bearings, typically installed at both ends of a shaft.
- They offer reliable support in various environments, including dusty or outdoor settings.
- The bearings within pillow blocks are easily replaceable, facilitating maintenance.
Principle of Pillow Blocks
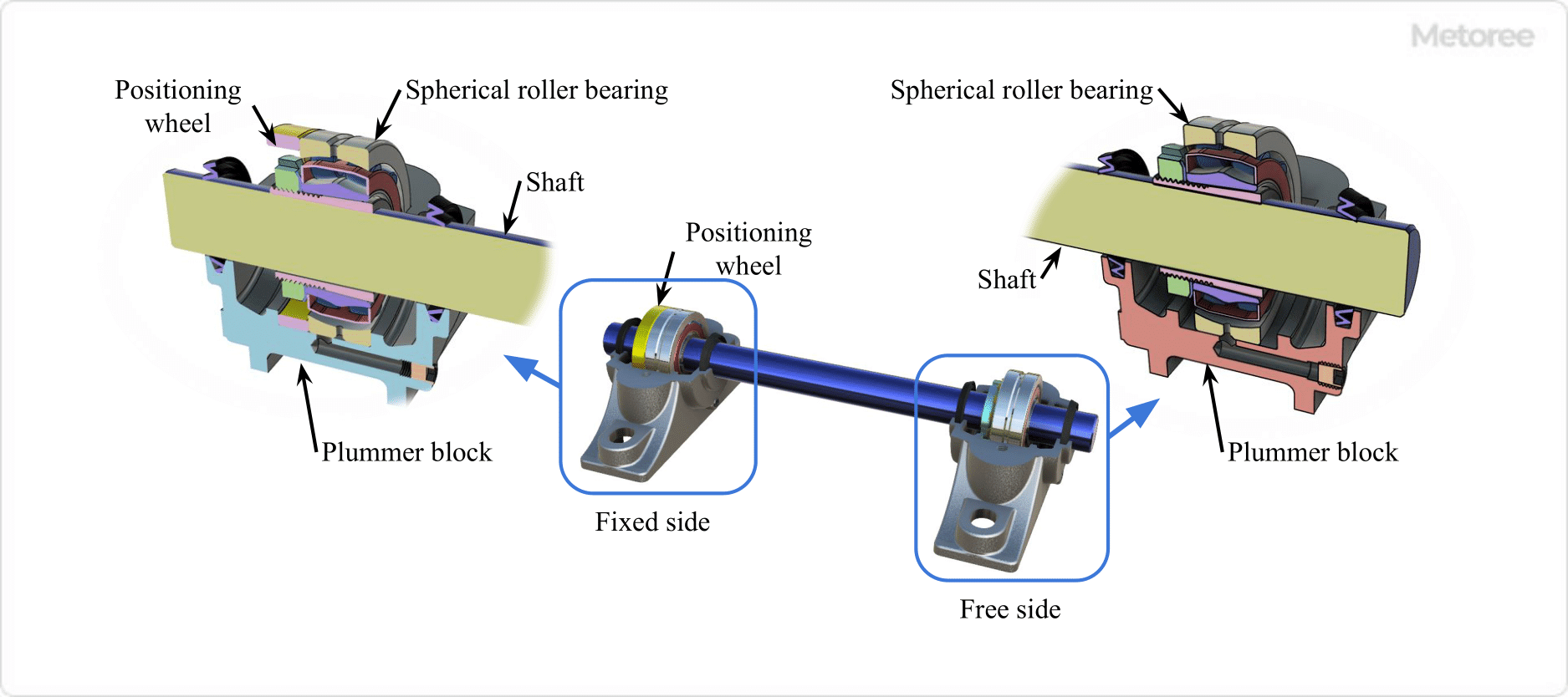
Figure 2. Fixed Side and Free Side
Pillow blocks, accommodating both radial and a certain amount of thrust loads, should differentiate between the fixed side and the free side for optimal performance, as illustrated in Figure 2.
Structure of Pillow Blocks
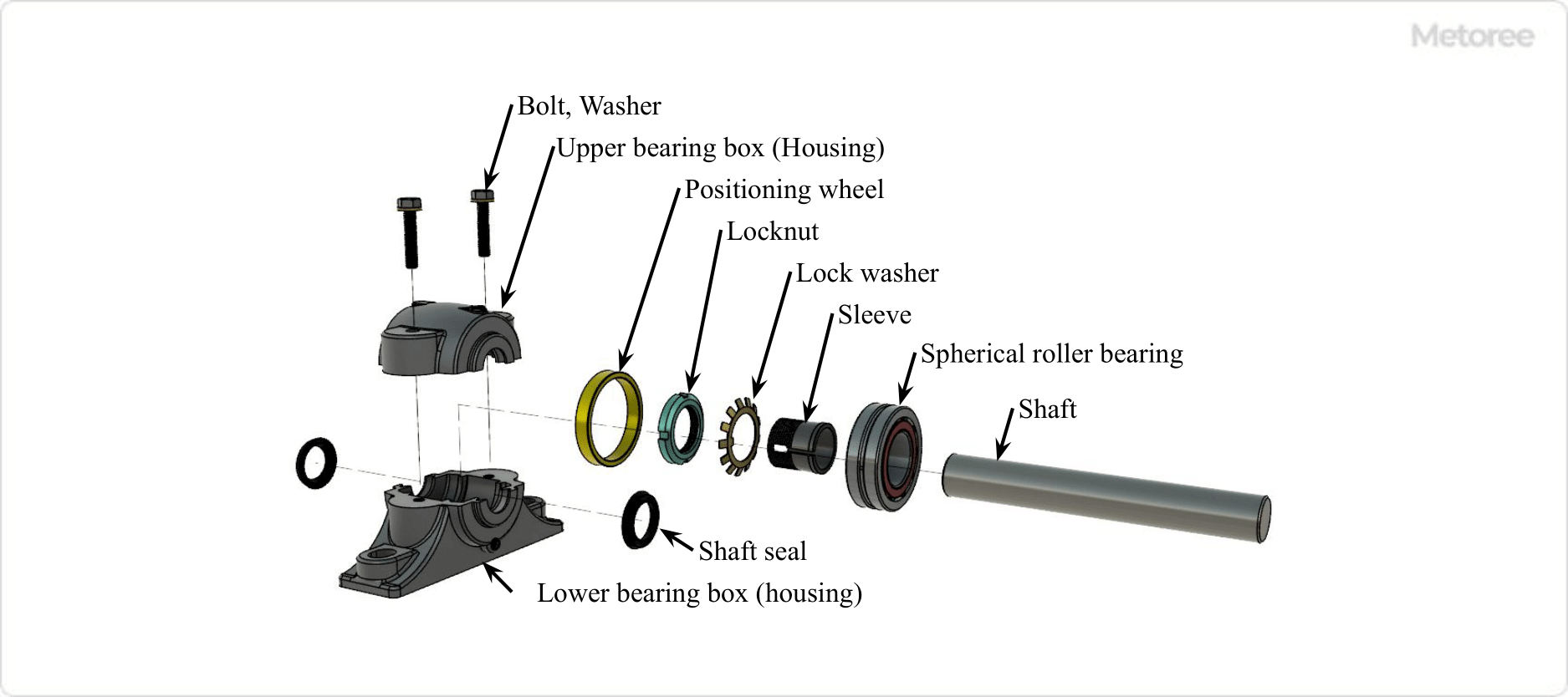
Figure 3. Structure of a Plummer Block (Segmented Type)
The structure of a pillow block includes a bearing housing, bearings, and a shaft seal, which can be of the split or integral type, each suited for different applications.
1. Bearing Housing
The split type, allowing for easy bearing replacement and maintenance, contrasts with the integral type, known for its rigidity and suitability for large shaft diameters.
2. Shaft Seal
Shaft seals, crucial for preventing lubricant leakage, vary between contact and non-contact types, each offering different benefits.
Other Information on Pillow Blocks
1. Standards for Pillow Blocks
Pillow blocks adhere to standards such as ISO 113, ensuring reliability and quality.
2. Material of Pillow Blocks
Materials used for pillow block housings include grey cast iron, spheroidal graphite cast iron, carbon steel castings, and carbon steel forgings, chosen for their durability and performance.
3. Difference Between Pillow Block and Plummer Block
Another bearing assembly with a similar shape and usage to the pillow block is the pillow block. Both are used by assembling a bearing housing and a bearing, but there are some differences.
While the plummer block allows the replacement of individual bearings, the pillow block does not allow replacement of individual bearings and requires replacement of the entire assembly.
Other differences in application are as follows.
| Pillow Blocks | Plummer Blocks | |
| Loads that can be supported | Large loads | Relatively small load |
| Applicable shaft diameter | Large diameter | Small bore diameter |
| Rotation supported | High-speed rotation | Low-speed rotation |
 A hang rail is a versatile fixture installed on ceilings and walls for hanging items like sliding doors, tools, and semi-finished products. It serves as a track for sliding mechanisms in various settings.
A hang rail is a versatile fixture installed on ceilings and walls for hanging items like sliding doors, tools, and semi-finished products. It serves as a track for sliding mechanisms in various settings. A leveling mount is a mechanical component that adjusts the height or maintains the
A leveling mount is a mechanical component that adjusts the height or maintains the