What Is a Log Splitter?
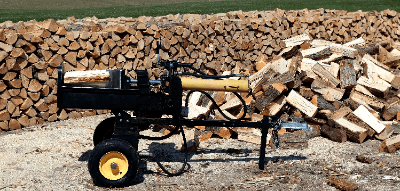
A log splitter is a machine designed to efficiently perform the task of splitting logs.
Compared to manual splitting, a log splitter allows for precise log splitting and makes the task much easier. It also reduces the chances of errors in log splitting.
Uses of Log Splitters
Log splitters are used for the production of firewood from logs. While logs can be split manually using an axe, using a log splitter enables efficient log splitting with minimal effort.
Features of Log Splitters
Advantages
One of the primary advantages of log splitters is their ability to produce a large quantity of firewood in a short amount of time. Manual log splitting with an axe can be time-consuming and physically demanding.
By introducing a log splitter, work can be conducted more efficiently.
Disadvantages
One of the disadvantages of log splitters is the associated cost. There are various types of log splitters, and the costs vary, but generally, there is an initial investment cost.
Additionally, log splitters such as electric or engine-powered ones may require regular maintenance, leading to ongoing operational costs beyond the initial purchase.
Types of Log Splitters/h3>
Log splitters can be categorized into three types: “manual,” “electric,” and “engine-powered.”
1. Manual Log Splitters
Manual log splitters operate by moving a lever to press logs against a blade to split them. They are ideal for locations without a power source. Additionally, they are quieter compared to electric or other types, making it possible to split logs quietly.
However, due to the manual operation, they require significant physical effort. For large-scale log splitting, considering electric or engine-powered options is advisable.
2. Electric Log Splitters
Electric log splitters automatically split logs when connected to a power source. They are particularly useful for efficiently splitting a large quantity of logs in a short time. They require less physical effort, making them suitable for individuals of various physical abilities.
However, it’s important to check the specifications of the power source before purchasing an electric log splitter.
3. Engine-Powered Log Splitters
Engine-powered log splitters can be used without restrictions on location, as they don’t depend on a power source. They have a strong horsepower, allowing for quick log splitting.
However, these log splitters tend to be heavy, which can make moving and operating them somewhat challenging. They are especially useful when used in a stationary setting.
Choosing a Log Splitter
When selecting a log splitter, it’s essential to consider factors such as “splitting force,” “work speed,” and “splitting method.”
1. Splitting Force
Start by assessing the splitting force when choosing a log splitter. For logs with a diameter of up to 30cm, a log splitter with a force of 6.5t is generally sufficient. For larger logs with a diameter exceeding 30cm, consider a log splitter with even greater force.
Additionally, keep in mind that the hardness of the wood can vary depending on the type and dryness, so consider these factors as well.
2. Work Speed
In addition to splitting force, work speed is crucial when selecting a log splitter. Each log splitter comes with a specification known as “cycle time,” which indicates the speed of log splitting. A shorter cycle time allows for more efficient log splitting.
However, be aware that log splitters with shorter cycle times may have lower splitting force, so it’s essential to strike a balance between the required force and cycle time.
3. Splitting Method
Log splitters typically offer either “vertical splitting,” “horizontal splitting,” or a “combined vertical and horizontal” splitting method. Vertical splitters allow logs to be split without lifting them, reducing the physical strain.
Horizontal splitters, on the other hand, require lifting logs for placement. Combined log splitters have both functions but tend to be heavier due to the inclusion of both features.