What Is Polyester?

Polyester is a general term for polymers formed by ester bonds.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a typical example. By changing the alcohol or carboxylic acid that forms the ester bond, the properties of the resulting polyester can be changed. It is used in various applications, but typical examples include materials for clothing, bedding, and curtains.
Uses of Polyester
Typical applications for polyester include polyethylene terephthalate (PET) for PET bottles, polyester fibers, and cable protectors for electronic devices and automotive parts. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) is also used as a polyester fiber.
Another type of polyester is unsaturated polyester, which has unsaturated bonds in the molecule. FRP is used in a wide range of industries, including aircraft and other transportation components, construction materials, sporting goods, and space-related components, such as rockets.
Production Process of Polyester
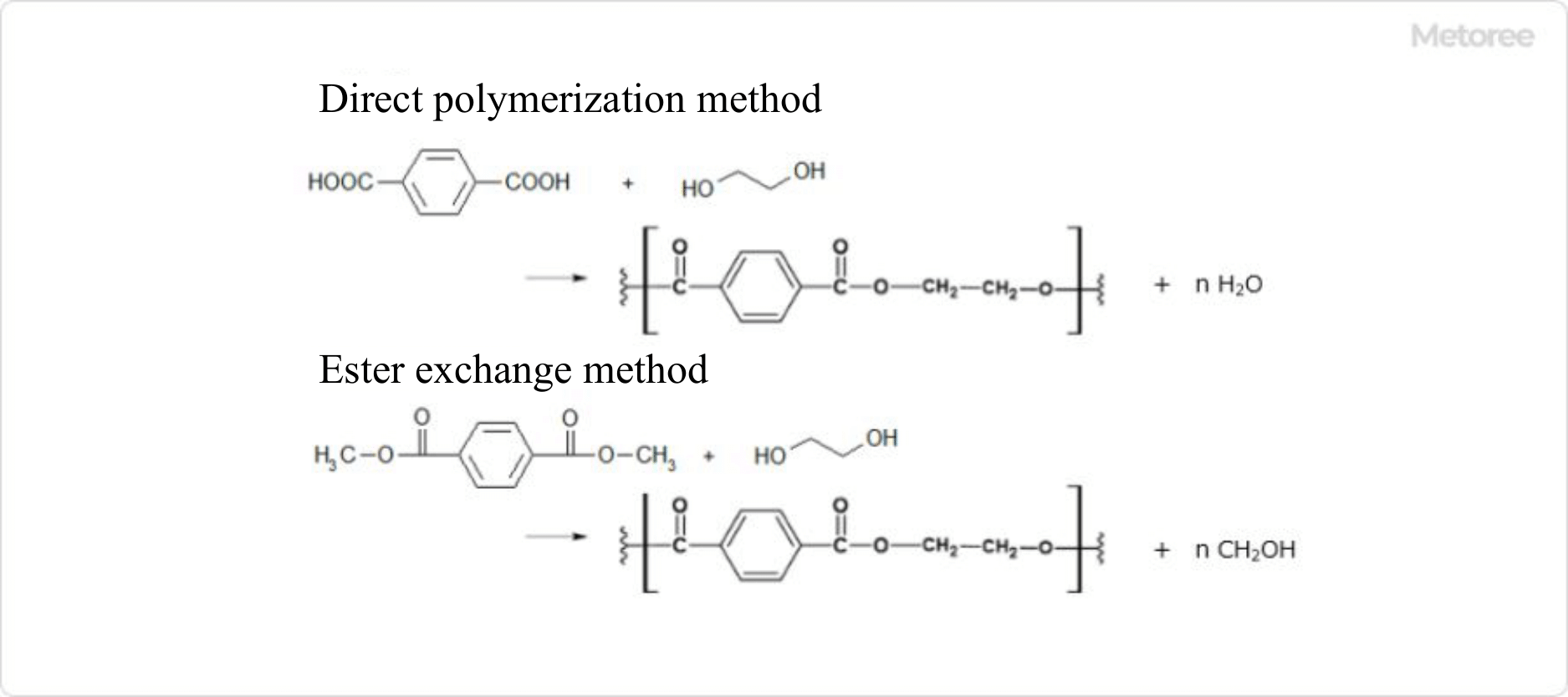
Figure 1. Production process for polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
There are two methods of polyester production: direct polymerization, in which a divalent alcohol and a divalent carboxylic acid are dehydrated and condensed to form an ester bond. The second method is ester exchange, in which a dicarboxylic acid ester and a divalent alcohol undergo an ester exchange reaction.
Various polyesters can be made by changing the divalent alcohol and divalent carboxylic acid used in the dehydration-condensation process, and their physical properties also change, resulting in different applications. For example, polyethylene terephthalate with two alcohol carbons is used as a material for fleece and other clothing, while polybutylene terephthalate with four alcohol carbons has high durability and stretchability and is used for sportswear and swimwear.
Polyester has different properties depending on their molecular structure. Their common characteristics are high strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity. On the other hand, its disadvantages are that it is easily electrified and has low heat resistance.
Other Information on Polyester
1. Differences Between Polyester and Nylon
Nylon is a polymer similar to polyester, but its chemical structures are very different. Polyester is formed by ester bonds, while nylon is formed by amide bonds.
Polyester fibers are characterized by their firmness, elasticity, resistance to wrinkling, and resistance to acids and alkalis. In contrast, Nylon fibers are lightweight and dry quickly. Polyester fibers are similar in appearance and feel to cotton and wool, and are used in women’s and men’s clothing. Nylon fibers, on the other hand, are used for innerwear and stockings as well as a material for automobile airbags.
2. Unsaturated Polyester
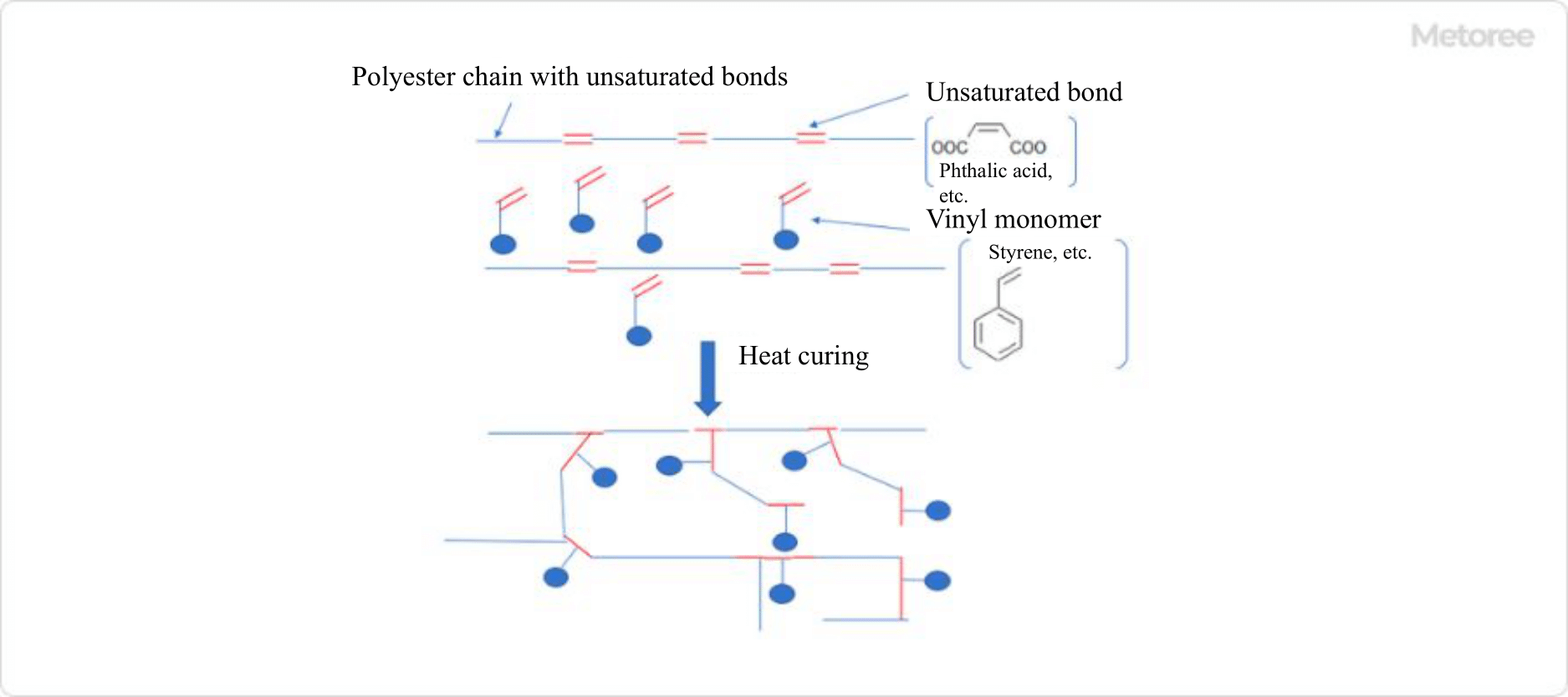
Figure 2. Three-dimensional crosslink formation reaction of unsaturated polyester
Unsaturated polyester is a thermosetting resin and differs from thermoplastics, such as PET, PEN, PBT, and PTT in this respect. Specifically, a mixture of polyester resin having unsaturated bonds in the molecule and vinyl monomer is made into a final product by three-dimensional cross-linking of the polyester resin with the vinyl monomer through heating.
3. Physical Properties and Applications of Unsaturated Polyesters
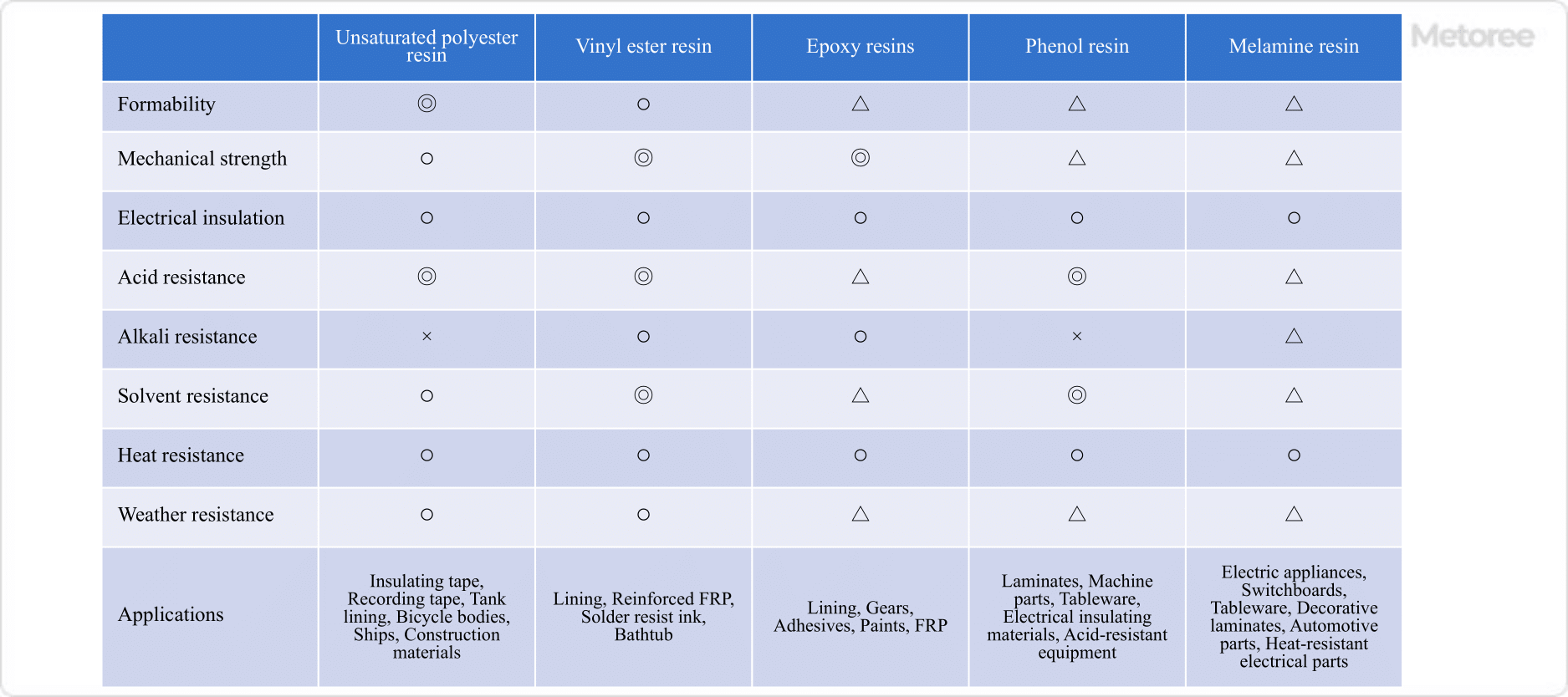
Figure 3. Comparison of physical properties of thermosetting resins
Unsaturated polyesters are particularly excellent in moldability due to their low viscosity during molding. When composited with glass fiber or carbon fiber, its toughness increases, so it is used for automobile bodies, ships, and other applications requiring strength. The weak point is that the ester bonds in the main chain are hydrolyzed by alkali, resulting in a decrease in molecular weight and low alkali resistance.