What Is a Pulse Oximeter?

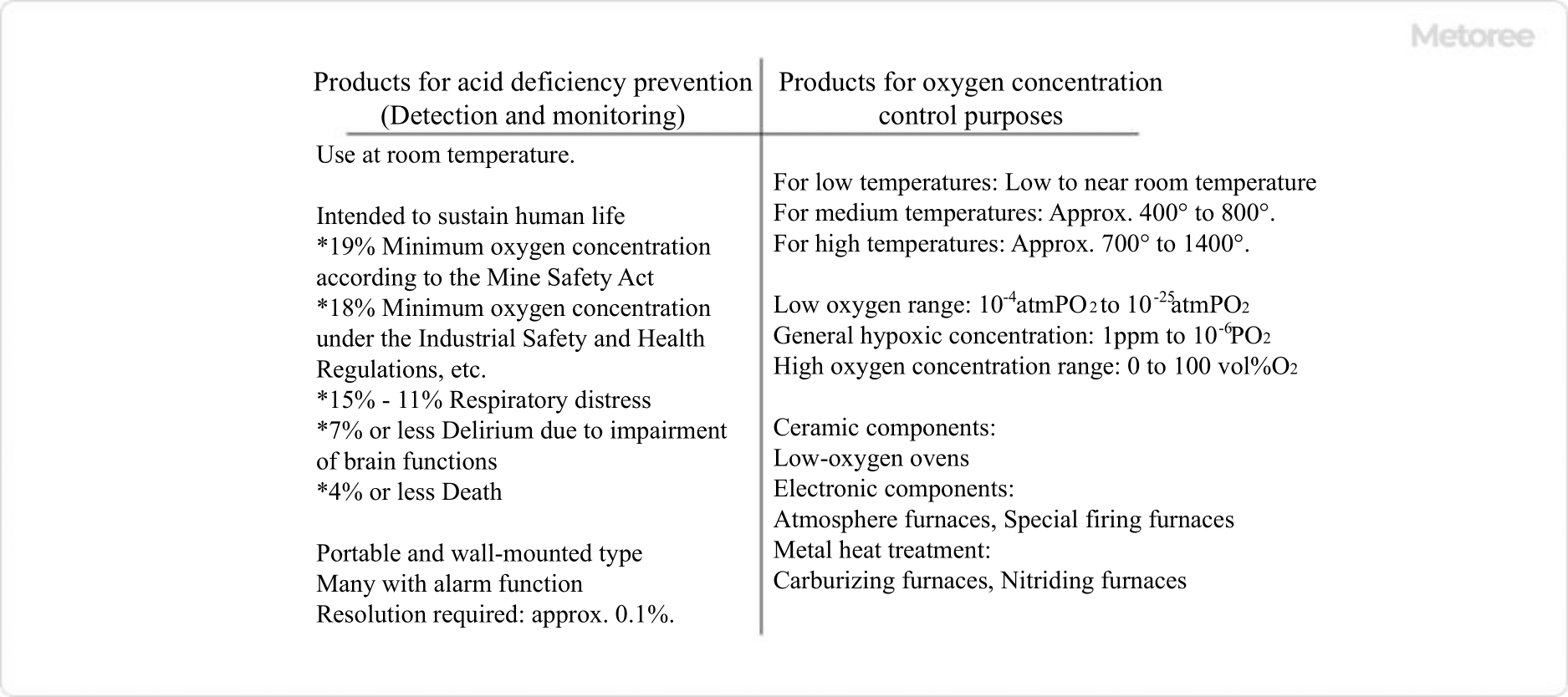
Figure 1. Oxygen meter overview
Pulse Oximeters are instruments used to measure the concentration of oxygen in the air.
It is sometimes referred to as an oxygen sensor or oxygen monitor. Because oxygen is essential for human life, it is extremely important to monitor the concentration of oxygen in the environment.
In addition, there are many cases in which accurate oxygen concentration control is required in various scientific and industrial fields, and instruments are manufactured to meet specific applications.
Uses of Pulse Oximeters
Pulse Oximeters are used in the following two major applications
- Monitoring (detection and monitoring) of oxygen concentration for the purpose of preventing oxygen deficiency
- Oxygen concentration control in industrial processes, etc.
In the prevention of oxygen deficiency, oxygen concentration is monitored for the purpose of life support in enclosed spaces such as tunnels. It is said that if the oxygen concentration falls below 15%, a person will have difficulty breathing, if it falls below 7%, brain function will be impaired, and if it falls below 4%, death will occur. The equipment comes in portable and wall-mounted forms.
In some industrial heat treatment processes, such as in the chemical industry, ceramics, and metals, oxygen levels must be kept low. Industrial furnace combustion processes also require monitoring and control of oxygen concentration to optimize combustion efficiency and the redox process. Pulse Oximeters for these industrial purposes must be durable enough to withstand harsh environments, such as high-temperature chemical reaction fields.
Principle of Pulse Oximeters
The two main operating principles of Pulse Oximeters are the “galvanic cell type” and the “zirconia solid electrolyte type. Other types include the “magnetic type” and “wavelength tunable semiconductor laser spectrometer type.
1. Galvanic Battery Type
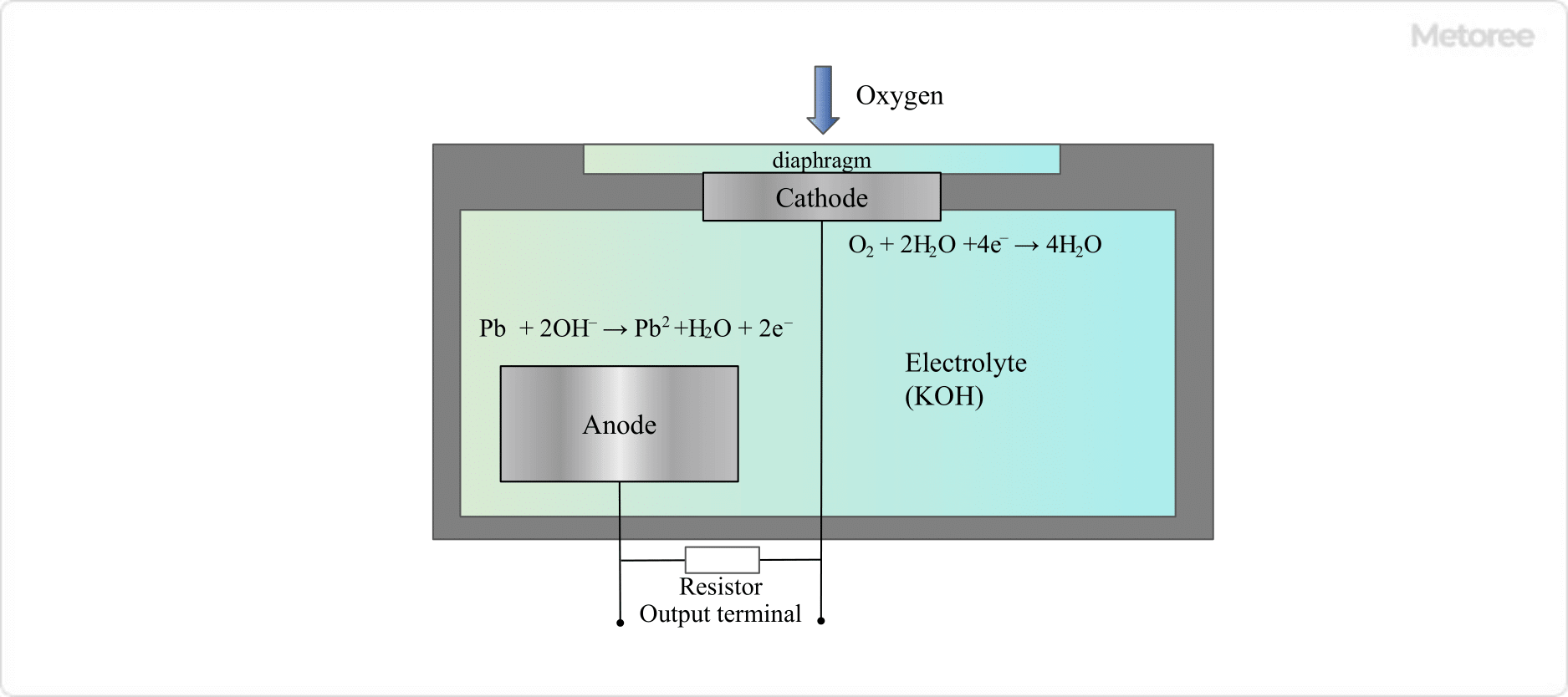
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of galvanic cell oxygen analyzer
The galvanic cell consists of a resin membrane that allows oxygen from the outside world to pass through, gold (Au) and lead (Pb) electrodes, and an electrolyte (potassium hydroxide solution). The following reactions take place at each electrode
- Anode: Pb + 2OH- → Pb2+ +H2O + 2e-
- Cathode: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4H2O
The electrons emitted at the anode reach the cathode, where oxygen taken in from the air takes up the electrons emitted at the anode. Since the flow of electrons (current) is proportional to the oxygen concentration, the oxygen concentration can be measured by measuring the current. Since this reaction occurs spontaneously, no power supply is required to drive the sensor.
2. Zirconia Solid Electrolyte Method
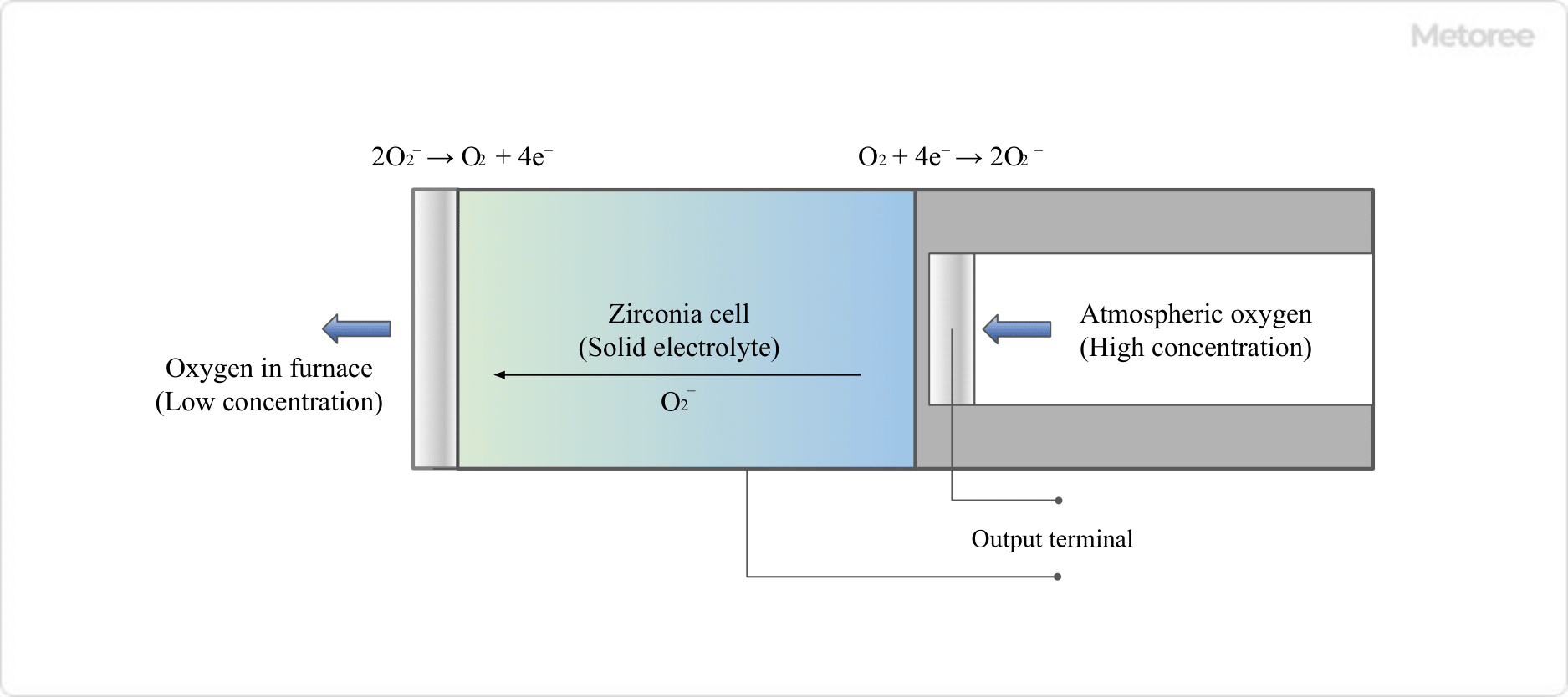
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of a zirconia solid electrolyte oxygen meter
This method uses a zirconia cell, taking advantage of the fact that zirconia exhibits solid electrolyte properties at temperatures of 500°C or higher.
Zirconia can conduct oxygen negative ions (O2-) in a solid state, and the ions are conducted from a gas with high oxygen concentration (in the air) to an atmosphere with low oxygen concentration (in an industrial furnace, for example).
This ionic conduction generates a potential difference, and electrodes are placed on the high O2 concentration side and the low O2 concentration side, respectively, to generate an electromotive force. The relationship is just like the positive and negative electrodes of a battery.
- High O2 concentration side: O2 + 4e- → 2O2-
- Low O2 concentration side: 2O2- → O2 + 4e-
The electromotive force generated between the electrodes obeys the Nernst equation (see below), so the oxygen partial pressure at each electrode can be determined.
- E=(RT/4F)-ln(PA/PB)
- (R: gas constant, T: temperature, F: Faraday constant, PA: oxygen partial pressure at high concentration (in air), PB: oxygen partial pressure at low concentration)
The temperature is measured by thermocouples attached to the zirconia.
In an atmosphere of approximately 400°C or lower, the target gas is introduced into the device via a sampling tube, and the zirconia cell is heated to a predetermined temperature using a platinum heater, etc. (sampling method). This is because zirconia requires a temperature of 500°C or higher to function as a solid electrolyte.
How to Select a Pulse Oximeter
Different Pulse Oximeters should be used for the prevention of oxygen deficiency and for maintaining low oxygen concentrations in industrial processes.
Portable and stationary oxygen meters designed to prevent oxygen deficiency use galvanic cell batteries, which do not require a power supply to drive the sensor. The life of the sensor is approximately 2 to 3 years. However, the usable environment is limited to an atmosphere similar to the general environment, and the accuracy is about ±0.5% O2. Some products are explosion-proof.
On the other hand, zirconia-type products are used to measure oxygen concentration in high-temperature industrial processes such as industrial furnaces, etc. Under an atmosphere of 700°C or higher, the direct insertion type is used by inserting the sensor directly into the atmosphere, while under 400°C, a separate zirconia cell is used by drawing in the atmosphere gas inside the furnace through a sampling tube, etc. For temperatures below 400°C, a sampling method that draws in atmospheric gas from the furnace through a sampling tube and separately heats the zirconia cell is appropriate.