What Is a Fuel Cell?
A fuel cell is a device that utilizes the electrical energy generated when hydrogen and oxygen react to produce water. Compared to the use of fossil fuels, the environmental impact is extremely low. Due to its superior energy efficiency, it is expected to find a variety of applications.
In addition to hydrogen itself, fossil fuels such as natural gas, LPG, and methanol can be used as an energy source by reforming them with a catalyst.
Uses of Fuel Cells
When fuel cells were first developed, they were used in spacecraft as a device that could simultaneously generate electricity and hydrogen.
Fuel cell-based household generators are installed to assist power generation during times of peak electricity use, and use city gas as a source of hydrogen for power generation.
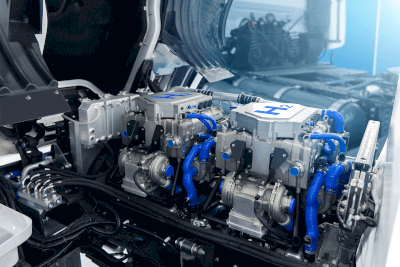
Another area attracting attention is fuel cell vehicles, which have various advantages such as long cruising range, low environmental impact, etc. Fuel cell vehicles that do not need to be recharged are already on the market.
Principle of Fuel Cells
There are four types of fuel cells, depending on the type of electrolyte used. The polymer electrolyte type and the solid oxide type are the most popular types in use today and are expected to become more popular in the future.
Solid polymer electrolyte fuel cells are characterized by the use of a fluoropolymer-based cation exchange membrane as the electrolyte, and the use of methanol or city gas as the fuel, in addition to pure hydrogen. Because of their relatively simple structure and compact size, they are used in many applications, including household generators and fuel cell vehicles. However, research is currently underway to reduce the use of platinum catalysts, which are expensive.
Solid oxide fuel cells are characterized by the use of ceramics as the electrolyte, and like the polymer electrolyte type, they use pure hydrogen, methanol, or city gas as fuel. The structure is simpler than that of the polymer electrolyte type and theoretically more efficient, and expensive platinum catalysts are not required. Verification and improvements are underway.
Advantages of Fuel Cells
Fuel cells have the following advantages:
① High power generation efficiency:
In the case of thermal power generation, heat from burning fuel is used to generate steam, which turns a turbine to produce electricity. Energy loss occurs as the chemical energy of the fuel is converted to electrical energy via thermal and kinetic energy. In addition, energy is also lost in the transmission of electricity from the power plant. On the other hand, residential-use fuel cells have extremely high power generation efficiency because they convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy without transmission loss.
② Stable energy source:
Hydrogen used in fuel cells can be obtained from various raw materials such as LP gas, natural gas, petroleum, methanol, and biomass, thus ensuring a stable supply of fuel.
③ Low environmental impact:
When fuel is burned, as in thermal power generation, not only carbon dioxide but also nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and other air pollutants are produced. On the other hand, fuel cells produce only water during power generation, making them environmentally friendly.
④ Extremely quiet:
Fuel cells do not require a turbine, etc. Since fuel cells do not require turbines, etc., and electricity is obtained only through chemical reactions, they are very quiet in operation and generate almost no vibration.
Although fuel cells have these excellent characteristics, they currently have some issues such as high cost and short life span.