What Is Linear Shafting?
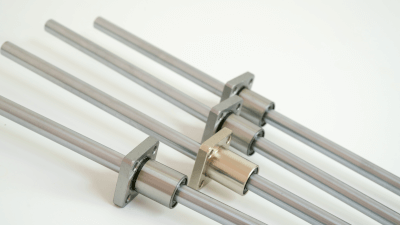
Linear shafting is a wear-resistant, high-precision round bar designed to guide linear (reciprocating) motion. These shafts are typically available with outer diameters in f8, g6, and h5 fits.
Common materials for linear shafting include iron, often with surface treatments like hard chrome, and stainless steel. High-frequency quenching can be used to create a robust surface condition. The shafts come in various shapes, such as straight, pipe-stepped, tapped on the end face, D-chamfered, or key-grooved.
Uses of Linear Shafting
Linear shafting is primarily used as a guide in linear reciprocating motion. They are often combined with dry bearings, linear bushings, or other sliding components to enhance the linearity of movement.
These shafts are commonly found in manual straight-line movement jigs, like vices. Additionally, linear shaft motors, which provide low vibration at standstill and high-speed movement, are gaining popularity in machining equipment where positional accuracy is critical.
Principles of Linear Shafting
Linear shafting plays a crucial role in providing inexpensive, high-precision linear drive and static positional accuracy. Their high standardization allows for achieving precise linear motion cost-effectively and easily.
Subject to wear from constant friction, these shafts often undergo surface hardening to increase durability. However, this hardening can make post-purchase machining difficult without a professional machining center.
While similar to linear guides in function, linear shafting is different in terms of strength and application. Linear guides are preferable for high accuracy and strength as their support points are closer to the load, whereas linear shafting is more suited for applications requiring simplicity and cost-effectiveness.