What Is a 3D Printer?
 A 3D printer is a device that produces three-dimensional objects by layering printed cross sections based on 3D data.
A 3D printer is a device that produces three-dimensional objects by layering printed cross sections based on 3D data.
3D printers can be produced using a variety of methods, including the FDM (fused deposition modeling) method, SLA (stereo lithography) method, SLS (selective laser sintering) method, inkjet method, inkjet powder laminate method, and inkjet powder laminate method.
For home use, two types of 3D printers are often used: “thermal melting lithography method” and “optical lithography method.”
Applications, Principles, and Advantages of Each Type of 3D Printer
1. Fused Deposition Modeling Method (FDM)
Uses
Production of figures, models, etc.
Principle
Thermoplastic resin is ejected through a thin nozzle of around 0.5mm to print.
Advantages
- Inexpensive main unit
- Printing is possible at low cost due to inexpensive materials
- Mainstream as 3D printer for general use
Disadvantages
- Requires support materials
- Appearance of the modeled object deteriorates due to stacking marks generated during printing
Printable Materials
PLA resin, ABS resin, etc.
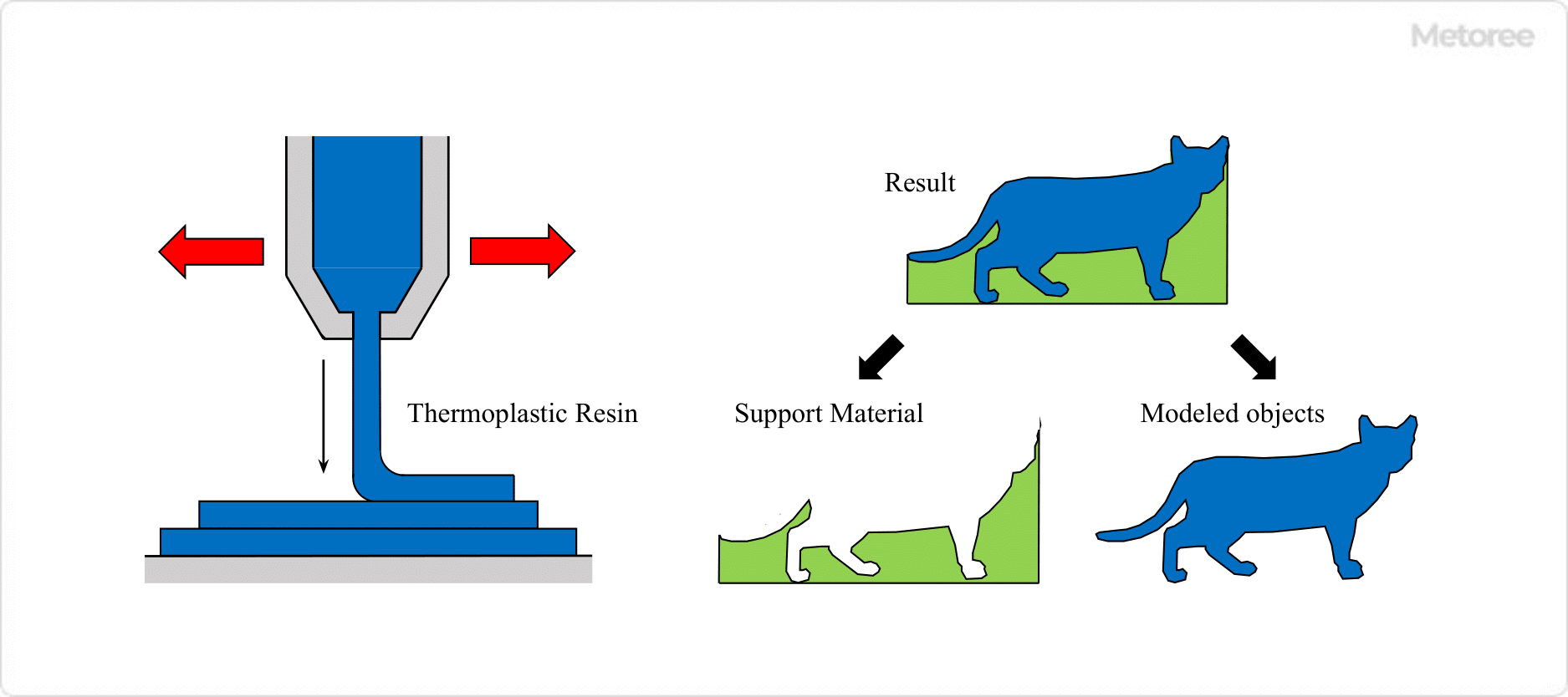
Figure1. Thermal Melting Lamination Method
2. Stereolithography Method (SLA)
Uses
SLAs are used for the creation of mock-ups, stage props, etc.
Principle
Printing is performed by exposing a light-curing liquid resin to light to cure it.
Advantages
Easy to process after modeling, and transparent printed materials can be created.
Disadvantages
- Printed materials are vulnerable to sunlight
- Time-consuming post-processing of printed materials
Printable Materials
Epoxy resins, acrylic resins, etc.
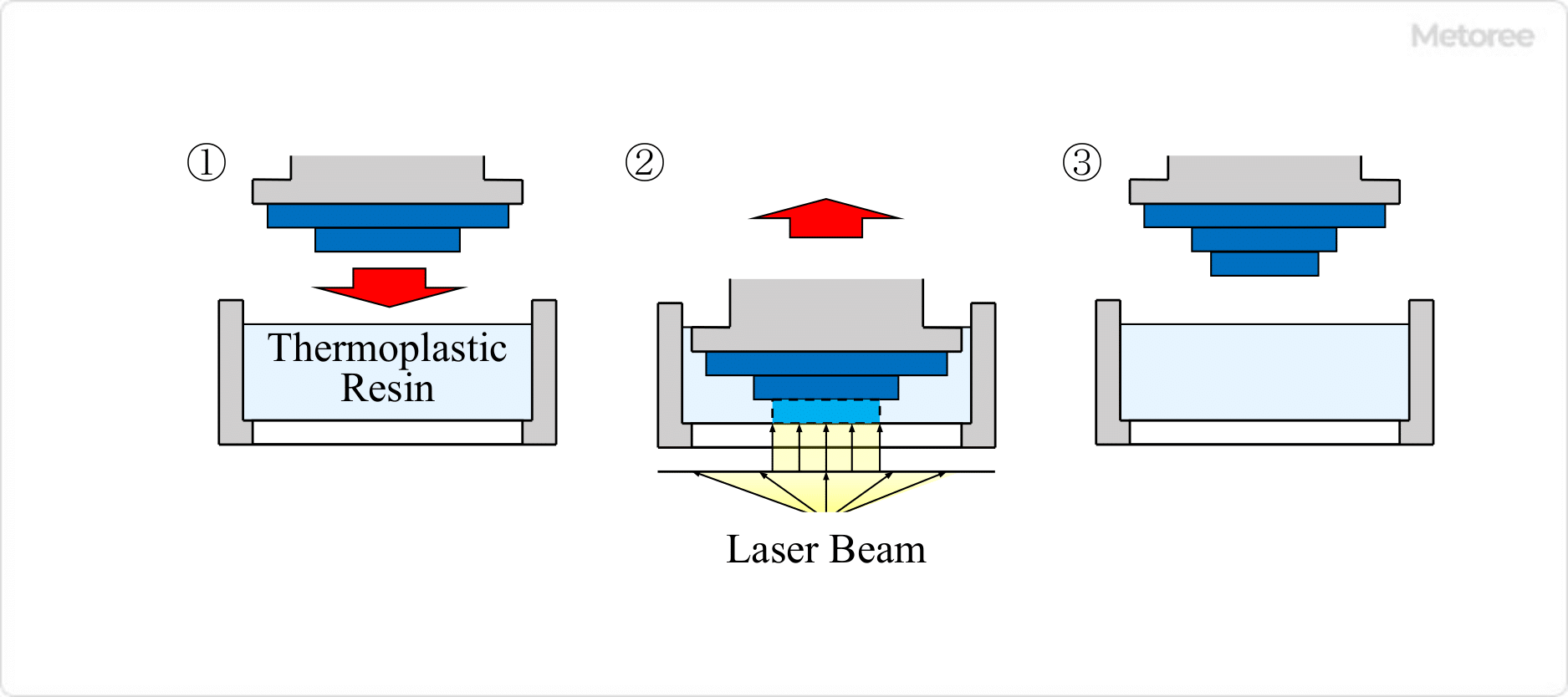
Figure2. Optical fabrication method
3. Selective Laser Sintering Method (SLS)
Uses
Parts for industrial equipment and medical implants
Principle
Printing is performed by repeating selective heating and sintering of powdered materials one layer at a time.
Advantages
Large-scale, strong structures can be printed without the need for support materials
Disadvantages
- Equipment, including the printer itself, is expensive
- Printed materials have rough surfaces.
Printable Materials
Nylon, metal materials such as titanium, etc.
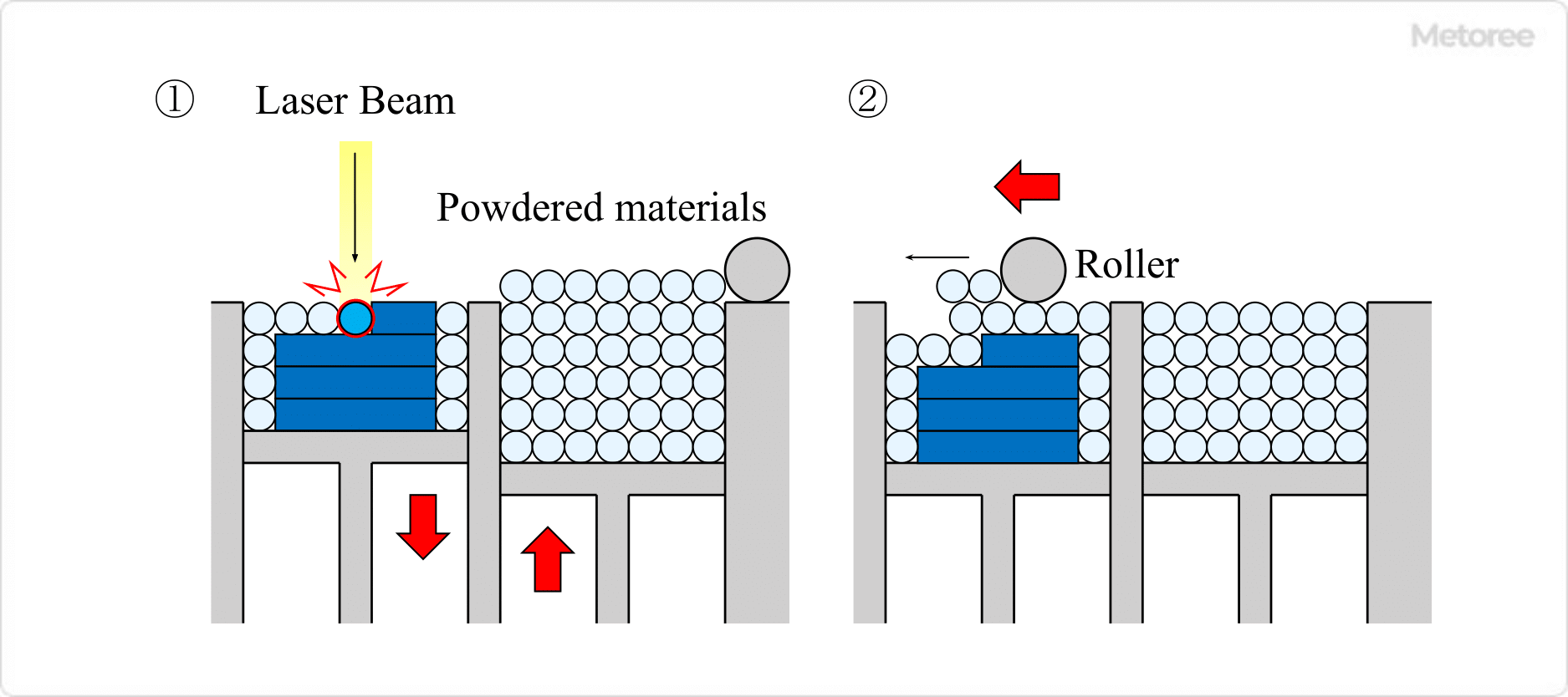
Figure3. Powder Sintering Additive Manufacturing Method
4. Inkjet Method
Uses
Manufacture of medical parts and small-lot products
Principle
UV-curable material is placed on a two-dimensional surface as if it were printed by an ordinary printer and then cured by UV irradiation to produce a print.
Advantages
Easy installation and high-resolution printing
Disadvantages
Printed materials are brittle and vulnerable to sunlight.
Printable Materials
Epoxy resin, acrylic resin, ABS resin, etc.
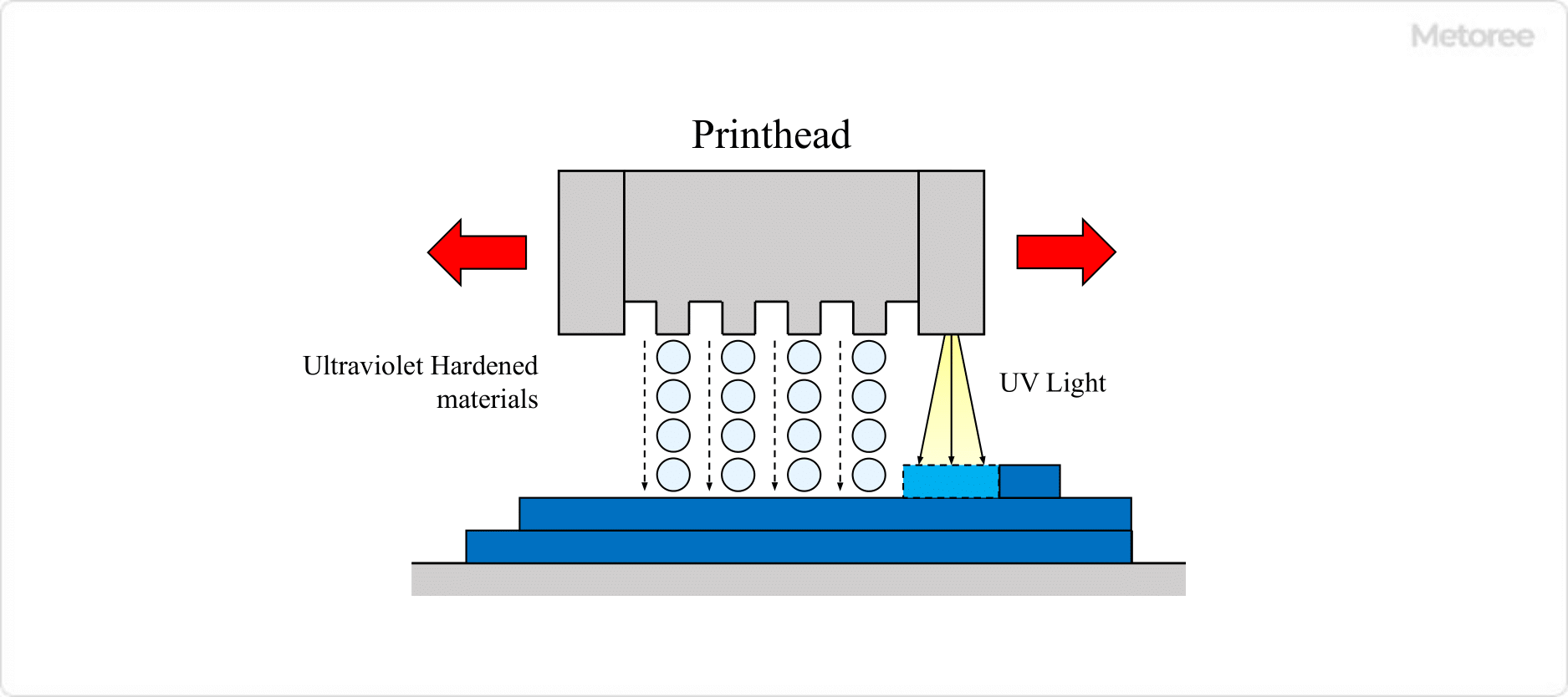
Figure4. Inkjet method
5. Inkjet Powder Lamination Method
Uses
Medical parts, small lot product manufacturing
Principle
Printing is performed by placing an adhesive on plaster and allowing it to cure. Color structures can be created by using colorants.
Advantages
Easy installation and high-resolution printing
Disadvantages
Printed materials have low strength
Printable Materials
Plaster, resin, metal, sand, etc.
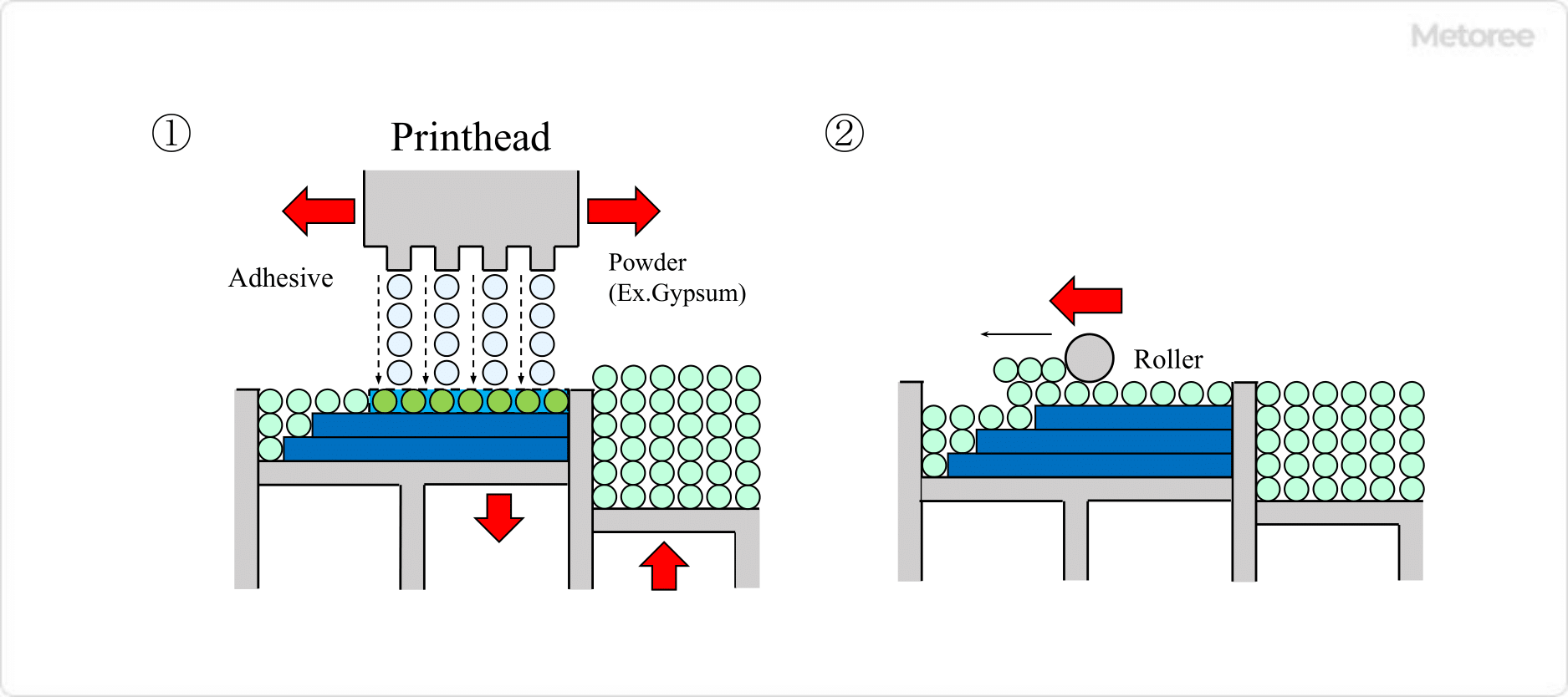
Figure 5. Inkjet powder lamination method
How to Use a 3D printer
3D printers can be used to layer the designed structure by melting the resin.
This section explains what you need to prepare and the actual procedure.
What You Need to Prepare
- Personal computer
- 3D printer
- 3D CAD software for designing three-dimensional CAD drawings
- Slicing software
Slicing software has the ability to convert 3D data into tool path data. - Filament
Filament is a material to be laminated; its type varies depending on the 3D printer’s lamination method, but PLA resin and ABS resin are most commonly used by beginning users.
Steps to Layering a Structure on a 3D Printer
-
- To laminate a structure, create 3D data by using 3D CAD software.
- Convert the 3D data to STL format so that the 3D printer can read the data.
- Convert STL data to tool path data.
- Activate the 3D printer.
- Remove secondary materials that are welded to the structure as support materials.
- Surface treatment of burrs, etc. for a smooth finish.
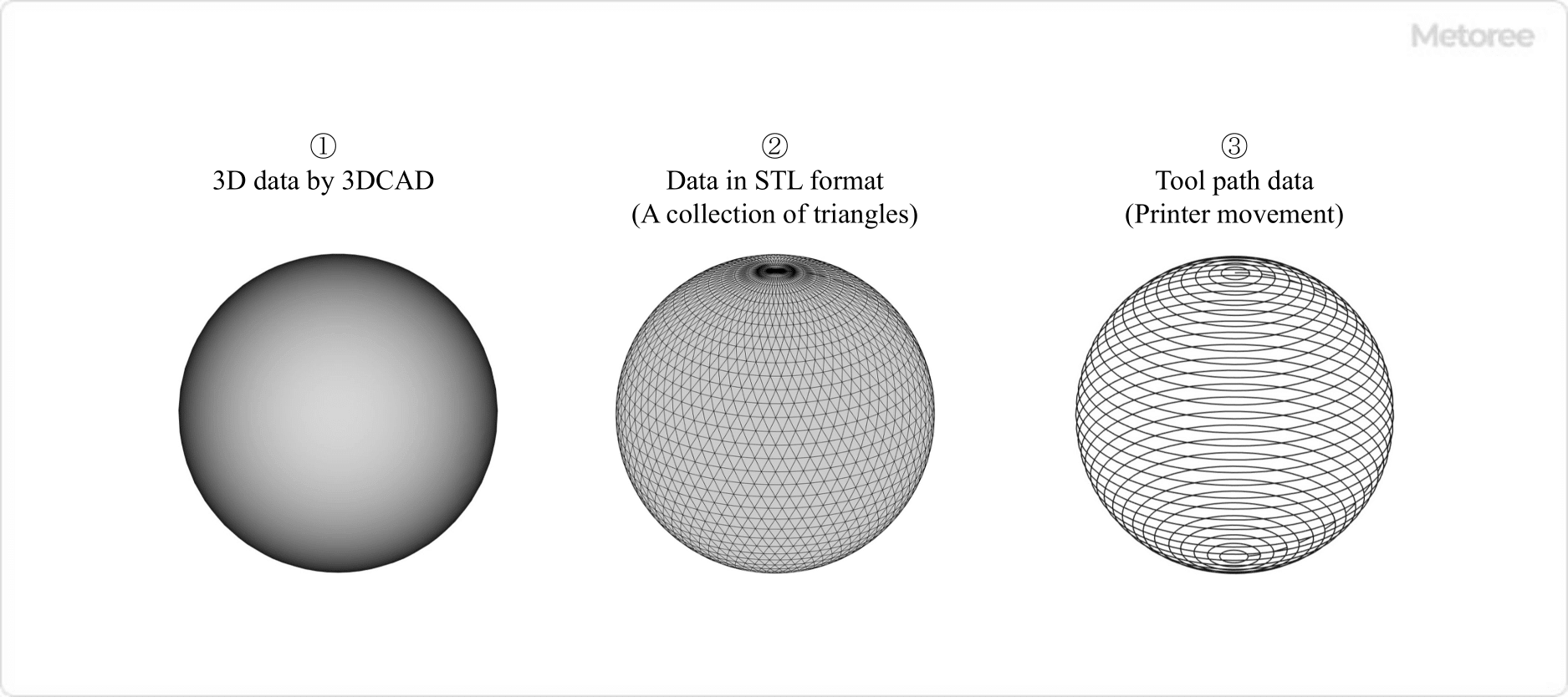
Figure 6. Conversion from 3DCAD data to tool path data
Filament Materials That Can Be Handled
3D printers are limited in the materials they can handle, depending on the type of equipment and the melting method of the material.
For example, a 3D printer that can handle resins can handle both general soft and hard resins. Some types of 3D printers can handle a wide range of materials.
Here, we will focus on resin and metal as filament materials that can be handled.
Resin Filament
The most commonly used types of resin filaments for both beginners and advanced users are PLA and ABS resins.
Other resin materials include nylon, plaster, rubber, and epoxy-based materials.
- PLA Resin
This resin is synthesized from recycled materials consisting of polylactic acid, which is mainly made from corn, etc. - ABS Resin
A synthetic resin composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
Metal Filament
Types of metal filaments include stainless steel, brass, titanium, platinum, silver, and gold.
Other special materials include filaments containing bronze as a powder.