What Is an Epoxy Paint?
 Epoxy paint is a type of coating derived from epoxy resin, a form of plastic. Epoxy resin paint stands out for its superior adhesion compared to other resins used in coatings, such as melamine resin and acrylic resin. Its exceptional corrosion resistance and adhesive properties make it ideal for areas susceptible to rust.
Epoxy paint is a type of coating derived from epoxy resin, a form of plastic. Epoxy resin paint stands out for its superior adhesion compared to other resins used in coatings, such as melamine resin and acrylic resin. Its exceptional corrosion resistance and adhesive properties make it ideal for areas susceptible to rust.
Uses of Epoxy Paints
Epoxy paints are notable for their excellent corrosion resistance, attributed to their impermeability to moisture and oxygen. They are commonly used in marine environments, such as on ships and fishing rods, to prevent rusting. These paints are also employed on exterior walls, roofs, and other surfaces of residential buildings that are prone to corrosion.
Additionally, the solvent resistance of epoxy paints makes them suitable for coating the interiors of tanks holding chemicals like concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Types of Epoxy Paints
Epoxy paints are primarily divided into two categories: room temperature curing type and heat (baking) curing type. The distinction is based on the curing process and the type of resin used.
The room temperature curing type is often a two-component paint, combining a main agent with bisphenol A epoxy resin and a curing agent (such as epichlorohydrin), which is mixed just before application and cures without heating. This variety is prevalent as a primer, particularly in settings requiring corrosion and chemical resistance, like on ships.
The heat (baking) curing type, a one-component paint, requires heating to form a durable coating film. It’s mainly used as a powder coating, applied as a dry powder, and then baked to cure. This method enhances the hardness and adhesion of the coating film and is typically used for the inner and outer surfaces of pipes, electrical and electronic components, and other applications.
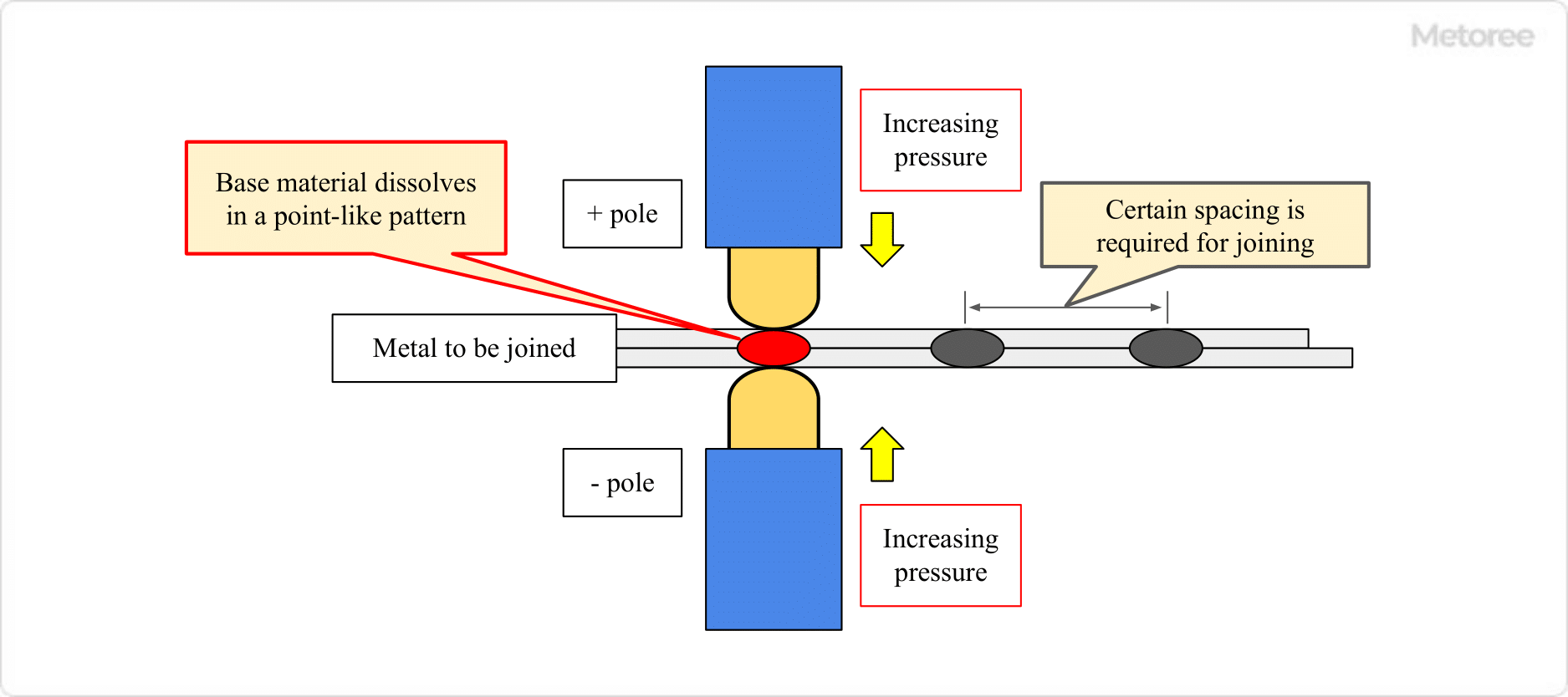
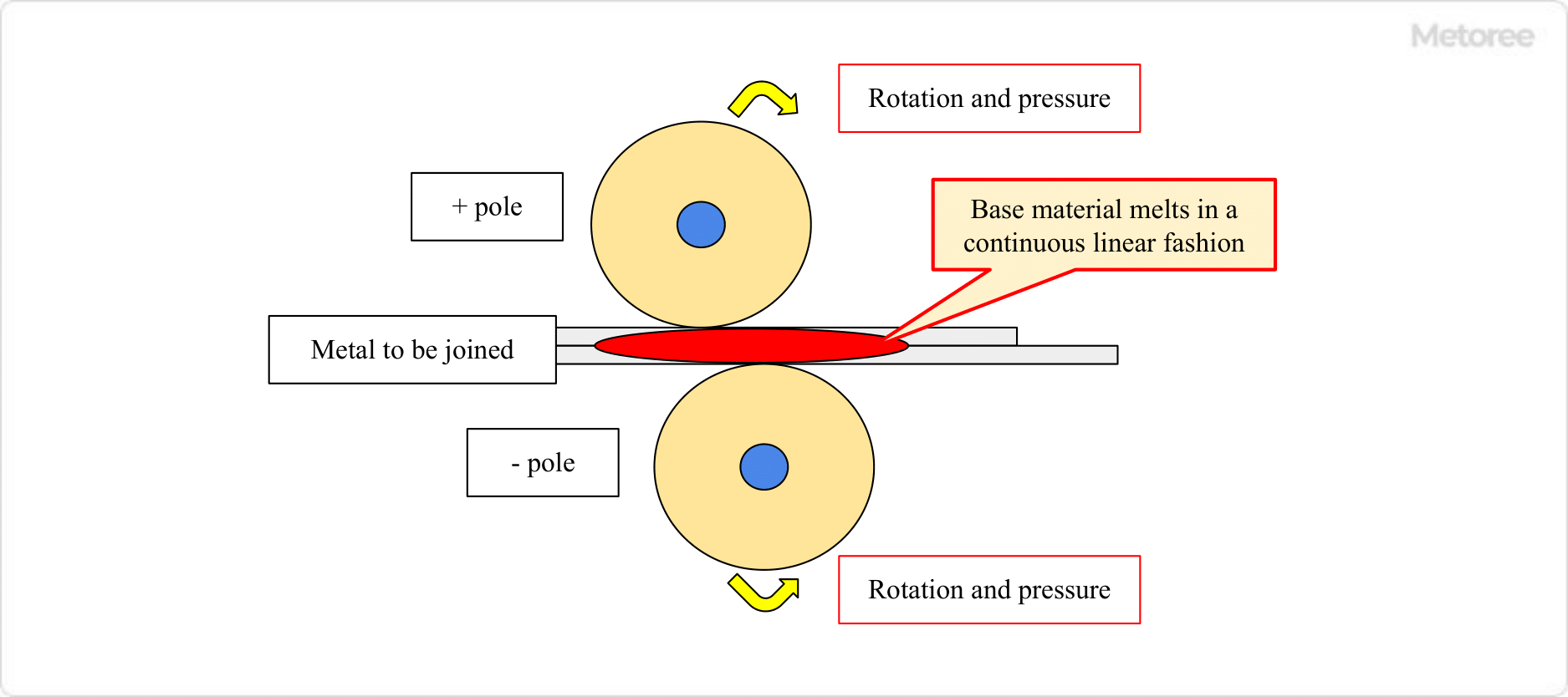
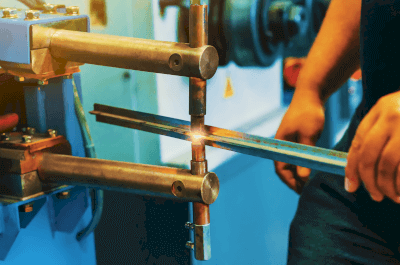 Resistance welding is a technique that utilizes the heat generated by electrical resistance when current is passed through metal. This process involves applying an electric current to the metals to be joined under moderate pressure. The heat generated melts the metal, which then cools and solidifies, forming a strong joint.
Resistance welding is a technique that utilizes the heat generated by electrical resistance when current is passed through metal. This process involves applying an electric current to the metals to be joined under moderate pressure. The heat generated melts the metal, which then cools and solidifies, forming a strong joint.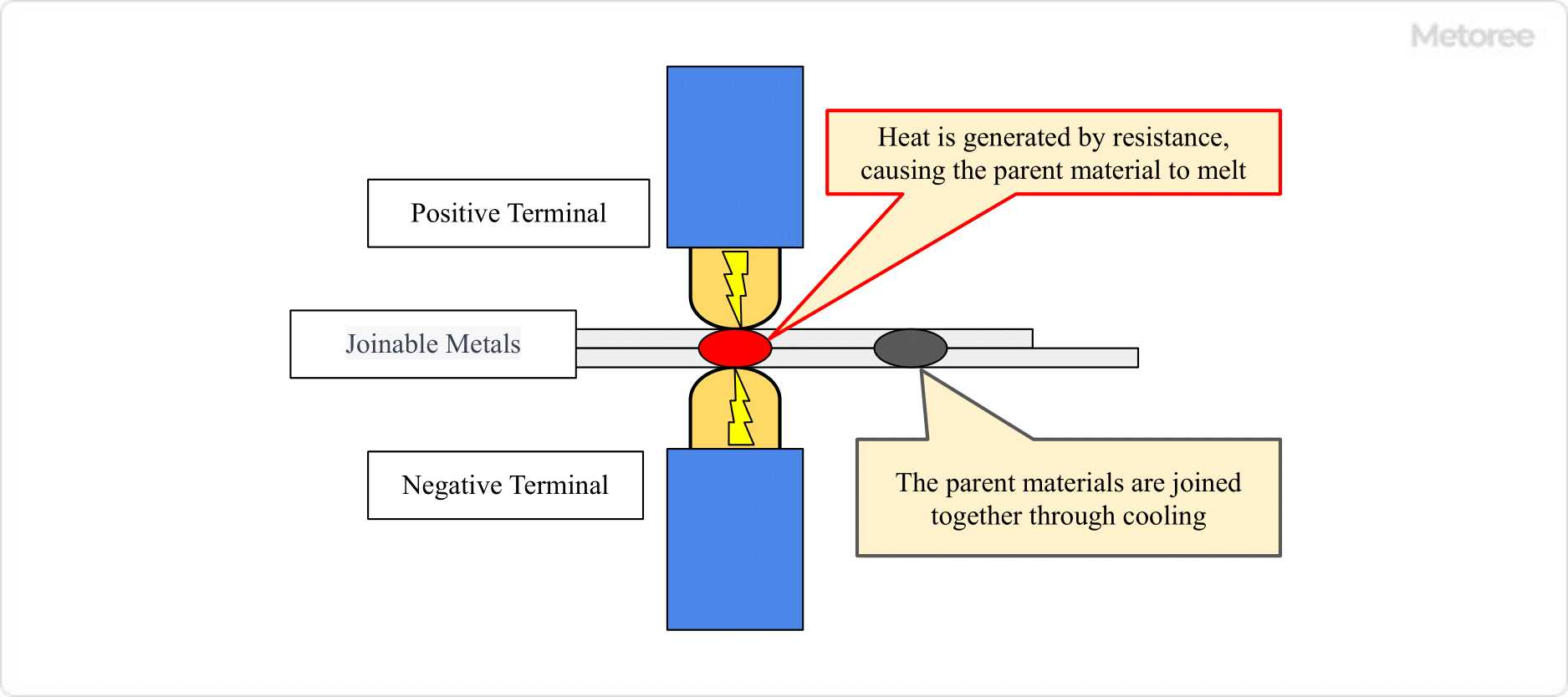

 Gun drilling is a
Gun drilling is a