What Is a Seismograph?
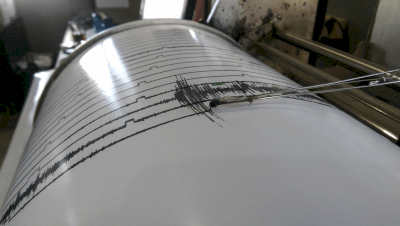
A seismograph is an instrument developed to record the seismic activity of an earthquake.
It is believed that the prototype already existed in China over 1,800 years ago, and is often referred to as the world’s oldest seismograph. The modern seismometer is said to have been invented in Japan in the late 1800s, which has gone under major improvements since then.
A similar term to seismograph is seismic intensity meter, which is a type of seismograph. A seismic intensity meter has the function of calculating seismic intensity in addition to the function of a seismometer, so the name is used to distinguish it from a seismometer.
Uses of Seismographs
The data measured by seismographs are used for various earthquake countermeasures.
Seismographs are also used as instruments to observe volcanic activity.
Principle of Seismographs
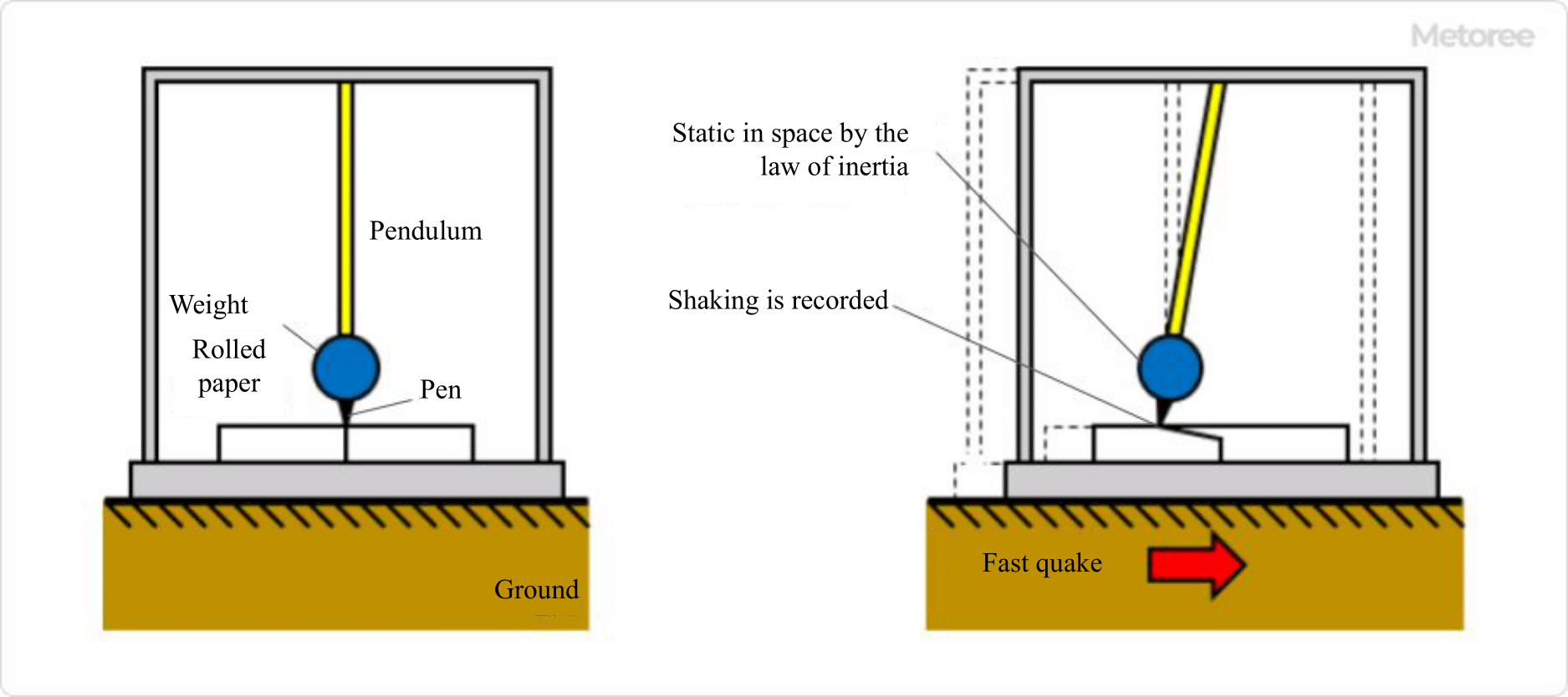
Figure 1. Principle of a seismograph
Seismographs are instruments that use the principle of a pendulum.
1. Securing a Fixed Point by the Law of Inertia
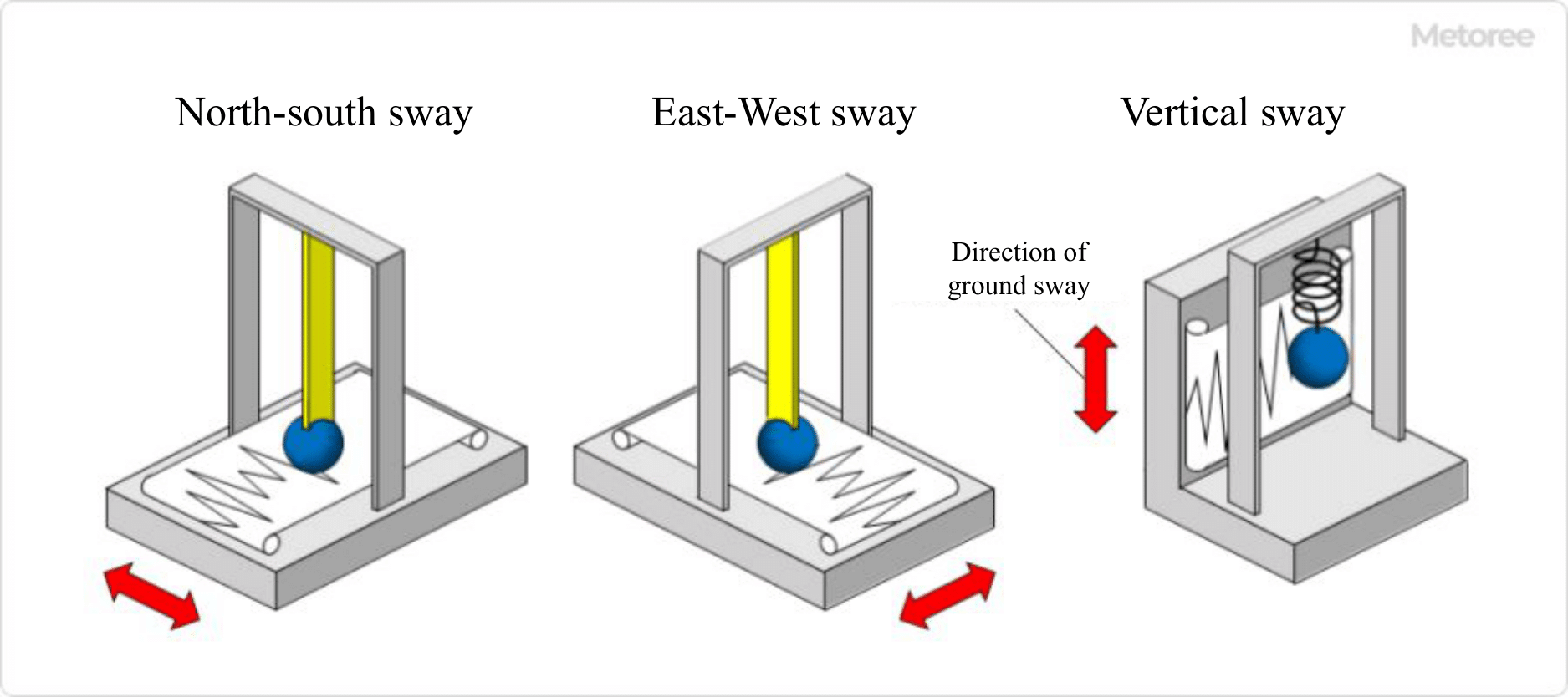
Figure 2. Observation of three-way swaying
Since seismographs are usually installed on the ground surface or underground and move with the ground when it shakes, a reference point, called a fixed point, is necessary to ensure that the seismographs will never move in relation to the ground.
Assuming that the fulcrum of the pendulum is the ground, a pen is placed at the position of the weight, and a roll of paper fed at a constant speed is placed at its end. If the ground shakes quickly, the entire device will shake, but the weight remains stationary in space due to the law of inertia, so the ground shaking is recorded on the roll of paper. Earthquake shaking usually occurs in all directions, but shaking parallel to the movement of the paper rolls is difficult to record, three seismographs are used, each recording the three components of north-south, east-west, and vertical directions.
Recently, seismographs that record the movement of a pendulum as an electrical signal using a coil and magnet instead of a paper roll are also utilized.
2. Observation of Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration
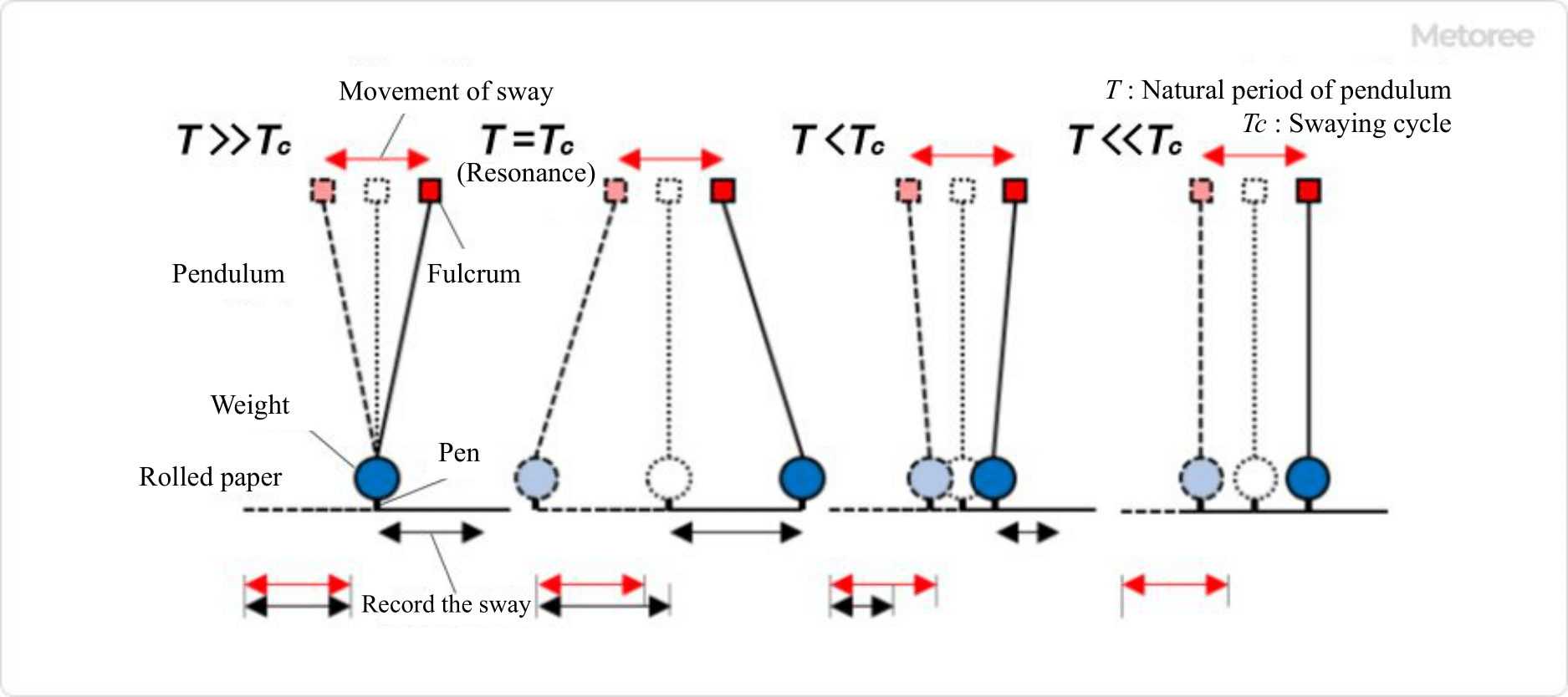
Figure 3. Relationship between the natural period of the pendulum and the period of swaying
The observation of displacement, velocity, or acceleration of the ground is related to the natural period of the pendulum.
The time required for the weight to return to its original position when the pendulum swings freely is called the natural period. If the period of swing of the ground is very short compared to the eigen period, the weight will remain stationary. On the other hand, if the period of swing of the ground is very long compared to the eigen period, the weight will swing just like the ground. If the period of ground shaking coincides with the natural period, the weight will shake much more than the ground because of resonance.
A damper is installed on the weight to prevent resonance, and a response curve of seismographs is considered with the period of the ground on the horizontal axis and the displacement on the vertical axis.
In a region where the period of shaking is much shorter than the natural period and the displacement is constant, the weights are stationary in space. Therefore, it is possible to observe how much the ground has moved from its original position due to shaking, in other words, the displacement.
In a region where the period of shaking is equal to the natural period, the velocity can be observed, and in a region where the period is longer than the natural period, the acceleration can be observed.
Other Information on Seismographs
1. Types of Seismographs
There are three main types of seismographs: high-sensitivity seismographs for small tremors, broadband seismographs for slow tremors, and strong seismographs for strong tremors.
These are used appropriately for different purposes. For example, a high-sensitivity seismograph, due to its characteristics, may detect tremors that have nothing to do with the intended purpose, so measures such as drilling observation wells may be necessary.
2. Observation Method Using Seismographs
There are two types of seismic observation: regular observation and temporary observation.
Regular observation is a method of continuous observation over a long period of time, while temporary observation is a method of limited observation over a short period of time. Temporary observations are conducted for specific purposes, such as aftershock observations after a major earthquake.
3. Using Seismographs
Seismographs are used in various efforts for disaster prevention and mitigation.