What Is a Bearing Unit?

Bearing units are bearings consisting of a bearing housing and deep groove ball bearings. The term “ball bearing unit” is also used synonymously.
Bearing units have ball bearings preinstalled in the housing. Housings are available in several shapes, such as pillow-top, square flange, and rhombus flange shapes, and it is important to select the most suitable shape according to the mounting location and conditions.
Since the mounting holes in the housing allow for easy installation in equipment and facilities with bolts, etc., they are used in many machines such as conveyors and rollers that perform various rotational motions. In particular, specifications and dimensions of bearing units are standardized, making it possible to design around bearings in a versatile and standardized manner.
Applications of Bearing Units
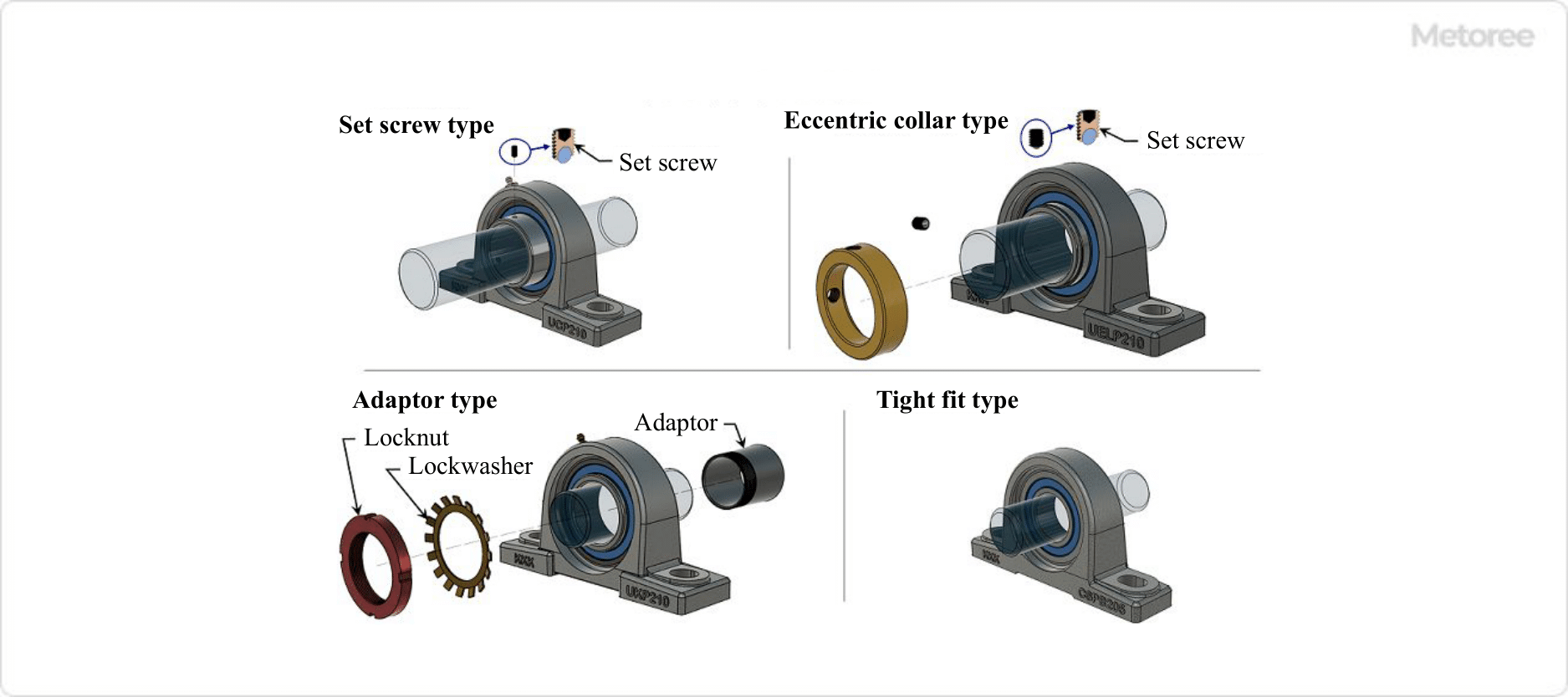
Figure 1. How to fix the shaft
Bearing units are mainly used to support shaft rotation and radial loads.
There are various types of bearing units, and the most appropriate selection must be made according to the mounting location, surrounding structure, and installation environment. This includes considerations for shape, mounting method, shaft fixing method, protective structure (with or without a cover, seal, etc.), and material.
Principles of Bearing Units
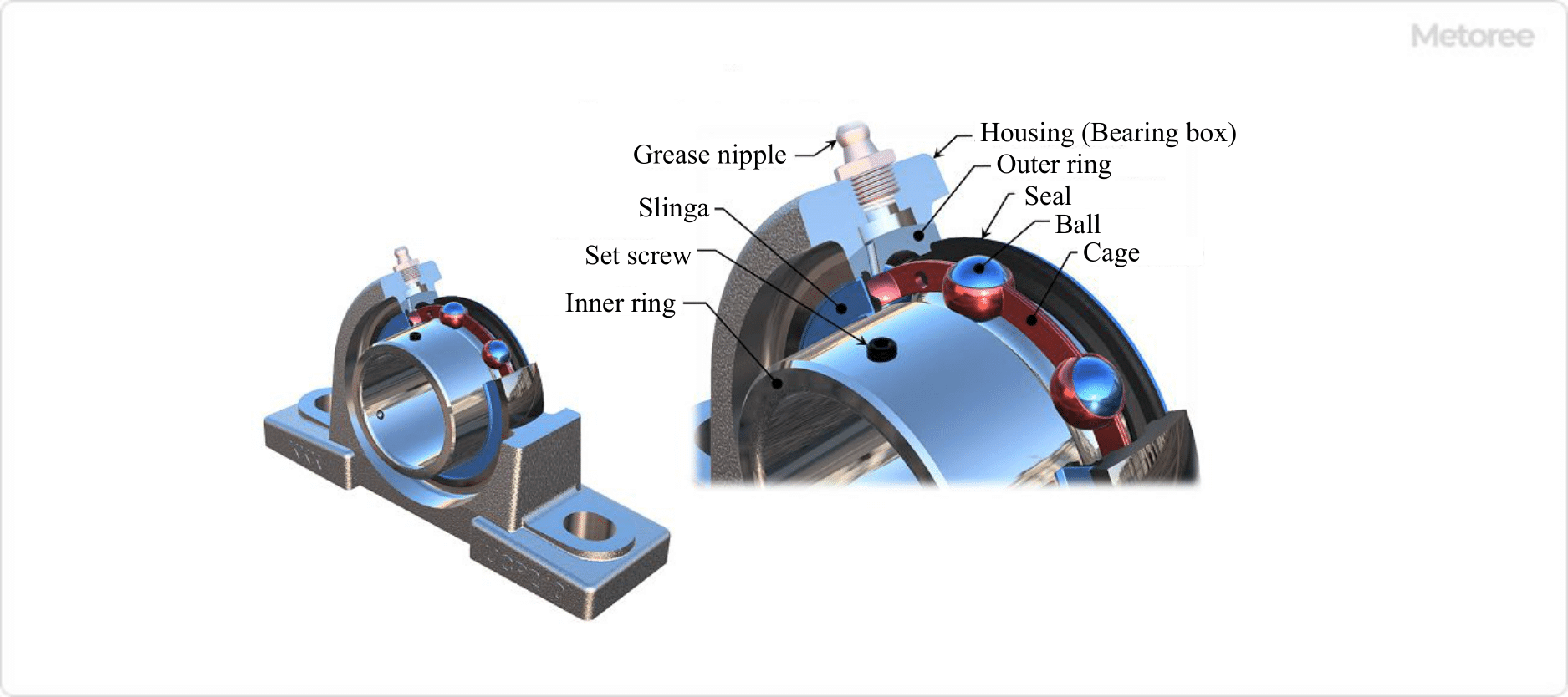
Figure 2. Structure of bearing unit
Bearing units, like other bearings, are available in radial bearing and thrust bearing types.
The load applied to the bearing is radial load, which is applied in a radial direction perpendicular to the rotating shaft axis center, and thrust load, which is applied in an axial direction parallel to the rotating shaft axis center.
Radial bearings are used when radial loads are applied, and thrust bearings are used when axial loads are applied. The basic structure consists of a bearing housing, rolling element balls, outer ring, and inner ring. The rolling element ball is sandwiched between the outer ring and inner ring of the raceway and rotates within the raceway. A cage (retainer) maintains the distance between the rolling element balls.
Friction occurs as the balls slide and rotate between the raceways. Lubrication is necessary to reduce this friction. There are two types of lubrication methods: one in which lubricant grease is pre-filled, and the other in which grease is supplied from a grease nipple attached to the housing through a hole in the outer ring.
Types of Bearing Units
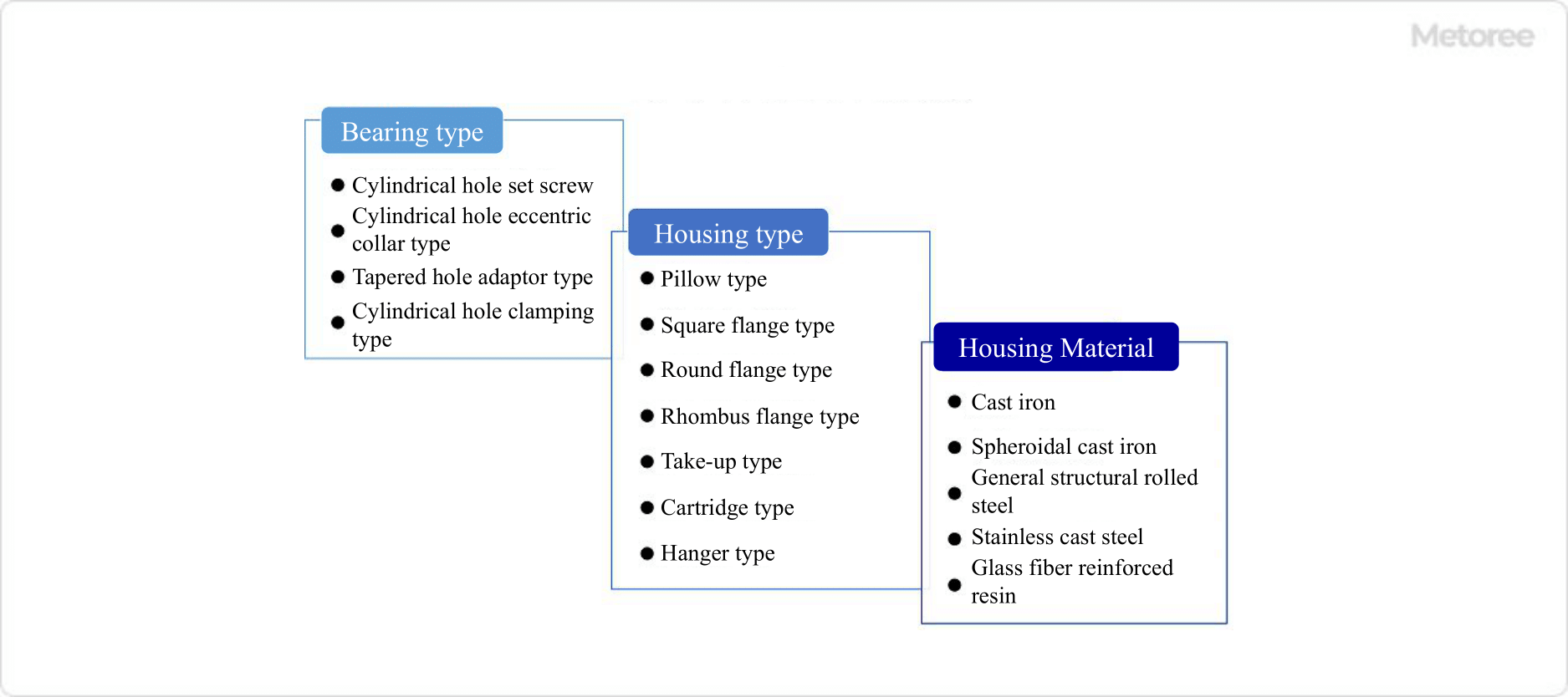
Figure 3. Types of bearing unit (1)
Bearing units can be classified in terms of Bearing Type, Housing Type, and Housing Material. Since there are so many types, it is important to select the appropriate one for the application.
1. Bearing Type
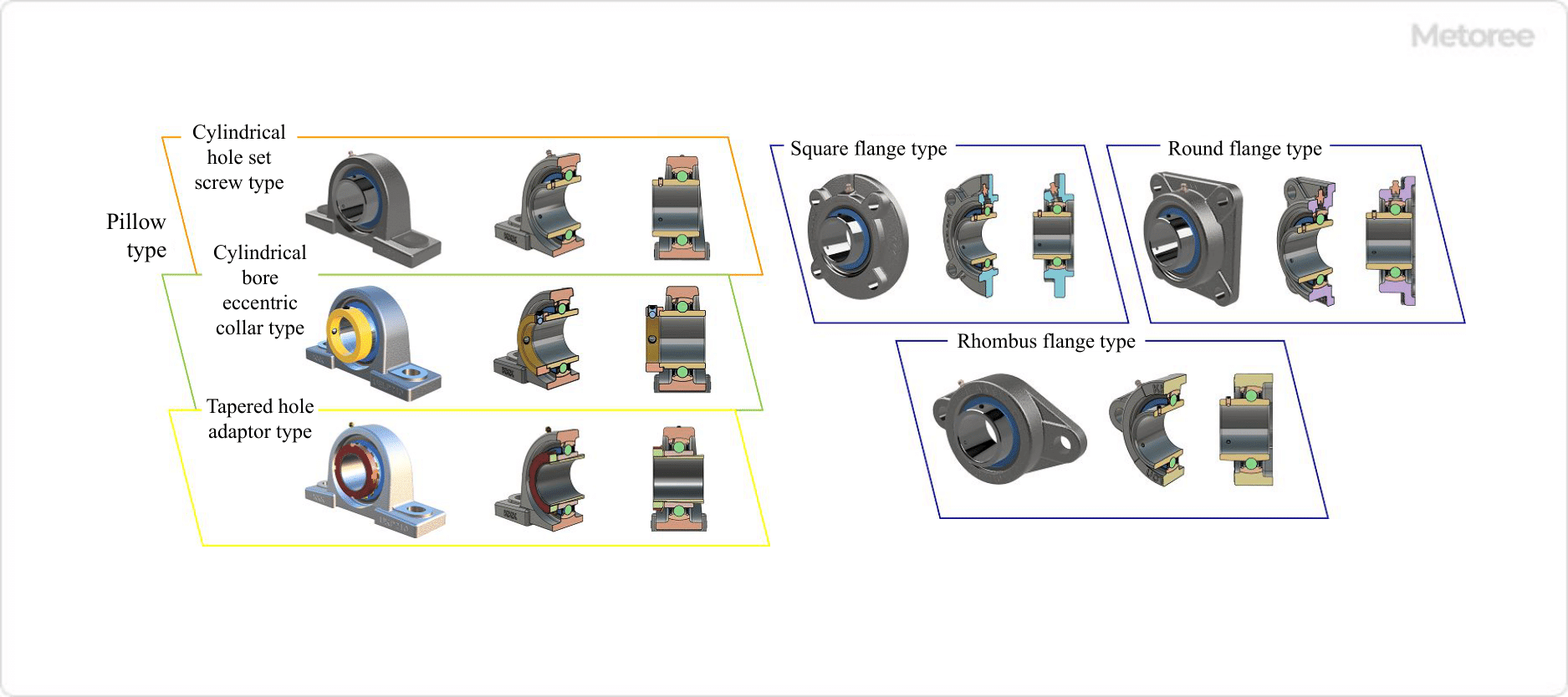
Figure 4. Types of bearing unit (2) / Figure 5. Types of bearing unit (3)
- Cylindrical Bore Set Screw Type
The inner ring has a cylindrical bore, and the shaft is installed inside. The inner ring set screw is then tightened to fix the bearing to the shaft. - Cylindrical Bore Eccentric Collar Type
The inner ring has a cylindrical bore, and the shaft is installed in the inner ring. An eccentric collar is attached to one side of the inner ring and tightened with a set screw to secure the bearing to the shaft. - Tapered Hole Adapter Type
The inner ring has a tapered bore, and a special adapter is installed between the shaft and inner ring and tightened with a bearing nut to secure the bearing and shaft. A dedicated lock washer is used to prevent the lock nut from loosening.
A tapered bore is a conical tapered bore. - Cylindrical Hole Type Clamping Type
The inner ring has a cylindrical bore, and the bearing and shaft are secured by making the fit between the shaft’s outer diameter and inner ring’s inner diameter a clamping fit.
The tight fit is defined as a fit where there is no gap between the shaft and the bore, and the minimum allowable shaft dimension is larger than the maximum allowable bore dimension.
2. Housing Type
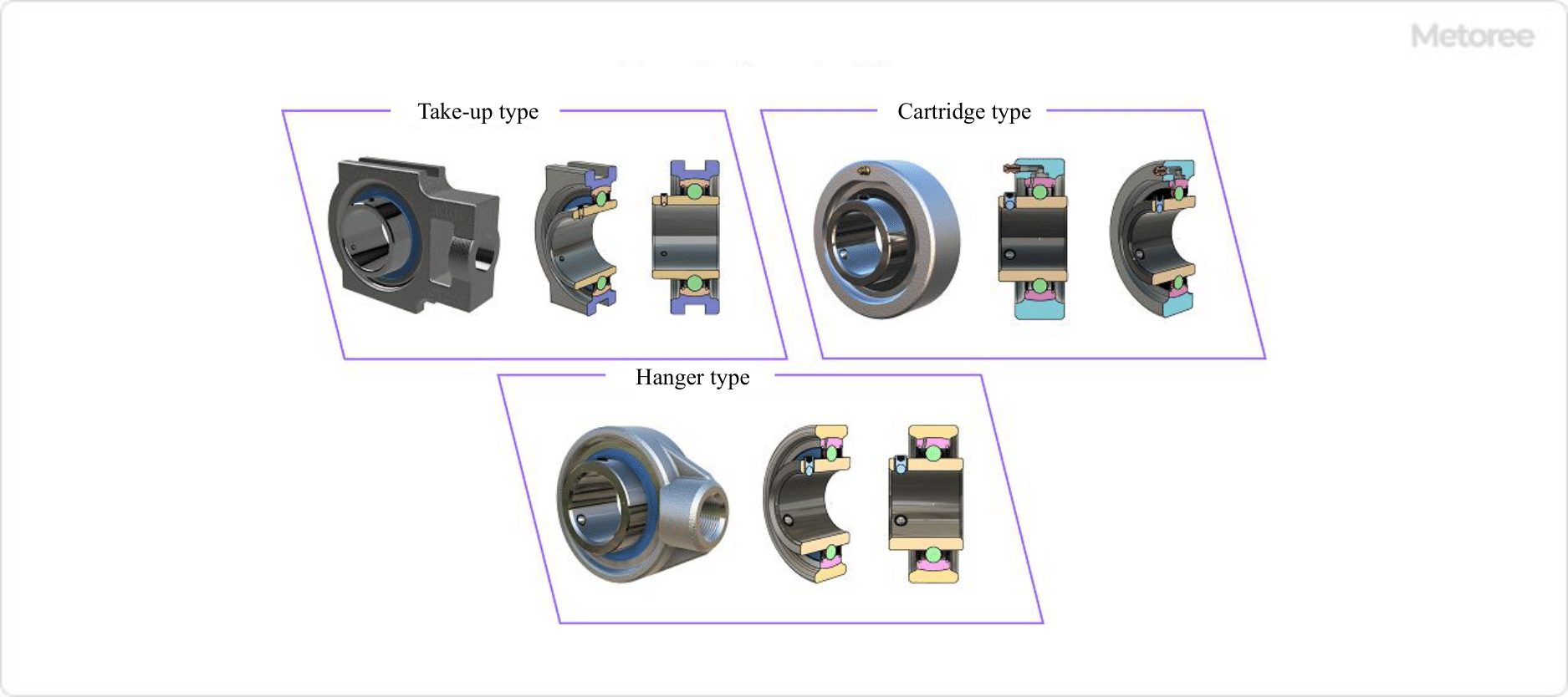
Figure 6. Types of bearing unit (4)
- Pillow Type
The pillow type housing is the most common housing type and consists of a cylindrical section that holds the bearings and a base section with holes drilled for bolts to secure the Bearing Units. It is used in many applications such as power transmission mechanisms and general machinery. - Square Flange Type
The square flange type has a square housing flange shape and is mounted on the wall of equipment or facilities with four bolts. - Round Flange Type
The round flange type has a housing with a round flange and is attached to the wall of the equipment or facility with four bolts. - Rhombic Flange Type
The rhombic flange type has a rhombus-shaped housing flange and is attached to the wall surface of the equipment or facility with two bolts. It is relatively small in external dimensions and can be installed in a small space. - Take-Up Type
The take-up type has a sliding groove on the left and right sides of the housing. This groove fits into a guide on the equipment, etc., and the entire Bearing Units move left to right or up and down, and the shaft position needs to be moved. - Cartridge Type
The cartridge type has a simple cylindrical housing without a base or flange shape. The housing and outer ring are spherical and aligned. Cartridge type is used to absorb the expansion and contraction of the shaft, such as moving it in the axial direction. Used on the free side (moving side) of expansion and contraction. - Hanger Type
The hanger type has a threaded hole on one side of the housing and is used to support the shaft by screwing in a suspension shaft or the like.
3. Housing Material
- Cast Iron
The housing material used is gray cast iron. This is the most common and standard housing material. - Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron
The housing material used is spheroidal graphite cast iron. It is applied when higher mechanical strength than cast iron housing is required. - Rolled Steel for General Structural Purposes
The housing material used is rolled steel for general structural purposes. - Cast Stainless Steel
Stainless steel casting is used for the housing material. Applicable to outdoor use environments or when splashed with water, or where nitric acid or sulfuric acid corrosion resistance is required. Martensitic stainless steel is used for the ball, inner ring, and outer ring. - Glass Fiber Reinforced Resin
Thermoplastic polyester resin, polypropylene, and polyethylene are used as housing materials. They can be used in environments subjected to water or seawater or underwater, and are applicable to environments where sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid corrosion resistance is required.