What Is Acrylic Resin Paint?

Acrylic resin paint is a type of paint primarily composed of acrylic resin. It was first developed around 1950. Acrylic resin is created through the copolymerization of components like acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, esters, styrene, and other monomers. Due to its versatility in molecular design, acrylic resin is used not only in paints but also in applications such as adhesives and organic glass.
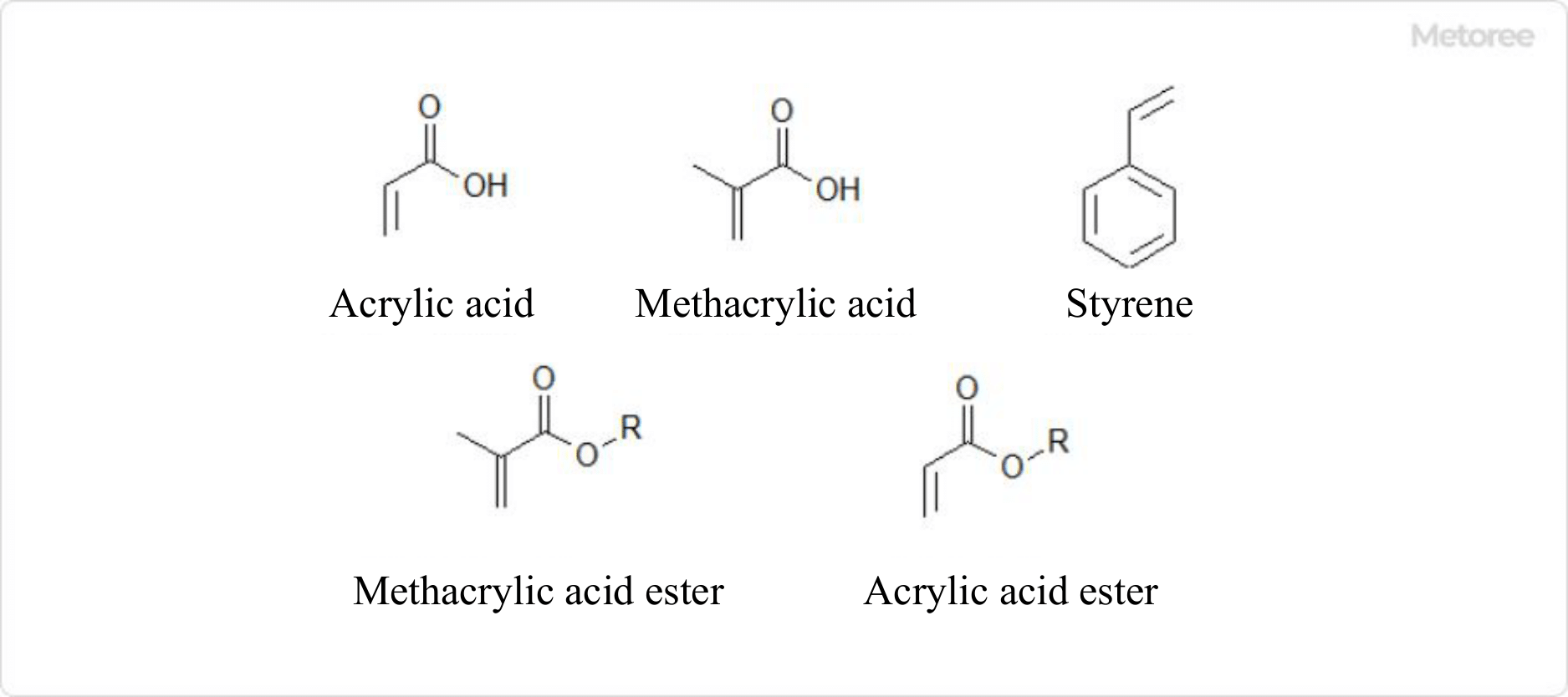
Figure 1. Typical monomers that make up acrylic resins
While acrylic resin paint initially gained popularity due to its excellent color and gloss, it has been largely replaced by higher-performance urethane and acrylic silicone resin paints today. Additionally, concerns about volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have led to a shift from solvent-based paints to water-based paints.
Uses of Acrylic Resin Paints
Acrylic resin paints are still widely used for applications such as exterior wall painting and DIY projects, although their use has decreased with the advent of urethane resin paints. They find application as topcoats on surfaces like concrete, mortar, roof tiles, and PC concrete, both indoors and outdoors.
These paints are also popular in furniture and DIY projects due to the wide range of available colors. Acrylic resins can be tailored to specific applications, resulting in coating films with varying levels of flexibility and hardness by adjusting the type of monomer and degree of polymerization.
Types of Acrylic Resin Paints
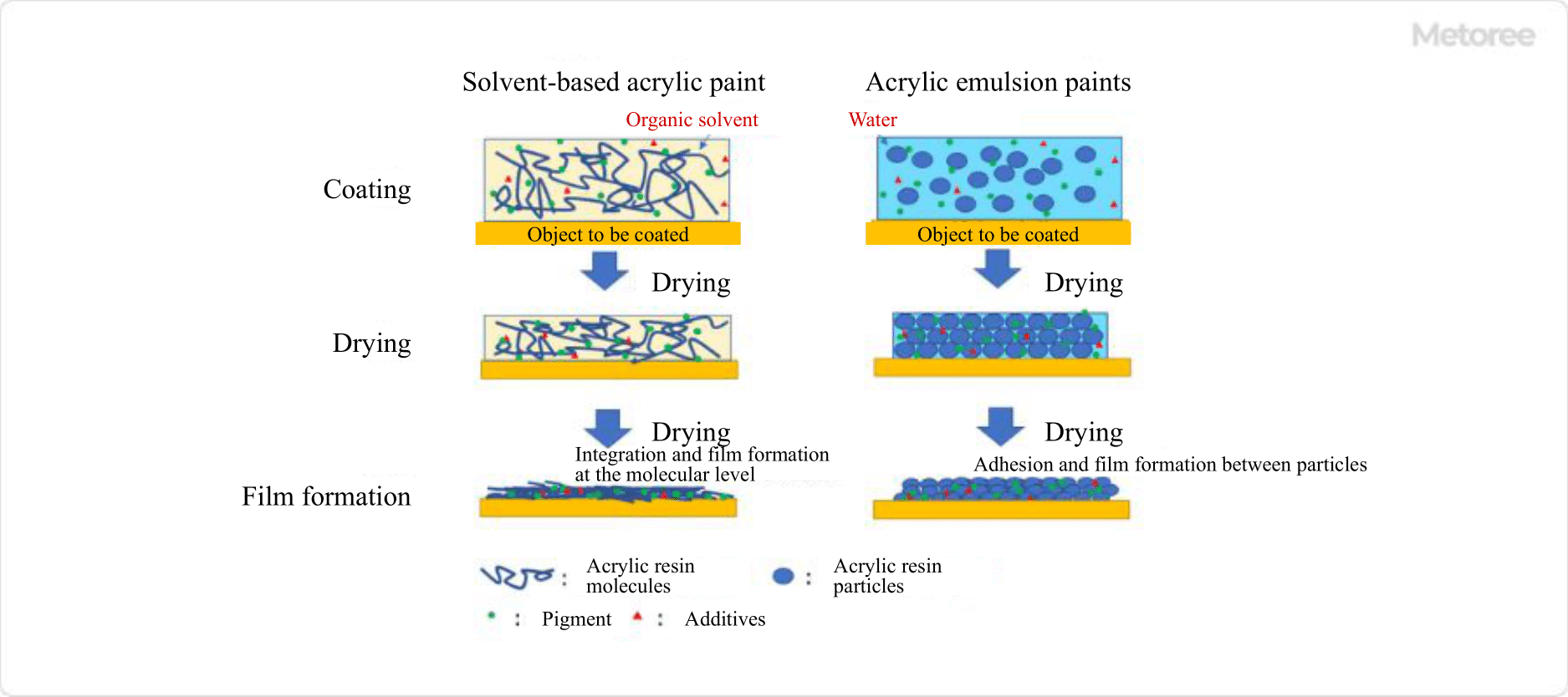
Figure 2. Different mechanisms of acrylic resin paint film formation
There are two main types of acrylic resin paints: solvent-based acrylic paints and water-based acrylic emulsion paints.
1. Solvent-Type Acrylic Paints
Solvent-type acrylic paints are formulated by dissolving the acrylic resin in a thinner, solvent. These paints offer excellent resistance to weather, water, alkali, and oil due to paint film formation at the molecular level. However, they are associated with the odor of the solvent and contain toxic substances.
Given their primary use in construction, consideration must be given to the environment and safety of workers who handle these paints.
2. Acrylic Emulsion Paints
Acrylic emulsion paints, also known as waterborne acrylic resin paints, are produced by emulsifying and dispersing acrylic resin in water. Similar to solvent-based acrylic paints, they can be tailored to enhance functionality. Recent developments have introduced additives such as antiseptic, antifoaming, antifungal, and antifouling agents to improve paint performance.
Acrylic emulsion paints are odor-free and free from damage caused by toxic substances, making them suitable for various architectural applications. Their functionality has expanded with the inclusion of additives, making them increasingly popular.
Additional Information on Acrylic Resin Paints
1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Acrylic Resin Paints
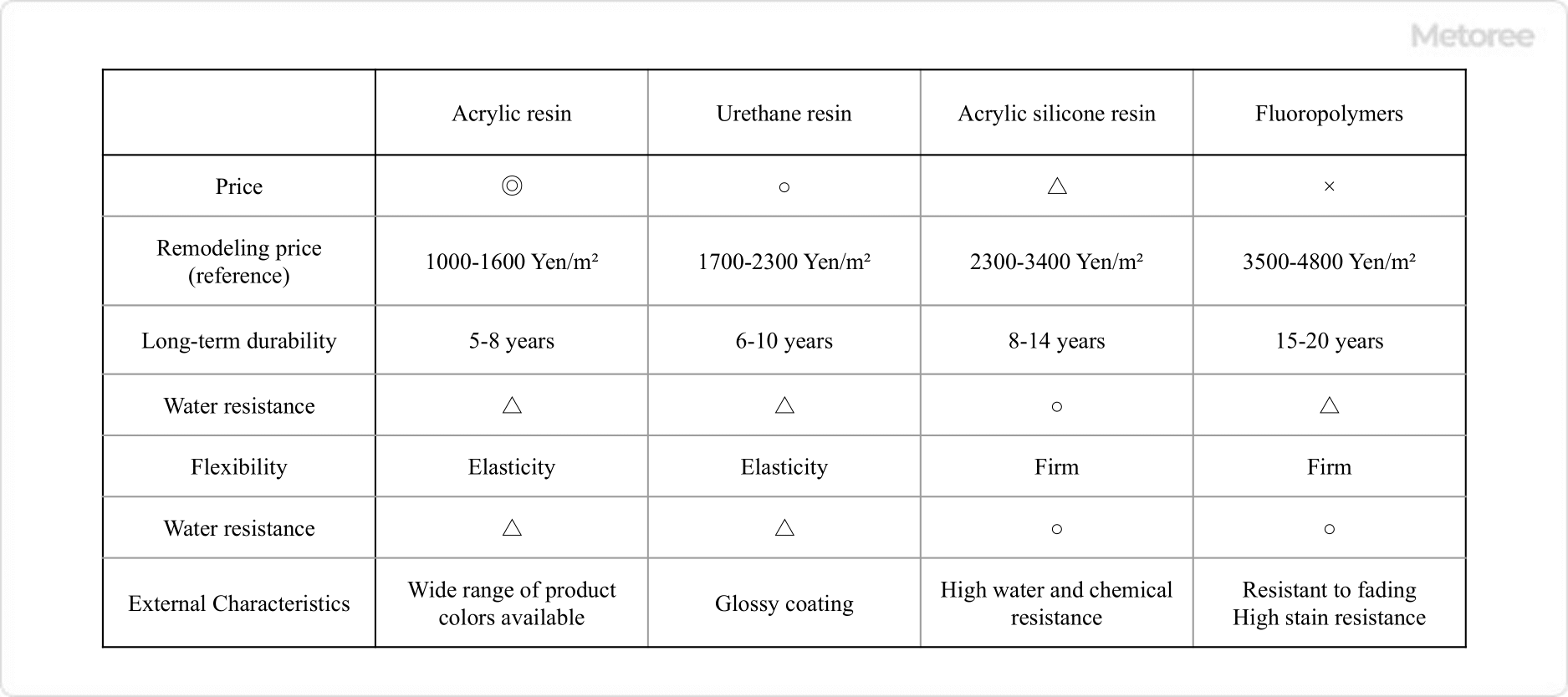
Figure 3. Comparison of characteristics of various paints
The advantages of acrylic resin paints include their affordability, excellent color and gloss, wide color variety, ease of use for amateurs, and suitability for layering. However, they are vulnerable to ultraviolet (UV) rays and degrade relatively quickly due to weathering factors.
UV rays and other environmental factors can cause plasticizers in acrylic resins to gradually decrease, leading to hardening and cracking of the coating film. As a result, the service life of acrylic resin paints is relatively short, typically ranging from 5 to 8 years. Acrylic silicone resin paints, which offer longer service life, have become more common.
Acrylic silicone resin paints incorporate a silicone component into acrylic resin molecules, mitigating the drawbacks of pure acrylic resins. These paints are often used for residential exteriors.
2. Acrylic Resin Paint Manufacturing Process
In general, paints undergo a five-step manufacturing process. Acrylic emulsion paints require additional dispersants and additives compared to solvent-based acrylic paints due to the dispersion of more particles in water-based formulations. Reactive cross-linking agents are sometimes added to increase the strength of the coating film.
- Pre-kneading: Resins, pigments, surfactants, and solvents are mixed to create a particle dispersion (mill base).
- Dispersion: The mill base is dispersed in a dispersing machine until uniform.
- Mixing: Additives and other ingredients are introduced to improve paint performance.
- Filtration: The paint is filtered to remove foreign substances.
- Coloring: Colored paints are mixed with the finished paint to add color. After coloring, each container is filled and shipped.
3. Characteristics of Acrylic Resin Baking Coating
Acrylic resin baking coating involves applying acrylic resin paints to an object and then subjecting the object to heat to thermoset the acrylic resin. This process significantly enhances the strength of the coating film. For acrylic resin, a high temperature of 140°C to 180°C is required for 20 to 30 minutes. Baking coating increases the hardness, scratch resistance, and adhesion of the coating film.
Baked coating improves weather resistance, reducing degradation, fading, and chalking caused by UV rays, which are common weaknesses of acrylic resins. However, baked-on acrylic resin coating may be less flexible and prone to cracking. Therefore, it is suitable for outdoor products.
Other applications include indoor and outdoor furniture, wall coatings, and painting small parts due to its unique characteristics. Examples include vending machines that require weather resistance and accessories that demand colored paints. However, the use of baking coating is limited by the heat resistance temperature of the object to be coated and its size.