What Is Ozone?
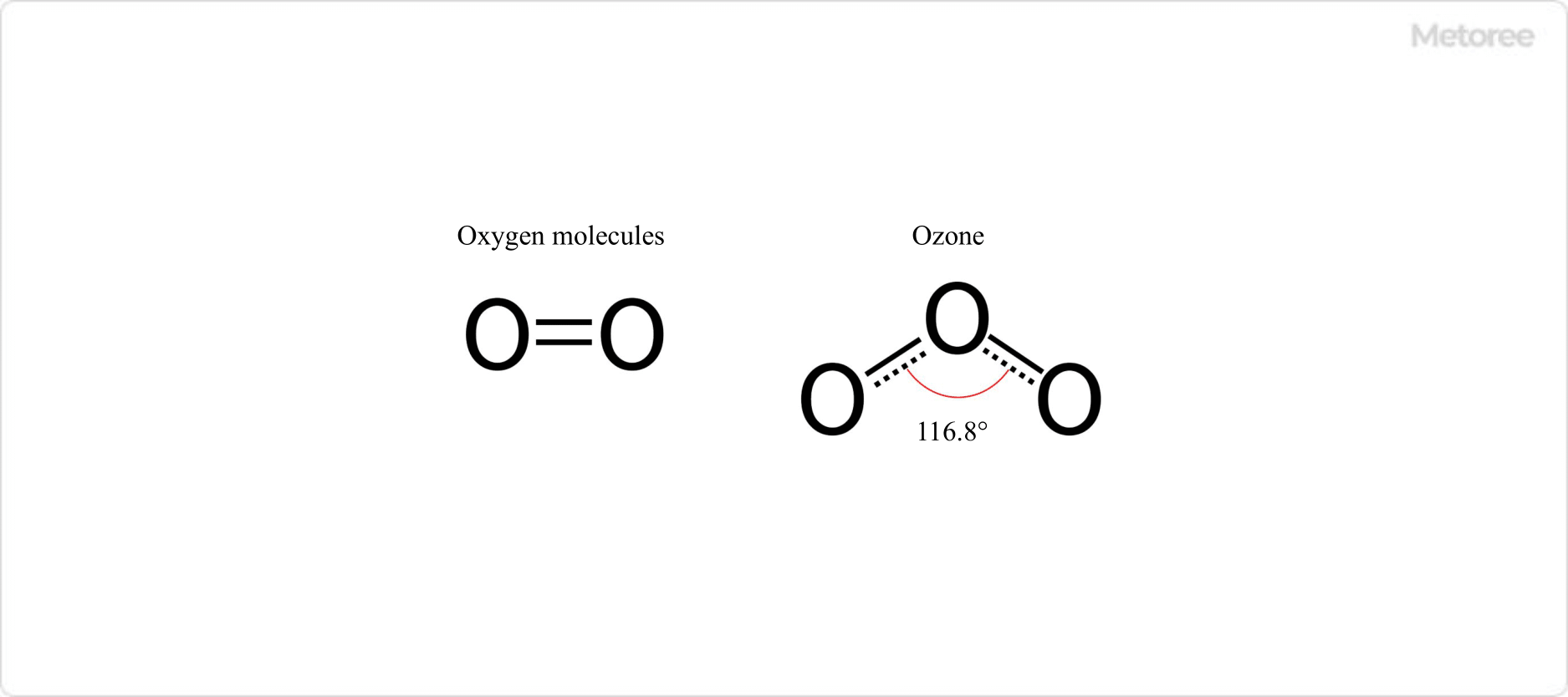
Figure 1. Molecular Oxygen and Ozone
Ozone (O3) is an allotrope of oxygen (O2), consisting of three oxygen atoms. Known for its distinctive, pungent odor, ozone is naturally produced from oxygen molecules under strong stimuli like ultraviolet rays or lightning, contributing to atmospheric self-cleaning through sterilization and deodorization.
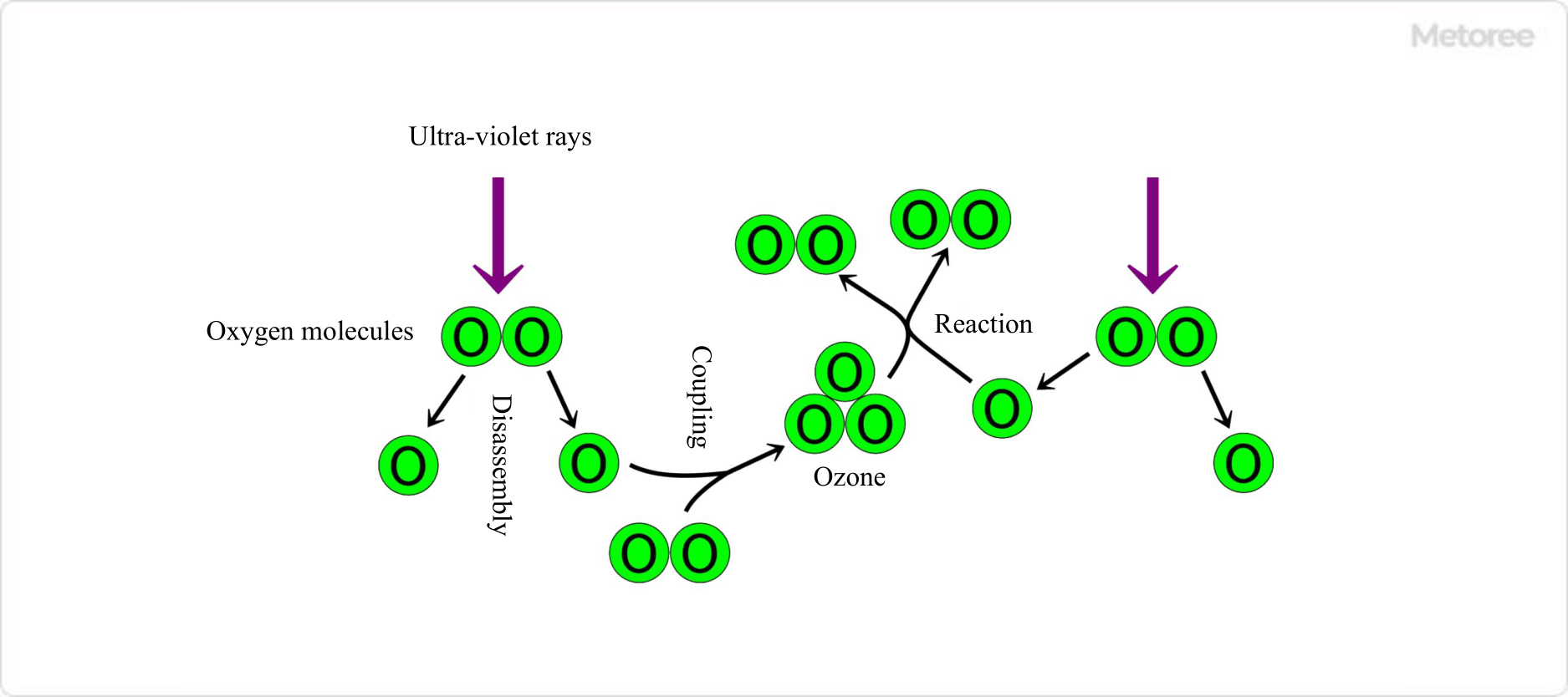
Figure 2. Formation and Dissipation of Ozone in the Stratospheric Atmosphere
Near the earth’s surface, ozone concentration is below 0.1 ppm, but it forms a protective layer in the stratosphere, absorbing harmful ultraviolet rays to shield terrestrial life.
Uses of Ozone
Ozone’s applications range from sterilization and deodorization in water treatment and food storage to medical and industrial settings. Its production from ambient air makes it accessible anywhere, with a variety of generators available for different scales of use.
Properties of Ozone
Ozone is a dense, colorless gas under standard conditions, with significant water solubility and an extraordinary oxidizing ability. It stands as one of the most potent naturally occurring oxidants, capable of oxidizing almost all organic matter and metals.
1. Oxidizing Power
Ozone’s high oxidizing power allows it to donate oxygen atoms readily, decomposing to oxygen over time even without a reactant. This makes it highly effective for oxidation processes.
2. Deodorizing and Sterilizing Effects
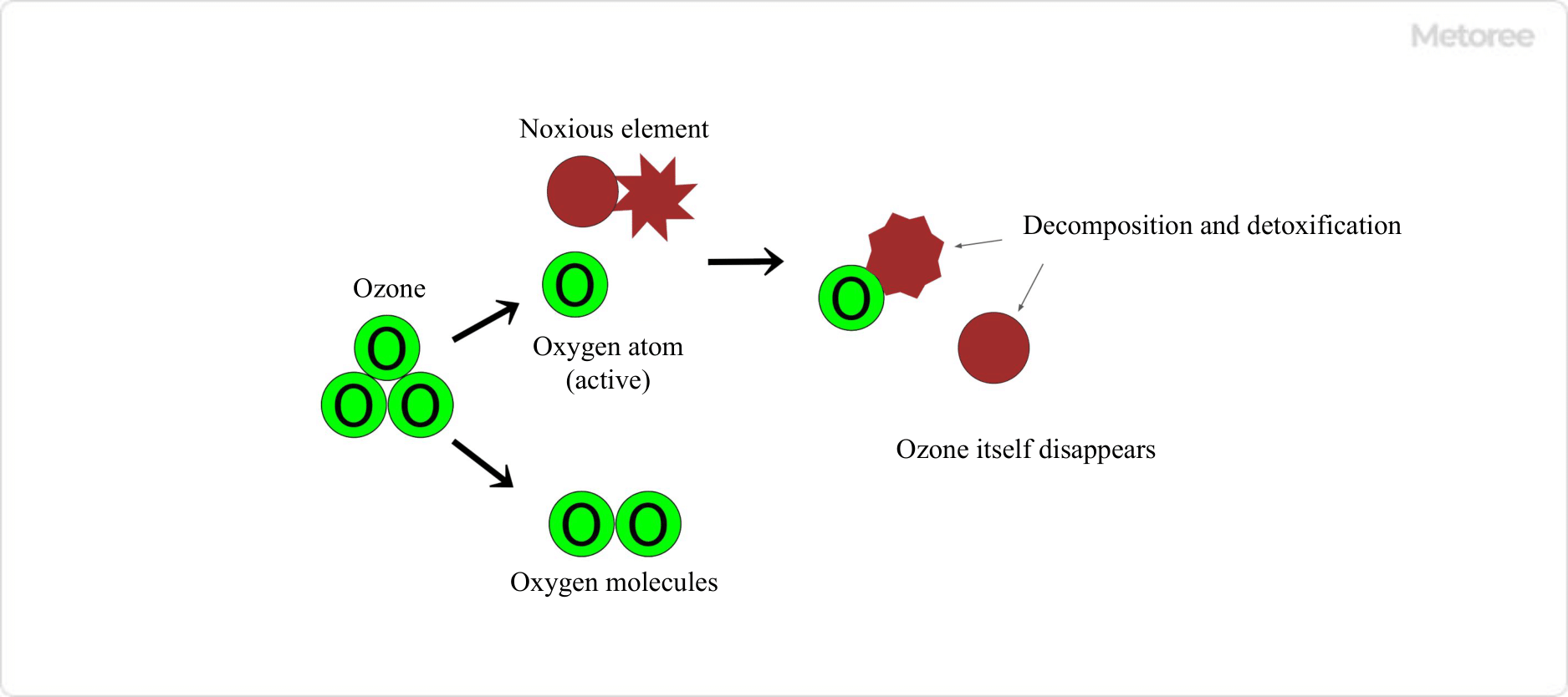
Figure 3. Detoxification of Harmful Molecules by Ozone
Ozone effectively deodorizes and sterilizes by oxidizing and decomposing organic and inorganic substances, surpassing other disinfectants like chlorine in efficiency at lower concentrations.
Other Information About Ozone
1. Advantages of Ozone
- No risk of bacterial resistance.
- Gas form allows for wide dispersal and effective odor and harmful gas decomposition.
- Capable of bleaching by decomposing dyes within fibers.
- Transforms into oxygen or harmless oxides, leaving no toxic residue.
- On-site production from air is feasible with proper equipment, making it versatile and safe.
2. Toxicity of Ozone
High ozone concentrations can cause respiratory issues and mucous membrane irritation, along with potential harm to plant life and material degradation. It is a key component of photochemical smog, posing environmental and health risks.