What Is Sulfamic Acid?
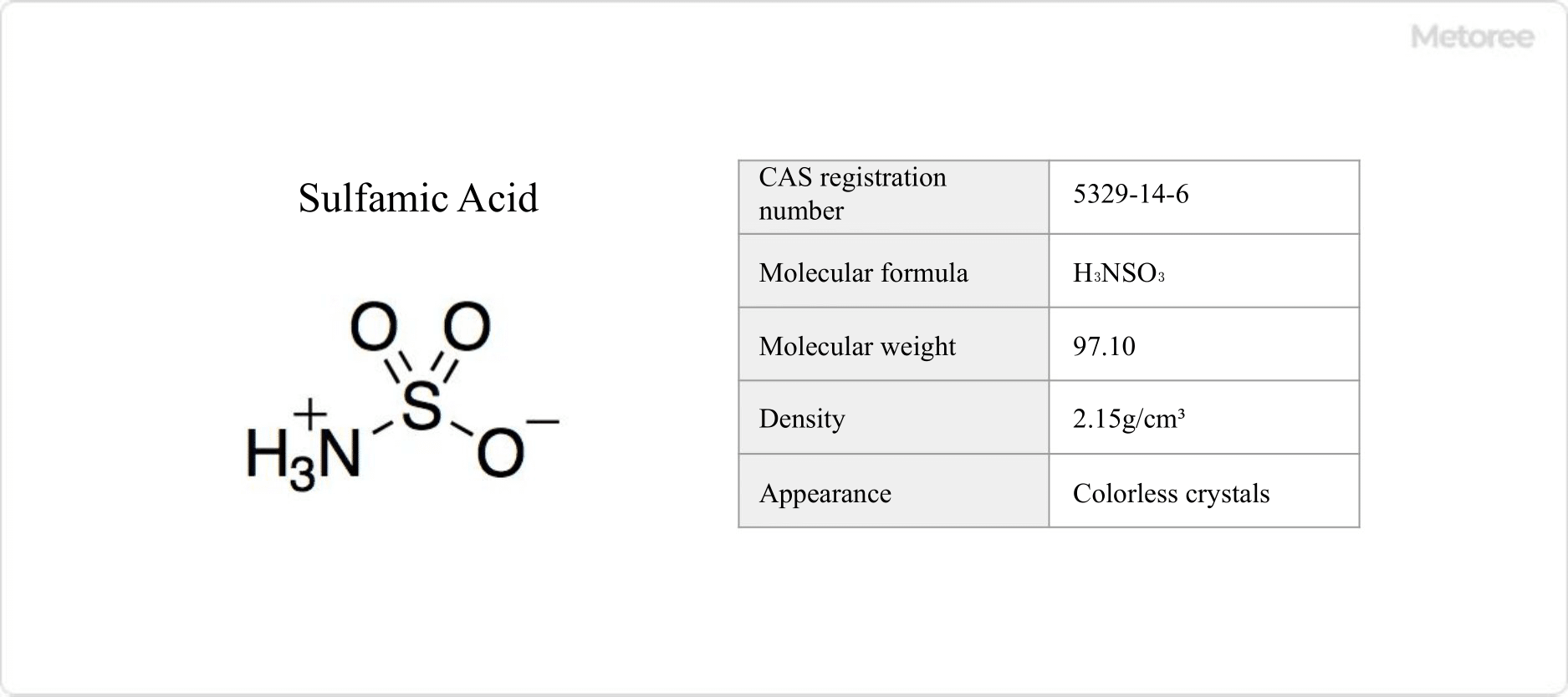
Figure 1. Basic Information on Sulfamic Acid
Sulfamic acid, known also as amidosulfuric acid, is a water-soluble chemical formed by substituting the hydroxyl group in sulfuric acid with an amino group. This white solid decomposes at 205°C and is insoluble in ethanol, not hygroscopic, facilitating the production of a pure form. Its synthesis involves urea and fuming sulfuric acid.
Reacting with nitrous acid yields nitrogen gas, and nitric acid, acts as a reducing agent, producing nitrous oxide.
Uses of Sulfamic Acid
As a precursor to the artificial sweeteners Cyclamate and acesulfame potassium, sulfamic acid finds extensive use. It also reacts with 2-ethyl hexanol to form 2-ethylhexyl sulfate, used in cotton silketing and as a standard in acid-base titrations for determining sodium hydroxide concentrations. Moreover, it serves as a cleaning agent and rust remover, offering an odorless alternative to hydrochloric acid-based cleaners.
Properties of Sulfamic Acid
In aqueous solutions, sulfamic acid exhibits strong acidity (Ka = 1.01×10−1), dissolving metal salts without corroding metals. It hydrolyzes to ammonium hydrogen sulfate above 80°C and releases ammonia when heated in water.
Structure of Sulfamic Acid
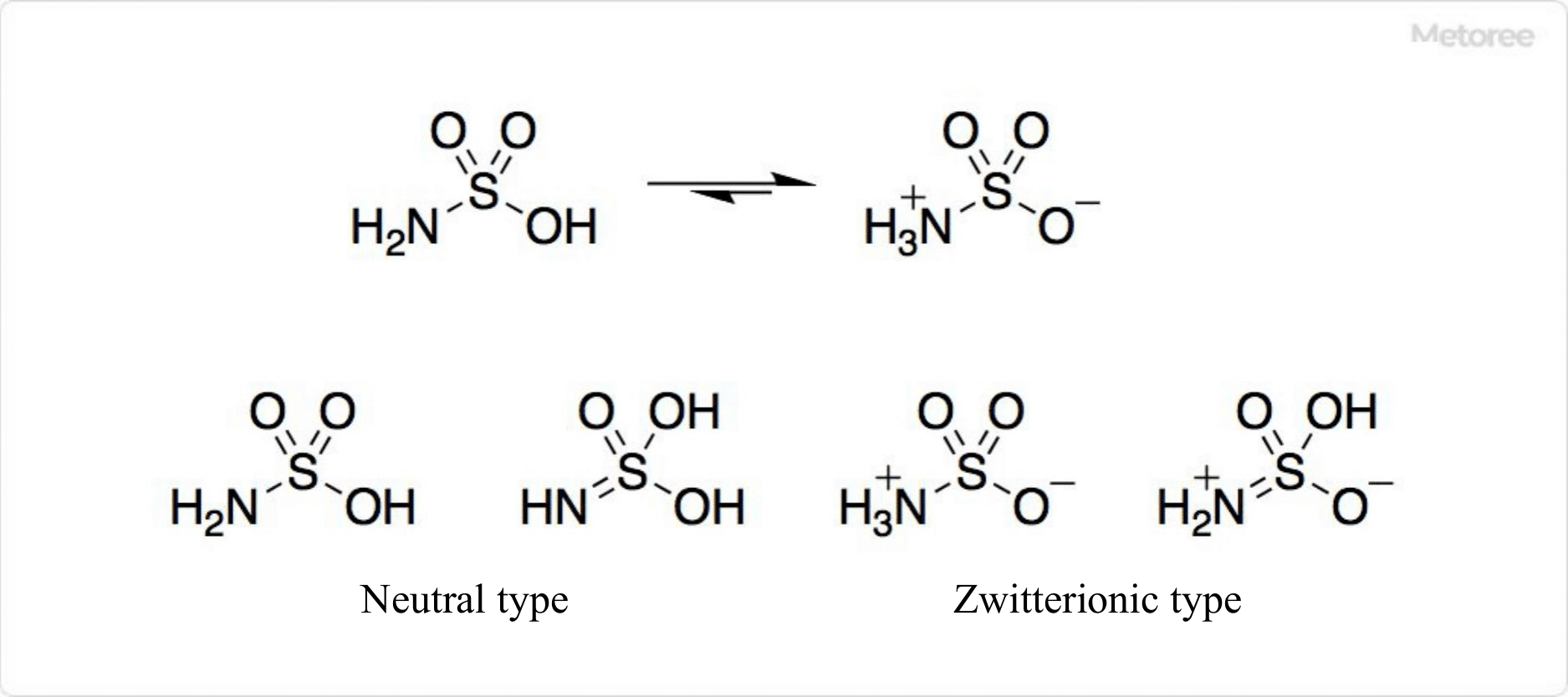
Figure 2. Structure of Sulfamic Acid
The chemical structure of sulfamic acid (H3NSO3), featuring a molar mass of 97.10 g/mol and a density of 2.15 g/cm3, includes a tautomeric zwitterionic form, as determined by neutron diffraction studies.
Other Information on Sulfamic Acid
1. Chemical Reactions
It acts as a scavenger of hypochlorite ions in various chemical oxidations and forms sulfate esters when reacted with alcohols under mild conditions, facilitated by urea as a catalyst.
2. Synthesis of Cyclo
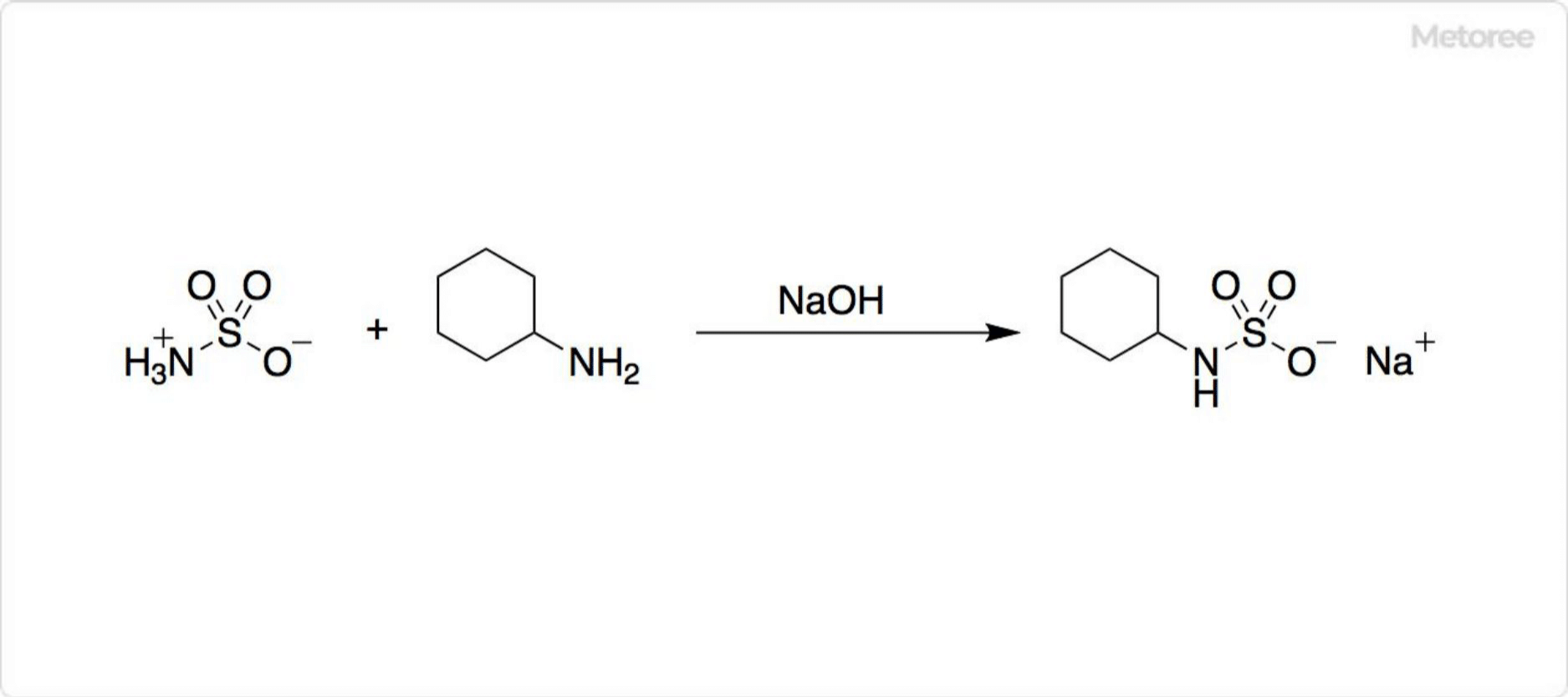
Figure 3. Synthesis of Cyclo from Sulfamic Acid
The reaction between sulfamic acid and cyclohexylamine, in the presence of sodium hydroxide, produces Cyclo, a sodium cyclamate sweetener, demonstrating a sweetness significantly greater than sugar but with a bitter aftertaste at high concentrations.