What Is an Electric Blower?
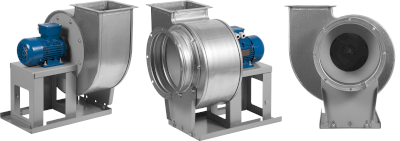
An electric blower is a device powered by an electric motor that draws in air, accelerates, and directs it outward. The generation of wind is facilitated by the rotation of fan blades. The electric motor enables precise control over the blower’s speed and volume, with many models featuring adjustable settings to modulate wind intensity for varying conditions and preferences.
Differentiation between fans, blowers, and compressors is based on airflow pressure; fans operate below 10 kPa, blowers between 10 kPa and 100 kPa, and devices above 100 kPa are considered compressors.
Uses of Electric Blowers
Electric blowers serve multiple roles across various sectors:
1. Industrial Applications
They are essential in factories for cooling machinery and processes, preventing overheating, and ensuring temperature control in industrial furnaces. Additionally, they are vital for ventilating spaces with organic solvent paints, contributing to workplace health and safety.
2. Air Conditioning
During hot weather, electric blowers help lower indoor temperatures and distribute cool air evenly, enhancing the efficiency of air conditioning systems and ensuring comfort.
3. Underground Parking
In underground parking facilities, blowers promote air circulation, drawing in fresh air and expelling stale air to maintain a clean and healthy indoor environment.
4. Drying Applications
Blowers are also used to regulate humidity, aiding in drying laundry by evaporating moisture, thus reducing humidity and preventing mold and moisture-related issues.
Principle of Electric Blowers
The core of an electric blower is its motor, which rotates a shaft connected to fan blades. These blades, designed at specific angles and shapes, draw in air and accelerate it outward. The airflow’s speed and volume are adjustable through the fan blades’ rotation speed and design.
Types of Electric Blowers
Electric blowers are categorized by the fan’s shape and airflow direction:
1. Axial Flow Blower
Axial flow blowers draw air parallel to the fan blades’ axis, pushing air out in the same direction. Ideal for widespread cooling and ventilation, they are frequently used in aircraft cooling and air conditioning systems.
2. Centrifugal Blowers
Centrifugal blowers intake air along the shaft and expel it at a right angle, excelling in situations requiring high-pressure airflow for exhaust, ventilation, and air conditioning applications.
3. Oblique Flow Blower
Combining features of axial and centrifugal blowers, oblique flow blowers direct air at an angle, offering a balance of volume and pressure suitable for various uses, including air conditioning, ventilation, cooling, and exhaust.