What Is a Hardness Testing Instrument?
Hardness testing instruments evaluate the hardness of various materials and products.
Depending on their basic principles, hardness testing methods can be broadly classified into indentation testing and dynamic testing. The indentation test is performed by pressing a hard indenter into the surface of a test specimen and measuring the size of the surface area or depth of the indentation. The smaller the indentation area and the shallower the indentation depth, the harder the material is evaluated.
In the dynamic test method, a hammer is dropped from a certain height, and its rebound height is measured. This test method is called the Shore hardness test and utilizes the property that the harder the specimen is, the higher it will bounce back.
Various hardness testing instruments are used to perform the above test methods, depending on the indenter, the load applied to the indenter, and how the indentation is measured. When evaluating hardness, it is essential to select the appropriate testing method and instrument based on the test specimen’s size, shape, and purpose, as well as on the agreement between the recipient and the testing party.
Uses of Hardness Testing Instruments
- Test Method to Measure Surface Area of Indentation
Vickers hardness test and Brinell hardness test are used to measure the surface area of indentation.
Vickers Testing Instrument
Vickers hardness testing instruments are used to test various materials, including metallic materials. It is characterized by a small test load and evaluates hardness in a narrow range. It is also used to assess the hardened layer depth of various surface treatments, such as carburizing, induction hardening, and nitriding layers, as well as the hardness distribution of welds.
Brinell Hardness Testing Instrument
The Brinell hardness testing instrument tests castings, forgings, and other metallic materials with rough surfaces and heterogeneous grain structures. It is characterized by a large test load and large indentation, allowing for average hardness evaluation over a relatively wide range.
- Indent Depth Test Method
The Rockwell hardness test is a test method to measure indentation depth. The Rockwell hardness testing instrument is mainly used for hardened metal materials. When evaluating the hardness of the hardened layer in hardened metal materials, the appropriate test conditions (set as a scale) must be selected according to the hardness and depth of the hardened layer.
Shore hardness testing, a dynamic test method, is used to test the hardness of large parts and rolling rolls and is a common test method used in the field within machine shops. The advantages of the Shore hardness testing instrument are that it can be used for product inspection because the indentation is less noticeable, and the instrument is small and portable.
Principles of Hardness Testing Instruments
The principles of hardness testing instruments differ depending on the type.
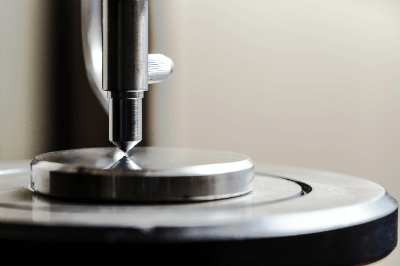
- Vickers Hardness Testing Instrument
In the Vickers hardness testing instrument, a diamond indenter with a 136° square face angle is pressed into a test specimen under a test load. The diagonal length of the square indentation created by this load is measured with a metallographic microscope attached to the tester.
JIS specifies test loads from 10gf to 100kgf. The test performed at one kgf or less is called the micro-Vickers hardness test. The testing instrument is the same for both Vickers and Micro-Vickers testing instruments. Both tests can be performed by changing the test load. Changing the test load does not change the hardness value as long as there is no irregularity in the material.
For the Vickers hardness test, the specimen should be no larger than the palm size. The surface to be tested also needs to be mirror polished, so it is almost always necessary to cut out the part of the specimen whose hardness is to be determined.
- Brinell Hardness Testing Instrument
The Brinell Hardness testing instrument uses a ball indenter, steel, or cemented carbide ball 10 mm in diameter. A test load of 3,000 kgf is often used. The load is calculated by dividing the load applied to a spherical indentation in the test surface by the surface area of the permanent indentation.
- Rockwell Hardness Testing Instrument
The Rockwell hardness testing instrument applies load in three stages. First, a reference load is used, then a higher test load is applied, and then the load is returned to the reference load. The hardness evaluation is based on the difference in indentation depths between the two reference loads applied before and after the test.
In the Rockwell hardness test, the scale is determined by the combination of several test loads and indenter types. For example, if a diamond cone with a tip radius of 0.2 mm and a tip angle of 120° is used and the primary load is ten kgf, the A scale is used if the test load is 60 kgf, the D scale if 100 kgf, and the C scale if 150 kgf.
A test using a 1/16″ (1.5875mm) steel ball with a basic load of 10kgf and a test load of 100kgf falls under the B scale. Tests conducted with a basic load of 3 kgf and test loads of 15, 30, and 45 kgf are called Rockwell superficial hardness tests. It is used especially for hardness testing of thin steel plates.
In today’s Rockwell hardness testing instruments, the indenter is interchangeable and can be set to different base and test loads. The advantage is that loadings and depth measurements are performed automatically.
- Shore Hardness Testing Instrument
In the Shore hardness test, a diamond hammer of a specific shape and mass is dropped on a test specimen from a certain height, and the bounce height is measured. Unlike other testing instruments, the Shore hardness testing instrument is very small and uses no electricity.
Other Information About Hardness Testing Instruments
Calibration of Hardness Testing Instruments
Hardness testing instruments need to be calibrated periodically to ensure that they are performing correctly. The testing machine manufacturer usually services this.
Also, in daily operations, checking the accuracy using test specimens is essential. A standard test specimen with guaranteed hardness is prepared, and before the actual test is conducted, it is checked to ensure the correct results can be obtained with the standard test specimen. This preliminary check can also help you notice mistakes in test load or indenter selection.