What Is a Parts Feeder?
A parts feeder is a device that can automatically supply parts on a factory production line. It is also called an automatic parts feeder. They are used in conjunction with automated systems such as assembly, packaging, cooperative, and inspection machines.
Generally, it vibrates the parts so that each part in a disparate orientation can be fed in the same aligned orientation. This allows various processes, such as assembly, packaging, and wrapping, to be performed efficiently.
Parts feeder can be combined with image processing equipment and artificial intelligence to inspect parts simultaneously or with equipment in the following process to help improve work accuracy and reduce human and installation costs.
Uses for Parts Feeders
Parts feeders are installed to improve the efficiency of factory production. They are used to manufacture mechanical and electronic parts, pharmaceuticals, and food products. Parts feeders are used to increasing work efficiency by automating the supply of parts in combination with image processing equipment and artificial intelligence.
The objective is to automatically supply parts and simultaneously inspect the parts, thereby improving work accuracy and product quality. Some parts feeders supply multiple parts assembled, such as a washer and a bolt together, or disassemble and supply assembled parts.
Principle of Parts Feeders
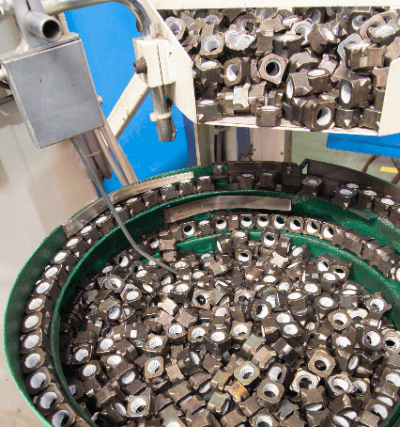
Parts feeders align parts by vibrating them. The part that vibrates the parts is called the vibrating element or oscillator and is the heart of the parts feeders. The vibration method is mainly electromagnetic, using an electromagnet, and the vibration generated is amplified through a plate spring to generate even greater vibration.
Other methods include the piezoelectric method, which uses piezoelectric elements. The supplied parts are first placed in a bowl, which is a container for parts, and then the bowl is vibrated by a vibrating element to align the parts. The aligned parts are sent to a chute, where they are fed to the machine for the next process.
The parts in the bowl are monitored by a device called a hopper. The hopper detects the number of parts in the bowl and controls the feeding. There are various types of hoppers, including electromagnetic, conveyor, and cylinder hoppers. Hoppers work to stabilize the parts feeders’ parts supply capacity by preventing parts from being overfilled or underfilled in the bowl.
Parts feeders are designed to incorporate various sensors and optional parts, allowing them to be customized for different purposes.
Selection of Parts Feeders
Various drive patterns are used in the bowl portion of the parts feeders, and the right parts feeders must be employed according to the parts.
The most common type of parts feeders are the electromagnetic parts feeders, but there are also various other types such as motor type, piezoelectric element type, and compound rotating disk type. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is essential to select the most suitable parts feeders after understanding the usage conditions and costs.
Types of Parts Feeders
There are various types of parts feeders, including electromagnetic, motor, piezoelectric (piezoelectric element), and compound rotating disk types, each of which has its characteristics.
1. Electromagnetic Parts Feeders
Electromagnetic parts feeders include half-wave type, full-wave type, high-frequency part type, and dual motion type.
- Half-Wave Method: The half-wave method has a frequency of 3,000 to 3,600 vibrations per minute, which provides a large amplitude and high conveying capacity, easy handling, and is often used for parts that are easy to sort.
- Full-Wave Method: The full-wave method, with a frequency of 6,000 to 7,200 vibrations per minute, is suitable for small or difficult-to-sort parts due to its good vibration frequency.
- High-Frequency Parts Feeders: An inverter controller generates a good frequency of 250 Hz to 350 Hz. It is suitable for minute workpieces.
- Dual Motion: Dual motion generates elliptical motion by setting up two vibration systems, one horizontal and one vertical. The vertical and horizontal vibrations are controlled separately to enable rapid feeding and smooth transfer. It is also possible to select either the vertical or horizontal vibration direction.
2. Motorized Parts Feeders
This type of parts feeder is driven by a motor in horizontal motion only and is characterized by its low noise level.
3. Piezoelectric Parts Feeders
Driven by a piezoelectric element. This type of parts feeder does not require vibration adjustment and is expected to save energy.
4. Combined Rotating Disk Parts Feeders
This parts feeder does not use vibration but uses a rotating disk to rotate parts for alignment feeding gently. Low vibration, low noise, and high-speed feeding are possible with this.