What Is an AUV?
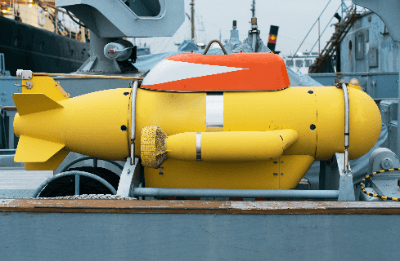
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), also referred to as unmanned underwater Vehicle (UUV), is a self-propelled underwater robot crucial as a platform for exploring areas inaccessible to humans during underwater exploration.
One of the major advantages of AUVs is their autonomy, operating without the need for human control or tether cables connecting humans to underwater robots. This eliminates the necessity for facilities such as control rooms or cable handling devices, resulting in minimal support equipment and, consequently, lower operational costs. The fully autonomous nature of AUVs allows them to operate independently of the range of human intervention, ensuring stable observations regardless of factors like water currents and waves.
Moreover, AUVs hold various promising prospects, such as operations without the need for support vessels and the efficient simultaneous operation of multiple AUVs.
Uses of AUVs
Currently, AUVs find applications primarily in relatively straightforward tasks, such as acoustically exploring terrain and conducting water quality surveys.
While the autonomy of AUVs is advantageous, the absence of human involvement poses a challenge in addressing issues or troubleshooting, requiring the robot to handle all problems independently. As a result, AUVs are mainly deployed for simpler tasks, given the difficulty of troubleshooting complex issues.
However, AUVs, with a broader operating range and lower costs compared to other underwater robots, excel in deep-sea exploration. The involvement of humans and tether cables is risky and challenging for underwater exploration in the deep sea when it comes to operating conventional underwater robots. The future holds expectations for the effectiveness of AUVs in applications such as the exploration of oil and gas, as well as offshore wind power facilities.