What Is R Screw?
R-Threads are a common name for tapered pipe threads.
The term “R-Threads” is so called because the male threads of R-Threads are called “R” and the female threads are called “Rc” in the JIS and ISO standards.
R Screws are used in “threaded pipe fittings” and “pipe end threads,” and are used for pipe joints.
Uses of R Screws
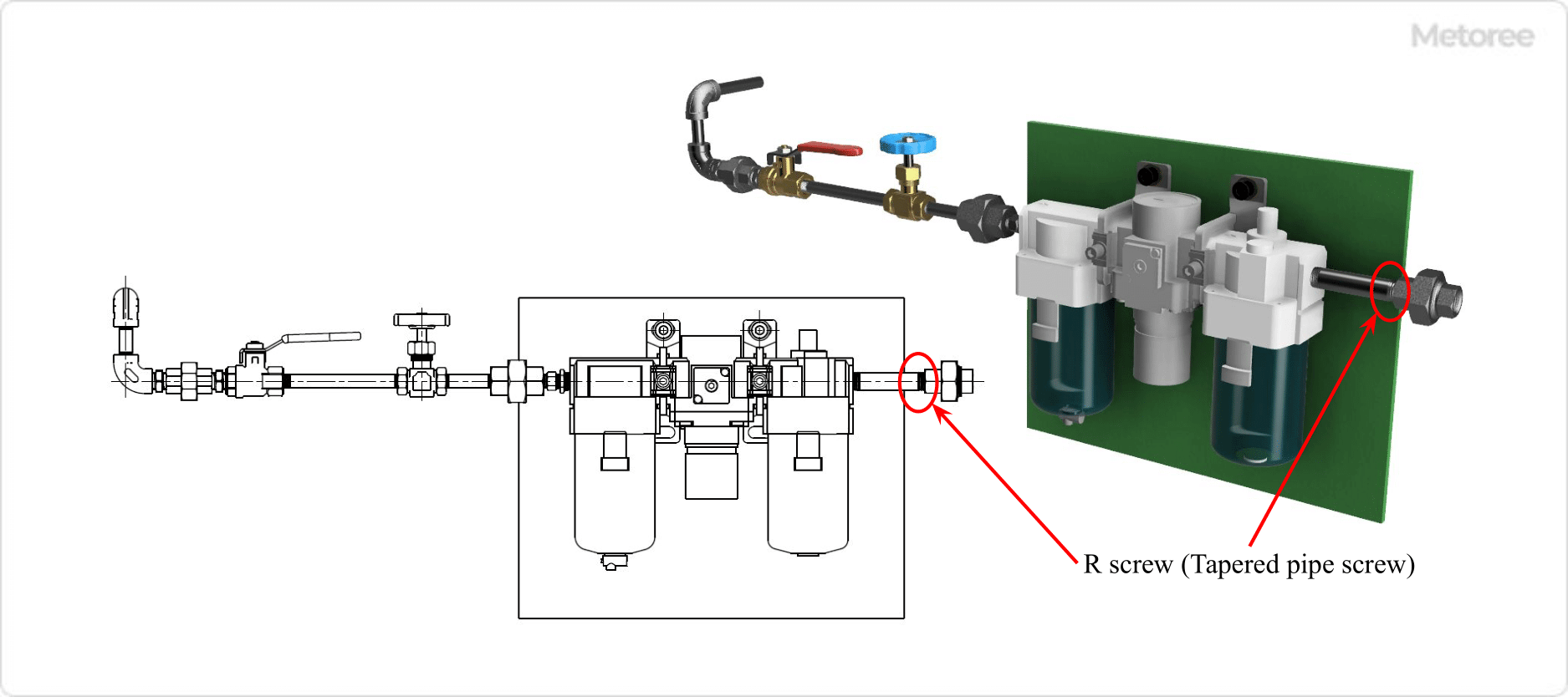
Figure 1. Example of piping use of R screw (tapered pipe screw)
R Screws (tapered pipe threads) provide excellent airtightness at joints in piping installation, with minimal leakage of fluid in the pipe. For this reason, R-Threads are used in joints of various types of fluid transport piping, pneumatic equipment, vacuum equipment, and other piping where fluid leakage is a fundamental problem.
Principle of the R Screw
The principle of the R Screw is explained here using the typical “JIS B0203 Tapered pipe threads. The standard profile of a tapered thread is a 1:16 taper to the center axis of the pipe or fitting thread.
Parallel female threads are threaded parallel to the center axis. See Figure 2 for reference profiles of tapered and parallel threads.
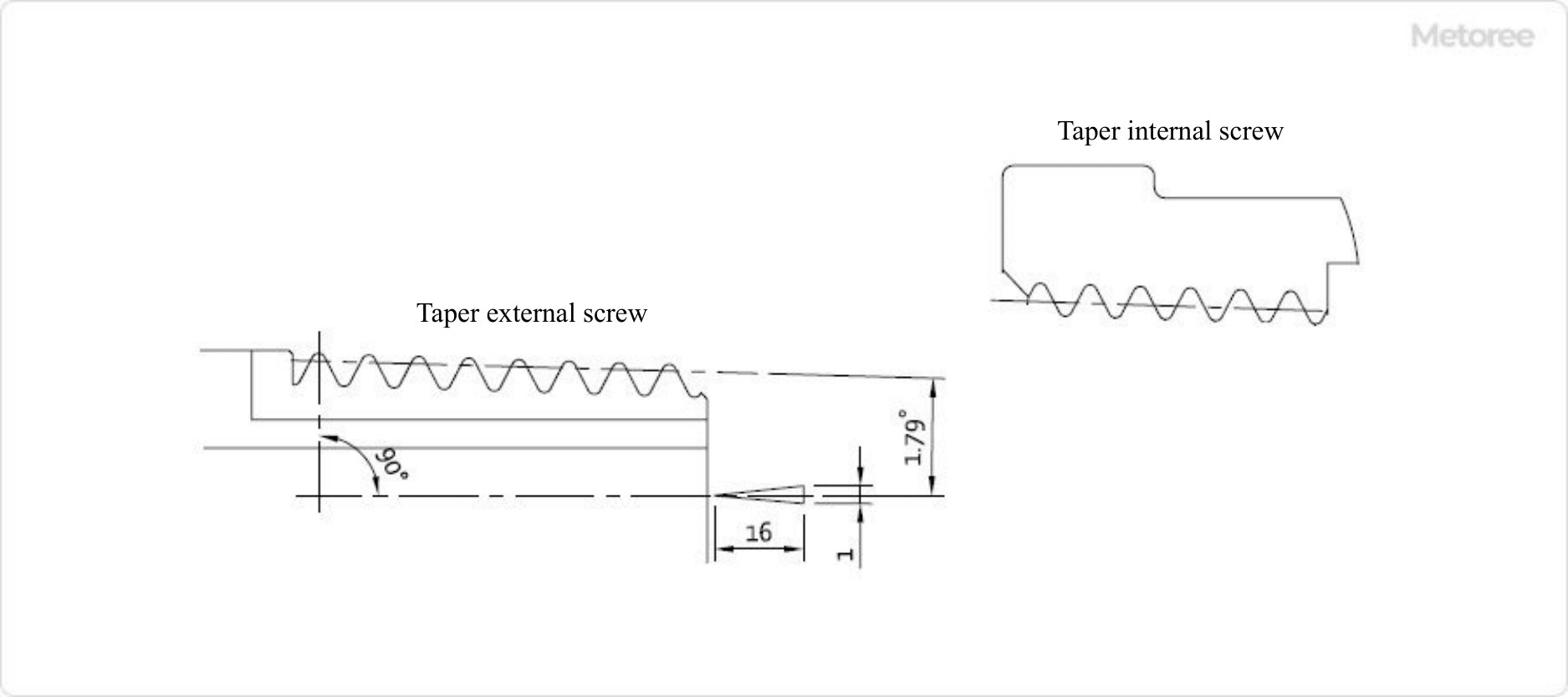
Figure 2. Taper external screw for pipes, internal screw, and parallel internal screw
In the R Screw, the outer diameter on the male thread side increases as one moves away from the tip, and the inner diameter on the female thread side decreases as one moves away from the end. Therefore, the deeper the threading depth, the more closely the male and female threads adhere to each other, resulting in a mechanism that increases airtightness.
As with pipes, pipe taper threads are generally nominated in inches, with 1/8-inch (for 1/8B or 6A pipes) threads called “itibu” and 1/4-inch (for 1/4B or 8A pipes) threads called “nibu”. As mentioned above, in addition to the R Screw, there are various other standards for pipe threads, such as Rp (parallel pipe threads for tapered pipe threads), G (parallel pipe threads), and NPT (tapered pipe threads for general use in the United States).
Since screws of different standards cannot be connected, it is important to select the appropriate standard screw according to the specifications of the equipment and joint to be used.
Other Information on R Screws
1. Typical Examples of Products Using R Screws
Typical examples of products using R Screws are as follows.
- JIS B2301 Threaded malleable cast iron pipe fittings
- JIS B2302 Threaded steel pipe fittings
- JIS B2308 Stainless steel threaded pipe fittings
Refer to Figure 3 for pipe fittings using R Screws and male threads at the pipe ends.
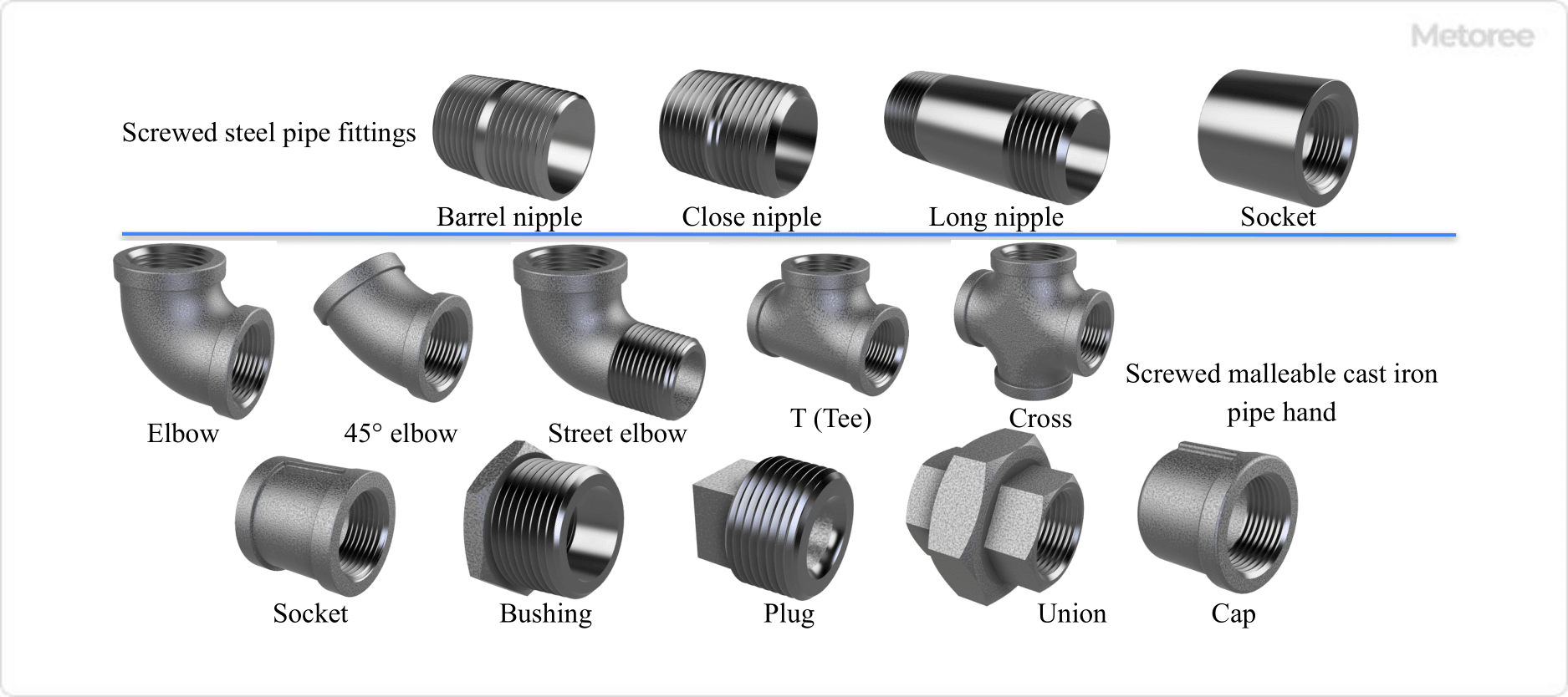
Figure 3. Pipe fittings using R screw, external screw at pipe ends
Since R Screws are threaded joints, they are much easier to install than welded or flanged joints.
2. Standards for R Screws
The standards for R Screws and Taper Pipe Threads are as follows
- JIS B0203, Taper Pipe Threads
- ISO 7-1, Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads-Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances, and designation.
- ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 NPT American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads
In JIS B0203, the notation of R Screw is as follows.
- Taper male thread for 1-1/2B (40A) pipe: R1 1/2
- 1-1/2B (40A) Taper female thread for threaded fittings: Rc1 1/2
- 1-1/2B (40A) Parallel