What Is Disposable Protective Clothing?
 Disposable protective clothing is protective clothing intended for onetime use only.
Disposable protective clothing is protective clothing intended for onetime use only.
It is worn over regular clothing, and the most appropriate type of clothing is used for each of the various uses of protective clothing. Conventional applications include training and exercises for the Self-Defense Forces, operational use, and treatment of infectious diseases in hospitals (e.g., H1N1 influenza, SARS, etc.). Infectious disease treatment in hospitals (e.g., H1N1 influenza, SARS), and so on. Recently, however, the need for use in the medical field in coronary disasters has been increasing, and availability has been decreasing.

Figure 1. Overview of protective clothing
Uses of Disposable Protective Clothing
Disposable protective clothing is used to protect workers from a variety of hazards in any workplace.
Hazards include acids, alkalis, chemicals, radioactive materials, and viruses. They also include sharp objects such as knives, high-speed flying objects, high temperatures, flames, and electrical sparks.
ISO/JIS standards provide detailed specifications depending on the characteristics of the clothing and the type of hazardous factor. Protective clothing for use in handling acids, alkalis, organic chemicals, other gases and liquids, and particulate chemicals. There are different types of protective clothing depending on the target hazardous substance and the structure of the chemical protective clothing, and the performance requirements are specified for each type.
Specific examples of disposable protective clothing include the following:
- Sites where skin may be exposed to or come in contact with acids, alkalis, organic chemicals, dust, or other hazardous chemicals, such as chemical plant construction
- Prevention of freezing when working in cold weather
- When working with asbestos
- Dioxin and PCB treatment
- Secondary infection control during treatment of new coronary infections
- Radioactive material handling and decontamination work
- Sites that need to cope with mechanical shocks such as chain saws
Types of Disposable Protective Clothing
Disposable protective clothing is classified into various types based on the uses of and materials used.
1. Classification by Use

Figure 2. Example of special protective clothing
Chemical Protective Clothing
Protective clothing is designed to prevent the penetration of toxic gases and chemicals.
Protective Clothing for Biohazard Control
Protective clothing to protect against the risk of exposure to or contact with biohazardous materials (pathogens and biologically derived substances that may harm humans).
Protective Clothing Against Heat and Flame
Protective clothing is used to protect the body from heat and flames. Examples include smelters in the steel industry, where workers are exposed to high radiant heat and high-temperature molten metal splatter.
Protective Clothing to Cope With Mechanical Shocks
Protective clothing is used to prevent cuts and puncture wounds caused by sharp objects such as knives. As a specific example, at a site where chainsaws are used, the lower half of the body, below the thighs and knees, should be protected.
Protective Clothing Against Radioactive Contamination
Protective clothing is used for the purpose of protection against contamination by radioactive materials.
Protective Clothing Against Electricity
Clothing used to protect the body from electrical hazards, and protective clothing used to prevent electrostatic charging.
Protective Clothing Against Cold
Protective clothing is used to protect the body from the cold in areas or special locations where the outside temperature drops to negative temperatures.
High Visibility Safety Clothing
Protective clothing is used to increase visual recognition of the wearer’s presence in order to prevent contact and collision accidents caused by vehicles, construction equipment, and other moving objects.
2. Classification by Material
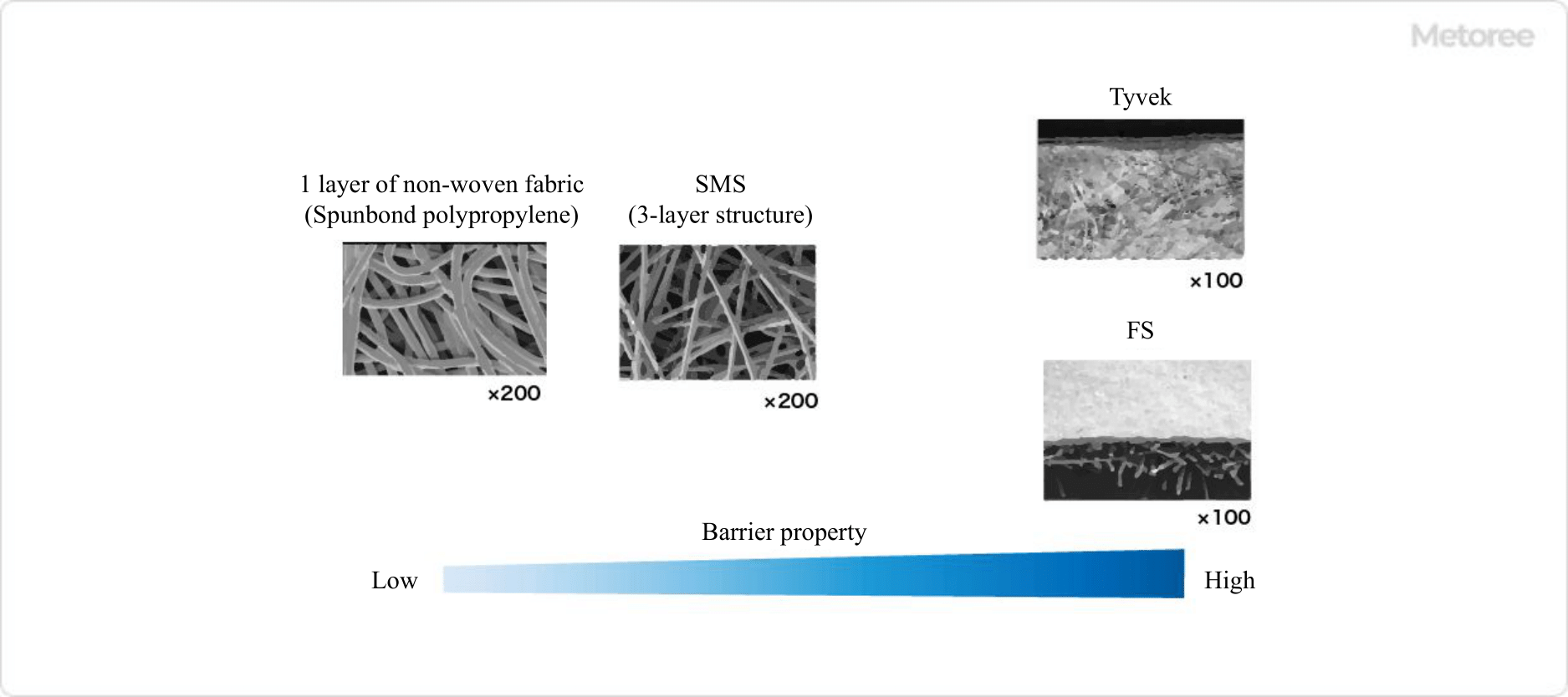
Figure 3. Various protective clothing materials
Non-woven Fabric One Layer Type
This product is made of spun bond polypropylene. The spun-bonded single-layer structure has many voids between fibers. Although the barrier property is somewhat inferior, it is inexpensive and suitable when cost is important. This fabric is sufficient for light soiling.
SMS
This product is made of SMS polypropylene. It has a three-layer structure of spun bond, melt blown, and spun bond. It features strong abrasion resistance and a cloth-like feel to the touch. Although relatively inexpensive, it is resistant to abrasion and light soiling, and has a high barrier effect against dust and splashes.
FS
This is a product in which film laminate is used. It has a structure in which a thin film material is attached to the surface of polypropylene, spun-bonded nonwoven fabric, or the like. It has high barrier properties against dirt and dust, and excellent waterproofing properties, making it suitable for work in watery areas.
Tyvek® (Japanese Brand of Polyester Foil)
Tyvek is a special material unique to DuPont, consisting of continuous microfibers of high-density polyethylene (0.5~10 microns) bonded together by heat and pressure, which provides excellent barrier properties against particles of 1 micron or less. Two-layer protective clothing with polymer coating is also available.
How to Choose Disposable Protective Clothing
As mentioned above, there are various types of protective clothing available, depending on the type of hazard. Work supervisors and personnel in charge of operations must acquire the correct knowledge of these hazards and protective clothing, and select protective clothing that matches the hazard. If used incorrectly, the possibility of health hazards increases.
In addition, if the knowledge is not sufficient, contaminated protective clothing may be taken outside the work area as it is, and there is a high risk of a secondary hazard if personnel other than those involved are exposed to the hazard. It is necessary to investigate the hazards in the surrounding environment, select appropriate protective clothing, and thoroughly educate workers on the correct way to use and put on and take off the clothing.