What Is Methylcyclohexene?
Methylcyclohexene, a cyclic olefin with the formula C7H12, includes three isomers distinguished by the placement of a methyl group on the cyclohexene ring. These isomers have unique CAS numbers and slight differences in their physical properties due to the arrangement of the double bond and methyl group.
Uses of Methylcyclohexene
Primarily a synthetic raw material, methylcyclohexene’s high reactivity is exploited in organic synthesis for creating various compounds, including chlorohexylsilane, and in producing resins by forming polymers. These resins are noted for their excellent heat resistance and balanced physical properties.
Properties of Methylcyclohexene
Methylcyclohexene exhibits properties typical of cyclic olefins, such as a low melting point and high boiling point for its isomers. It appears as a colorless to slightly yellow liquid, with each isomer having a distinct molecular weight, boiling point, and density.
1. 1-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene Properties
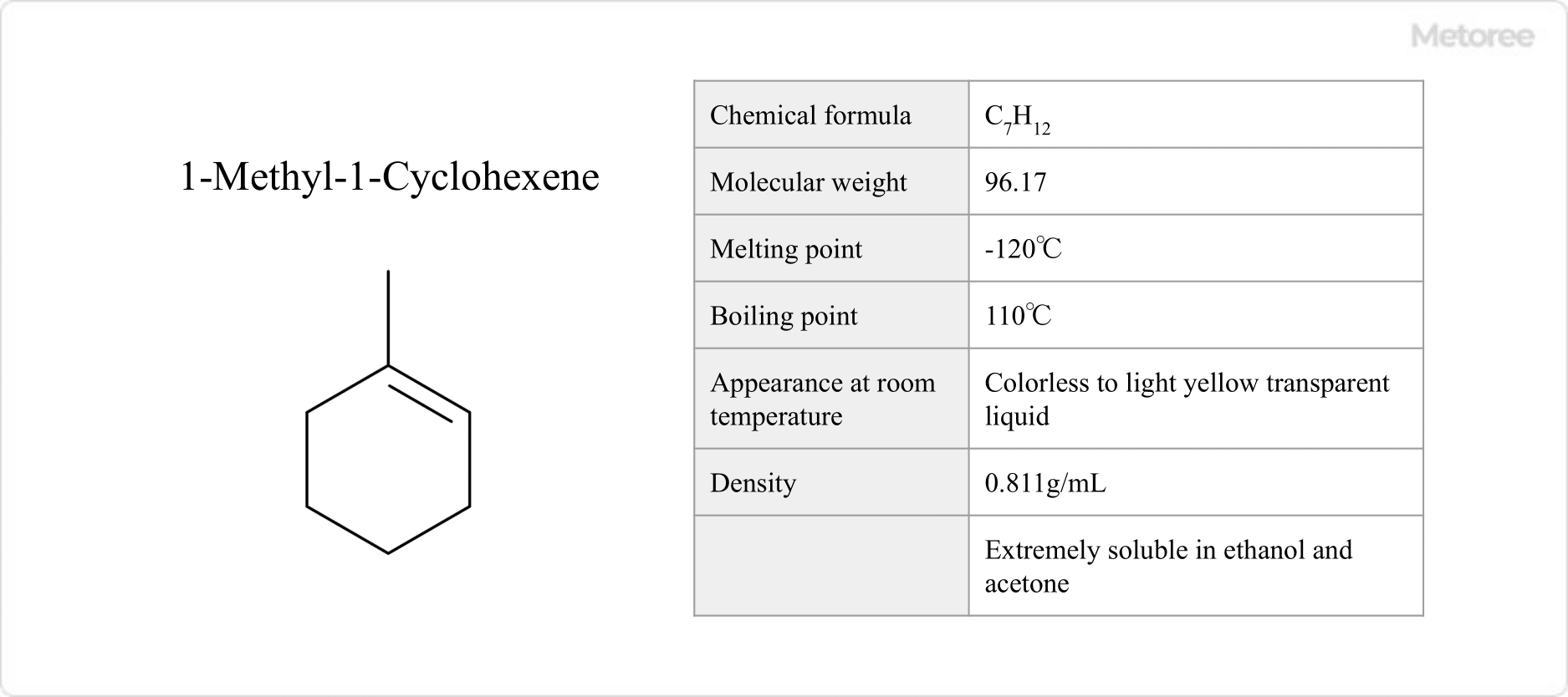
Figure 1: Basic Information on 1-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene
2. Properties of 3-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene
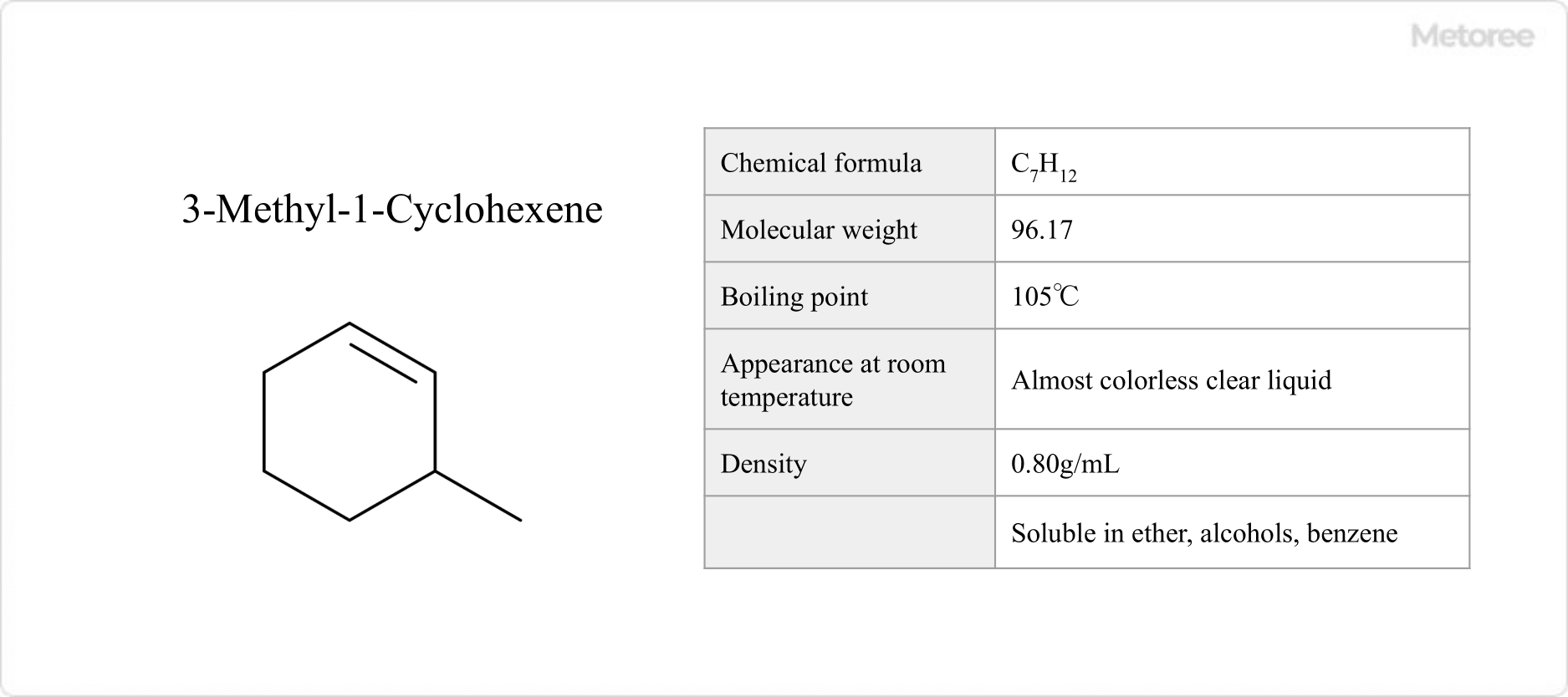
Figure 2. Basic Information on 3-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene
3. 4-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene
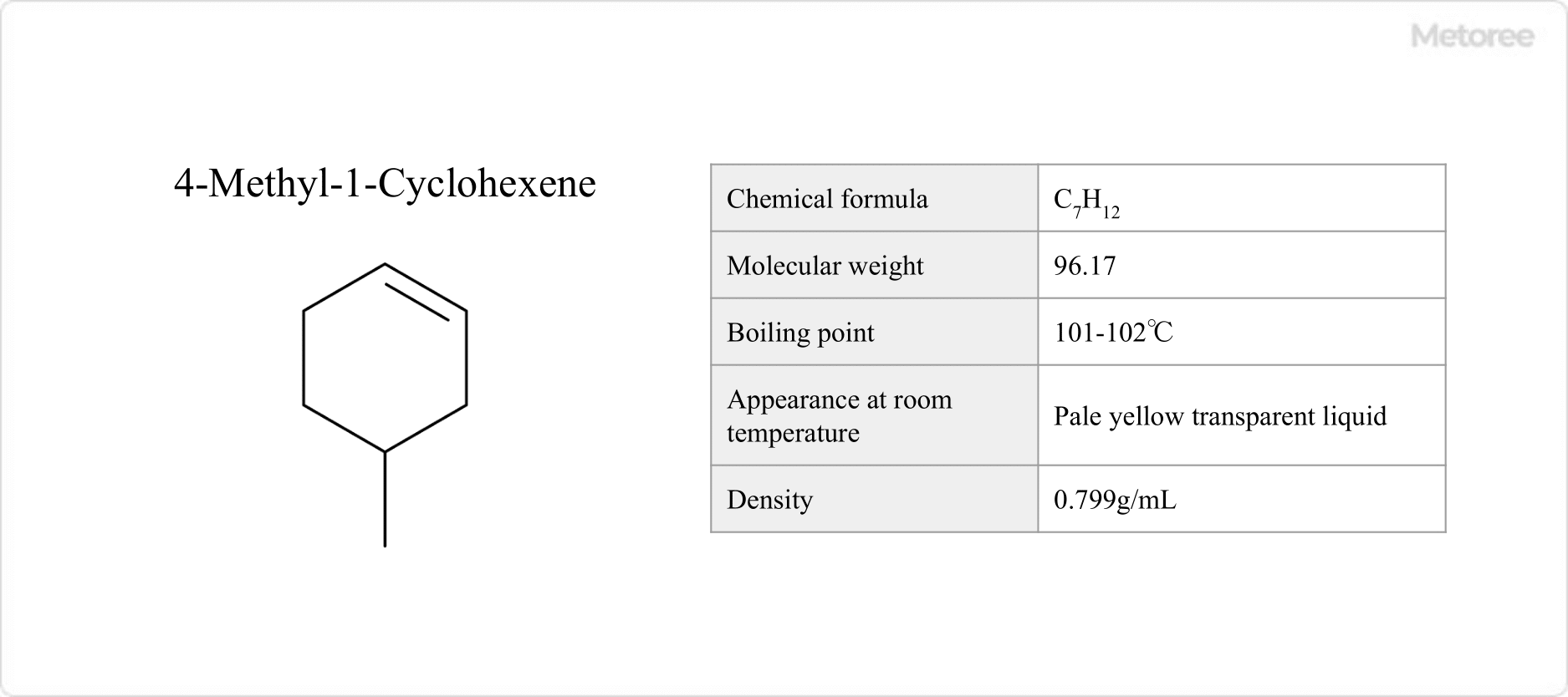
Figure 3. Basic Information on 4-Methyl-1-Cyclohexene
Other Information on Methylcyclohexene
1. Synthesis of Methylcyclohexene
Synthesis involves the olefination of methylcyclohexanol, a product of cyclohexanone and Grignard reagents, through a dehydration reaction.
2. Toxicity of Methylcyclohexene
Each isomer is classified under GHS for flammability and additional hazards, with 1-methyl-1-cyclohexene also noted for respiratory hazards. Safety measures, including protective equipment, are crucial when handling.