What Is Hexene?
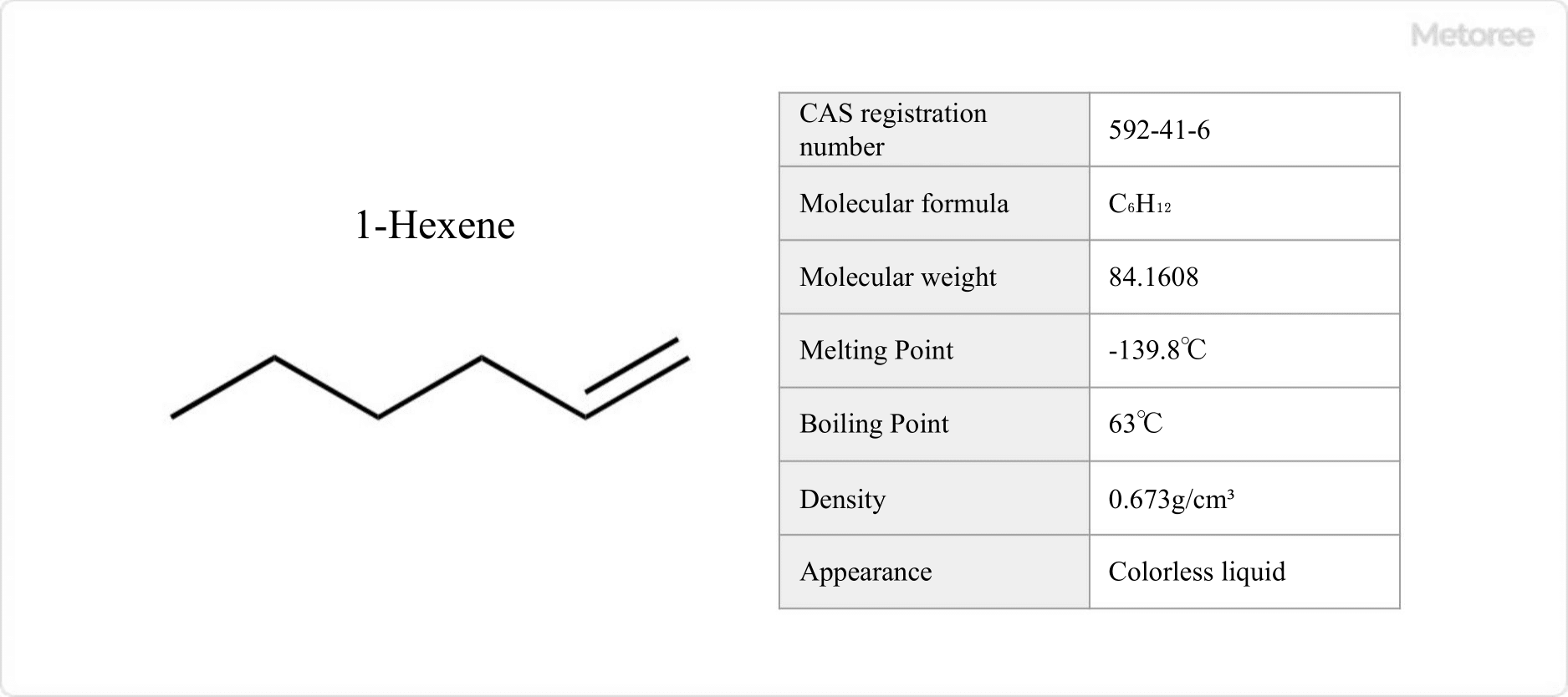
Figure 1. 1-Hexene Basic Information
Hexene is an alkene with the molecular formula C6H12.
There are 13 structures of isomers, depending on the arrangement and branching of the double bonds in the chain. The isomer most commonly used industrially is the α-olefin 1-hexene.
1-Hexene is highly reactive because of the double bond in the α-position. It is a chemically useful isomer of hexene and is used as a co-monomer, for example, to produce polyethylene.
Uses of Hexene
Among the isomers of hexene, 1-hexene is the most widely used. 1-hexene can be used as one of the monomers of polyethylene. It is found in 2-4% in high-density polyethylene and 8-10% in linear polyethylene.
1-Hexene can also be hydroformylated to aldehydes, which are used to obtain enanthate from aldehydes. The isomer of hexene, 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene, has a very high octane number.
The octane number is a value that indicates the resistance of gasoline to auto-ignition or knocking in the engine. Therefore, it is used in gasoline additives because it is less likely to cause knocking. In addition, 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene can be used as a raw material in the synthesis of terbinafine, which is used in antifungal drugs, and tonalid, which is used in synthetic musk-based fragrances.
Properties of Hexene
Hexene has a double bond and is subject to bromination and oxidation.
1-Hexene has a melting point of -139.8 °C, a boiling point of 63 °C, and a density of 0.673 g/cm3. 3,3-Dimethyl-1-butene has a boiling point of 41 °C and a flash point of -21 °C.
Structure of Hexene
Hexene is an organic compound with six carbon atoms and at least one double bond. Its molecular weight is 84.1608.
3,3-Dimethyl-1-butene is also called neohexene. It can be synthesized by contacting isobutene with a tungsten catalyst.
Other Information on Hexene
1. Linear Alkene Structure of Hexene
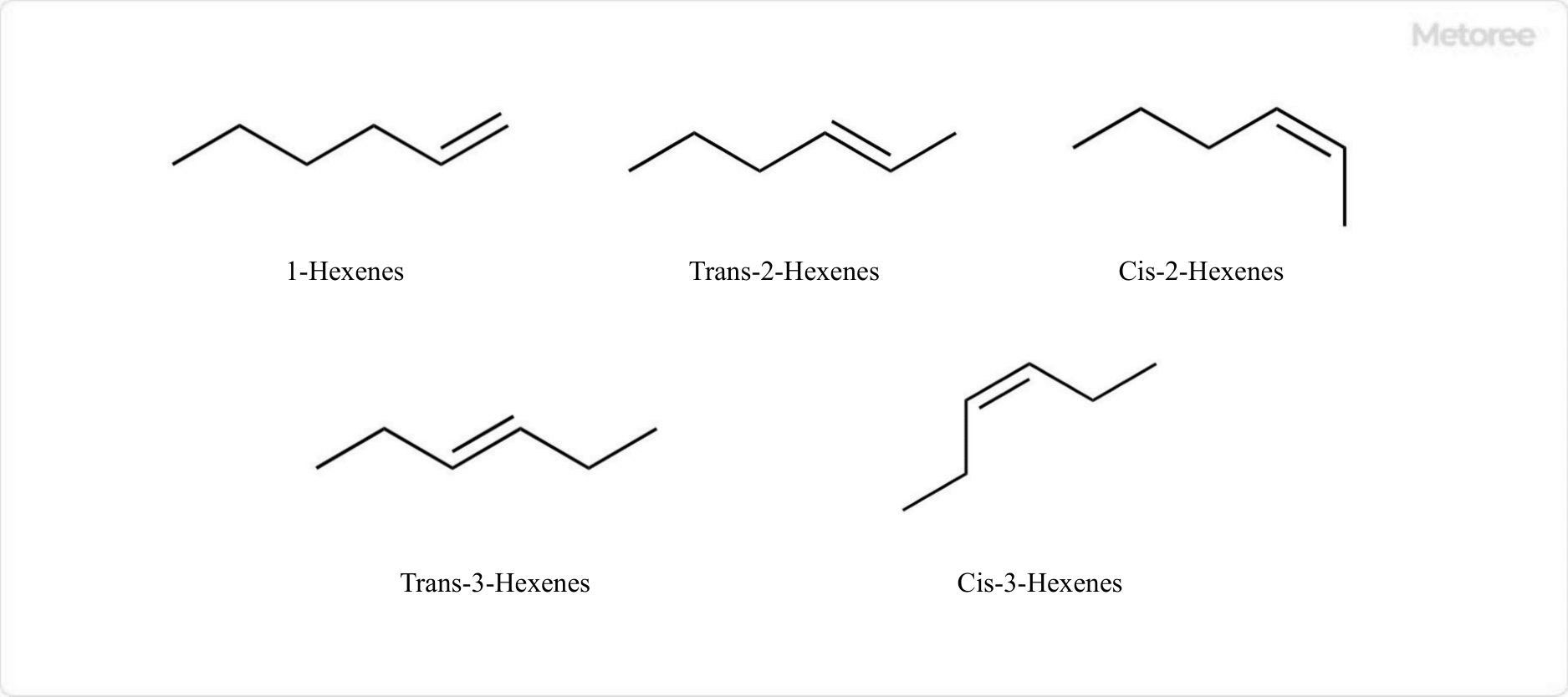
Figure 2. Structural isomers of linear alkenes of hexene
Hexene has three structures of isomers, depending on the position of the double bond. Specifically, they are 1-hexene, 2-hexene, and 3-hexene.
2-Hexene has two geometric isomers, cis-2-hexene and trans-2-hexene, respectively, while 3-hexene also has two geometric isomers, cis-3-hexene and trans-3-hexene.
2. Structure of the Branched Alkene of Hexene
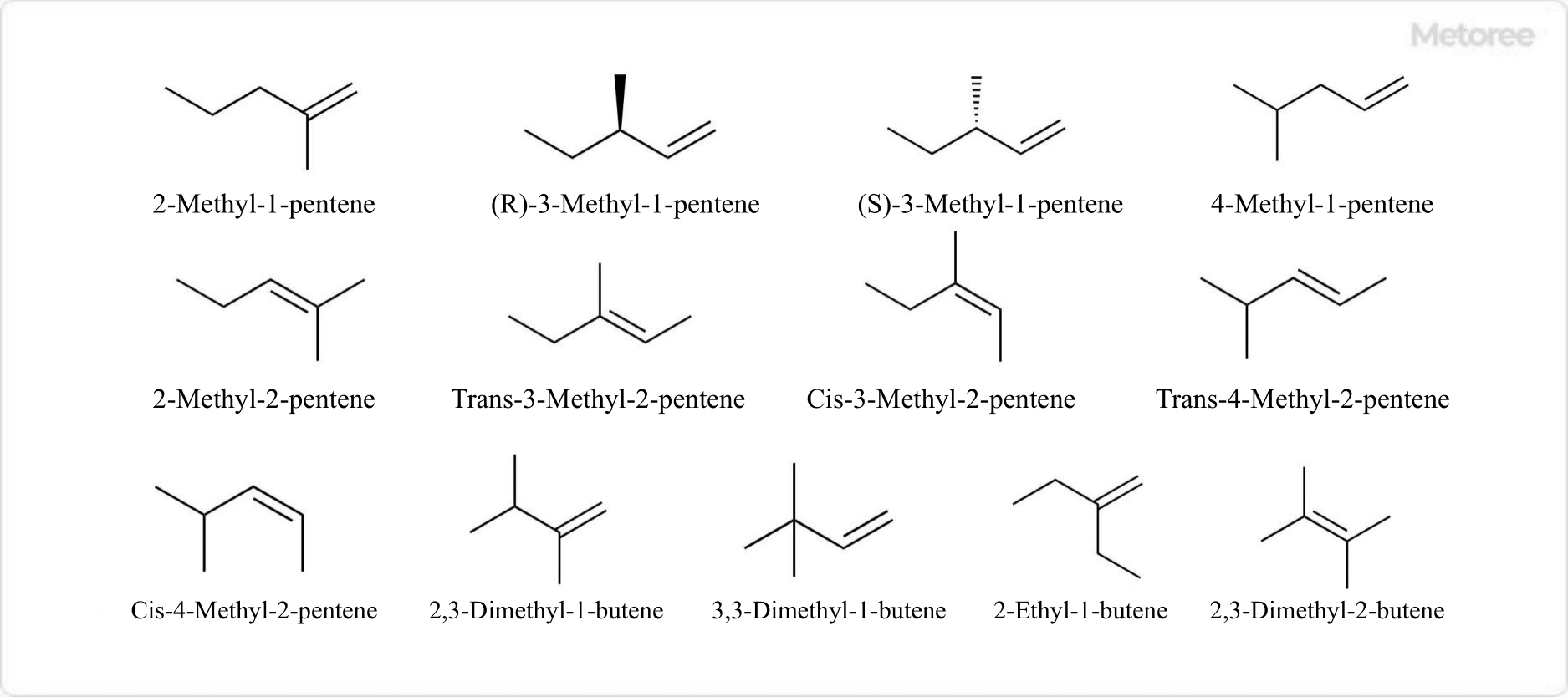
Figure 3. Structural isomers of branched alkenes of hexene
If branching is also considered, there are a total of 13 different structures of hexene isomers. The structure of hexene with 5 carbon atoms in the main chain includes 2-methyl–1-pentene, 3-methyl-1-pentene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, 2-methyl-2-pentene, 3-methyl-2-pentene and 4-methyl-2-pentene.
The only structure of the hexene isomer with four carbon atoms in the main chain and one side chain is 2-ethyl-1-butene. The structure of hexene with 4 carbon atoms in the main chain and 2 side chains includes 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene, 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene, and 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene.
3. Geometric Isomers of Hexene
One of the branched alkene isomers of hexene, 3-methyl-2-pentene, has geometric isomers. 4-Methyl-2-pentene also has two geometric isomers, cis-4-methyl-2-pentene and trans-4-methyl-2-pentene.
4. Optical Isomers of Hexene
There are optical isomers of 3-methyl-1-pentene, one of the branched alkene isomers of hexene. They are (R)-3-methyl-1-pentene and (S)-3-methyl-1-pentene, respectively.