What Is a Chlorophenol?
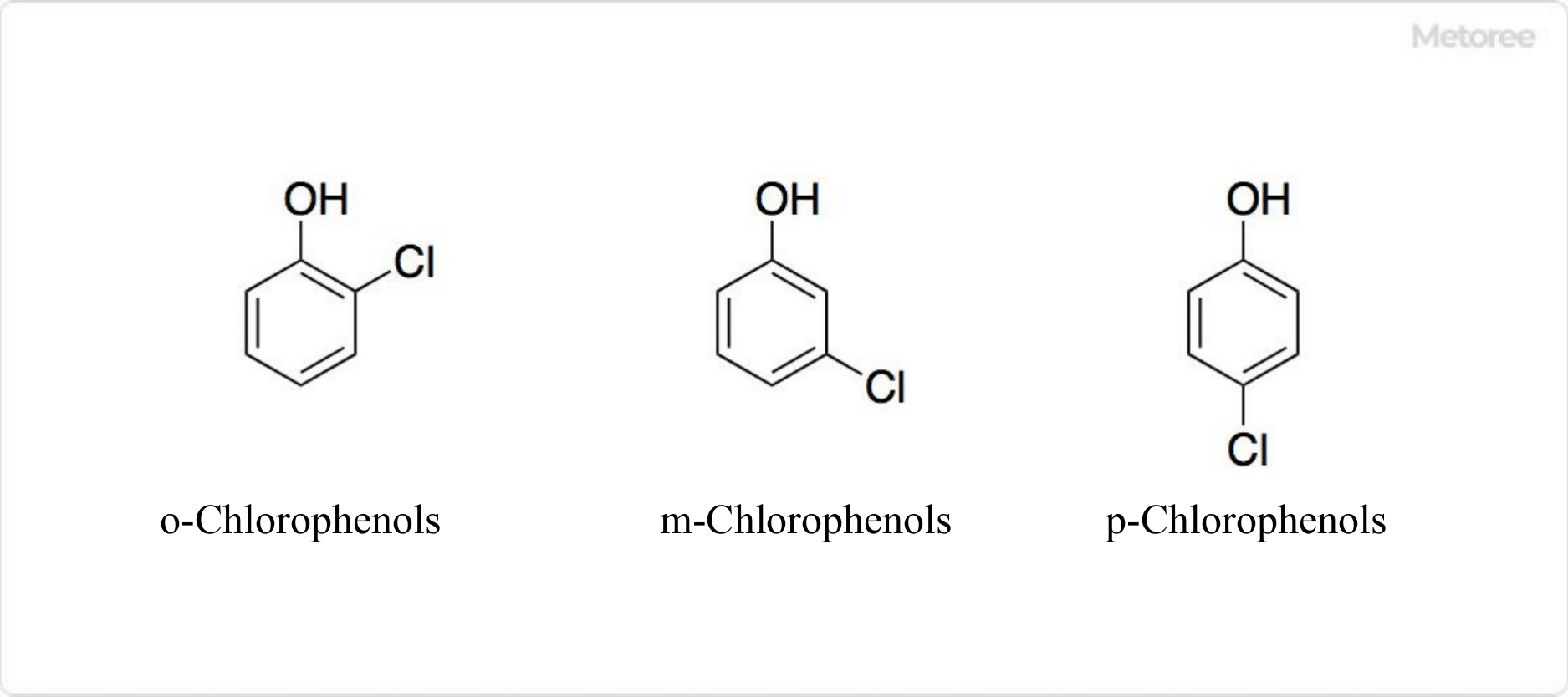
Figure 1. Structure of Monochlorophenol
Chlorophenol is an aromatic compound consisting of phenol bonded with chlorine.
It is classified into monochlorophenol, dichlorophenol, trichlorophenol, tetrachlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol according to the number of chlorine atoms. Monochlorophenol has three isomers: o-chlorophenol, m-chlorophenol, and p-chlorophenol. Taking into account positional isomers, there are a total of 19 chlorophenols.
Most chlorophenols are solid at room temperature and have a strong medicinal taste and aroma. They are generally available as herbicides, insecticides, and disinfectants. Chlorophenol is an endocrine disruptor and is regulated by law because it affects the thyroid gland and other organs.
Uses of Chlorophenols
Chlorophenol is mainly used as an intermediate in agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyes.
- o-chlorophenol is used as an intermediate in dyes and as a raw material for agricultural chemicals.
- m-chlorophenol is available as an intermediate in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, for dyeing nitrogen-containing fibers, and as a raw material for adhesives and heat-resistant resins.
- p-chlorophenol is used as an intermediate in dyes, as a disinfectant, and as a preservative in cosmetics. It was previously used as a preservative in textile and leather goods.
Properties of Chlorophenols
O-chlorophenol, also called 2-chlorophenol or 2-chloro-1-hydroxybenzene, is a colorless to light red liquid. It is insoluble in water and very soluble in ethanol and acetone.
m-chlorophenol, also called 3-chlorophenol or 3-chloro-1-hydroxybenzene, is a colorless to yellowish-brown liquid. It is almost insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol and acetone.
p-chlorophenol, also called 4-chlorophenol or 4-chloro-1-hydroxybenzene, is a white to light brown mass or liquid. It has a characteristic odor and is insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol.
Structure of Chlorophenols
Chlorophenol is an organic chloride of phenol containing one or more covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Chlorophenol is formed by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine.
Except for the carbon atom to which the hydroxy group is attached, chlorine atoms are attached to five carbon atoms of the benzene ring of the phenol molecule, making a total of 19 types of chlorophenol.
There are three types of monochlorophenol, in which one hydrogen atom of phenol is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Other Information on Chlorophenol
1. Structure of Dichlorophenol
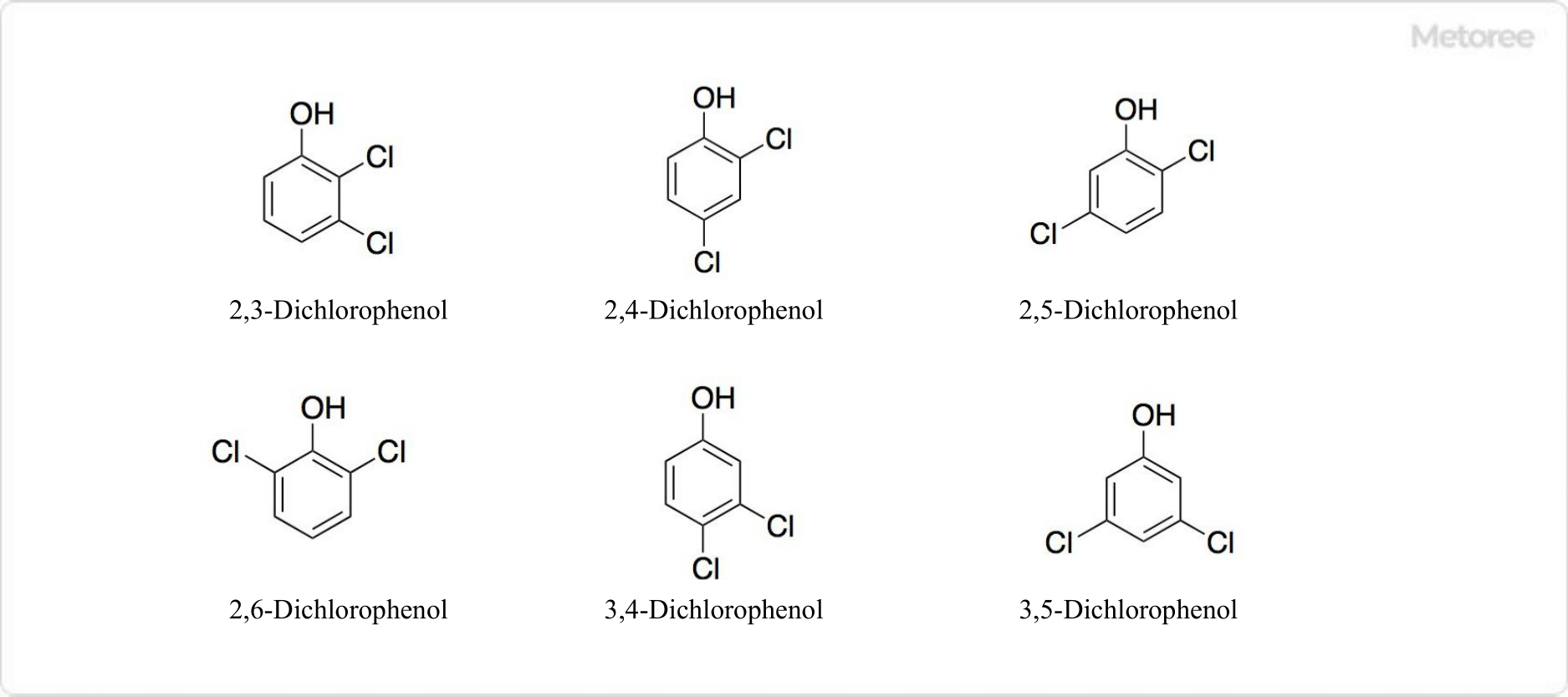
Figure 2. Structure of Dichlorophenol
Dichlorophenol is a compound in which two hydrogen atoms of phenol are replaced by chlorine atoms. There are six isomers of dichlorophenol: 2,3-dichlorophenol, 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,5-dichlorophenol, 2,6-dichlorophenol, 3,4-dichlorophenol and 3,5-dichlorophenol.
2. Other Isomers of Chlorophenol
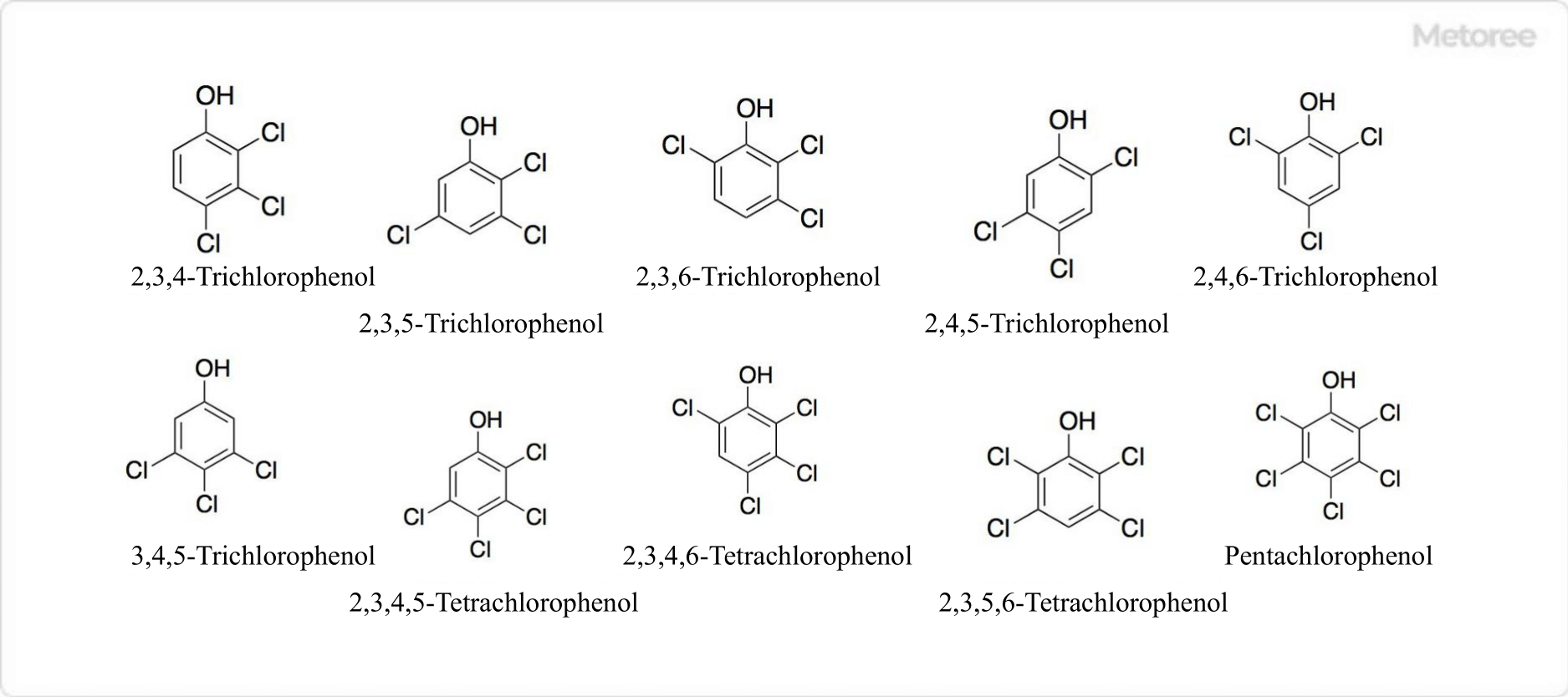
Figure 3. Structure of Chlorophenol
Trichlorophenol is a compound in which three hydrogen atoms of phenol are replaced by chlorine atoms. 6 isomers exist: 2,3,4-trichlorophenol, 2,3,5-trichlorophenol, 2,3,6-trichlorophenol, 2,4,5-trichlorophenol, 2,4,6 -trichlorophenol, and 3,4,5-trichlorophenol.
Tetrachlorophenol is a compound in which the four hydrogen atoms of phenol are replaced by chlorine atoms. 3 isomers exist: 2,3,4,5-tetrachlorophenol, 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol and 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorophenol.
Pentachlorophenol is a compound in which the five hydrogen atoms of phenol are replaced by chlorine atoms. Because all five hydrogen atoms of phenol have been replaced by chlorine atoms, there is only one structure of pentachlorophenol.