What Is Coumaric Acid?
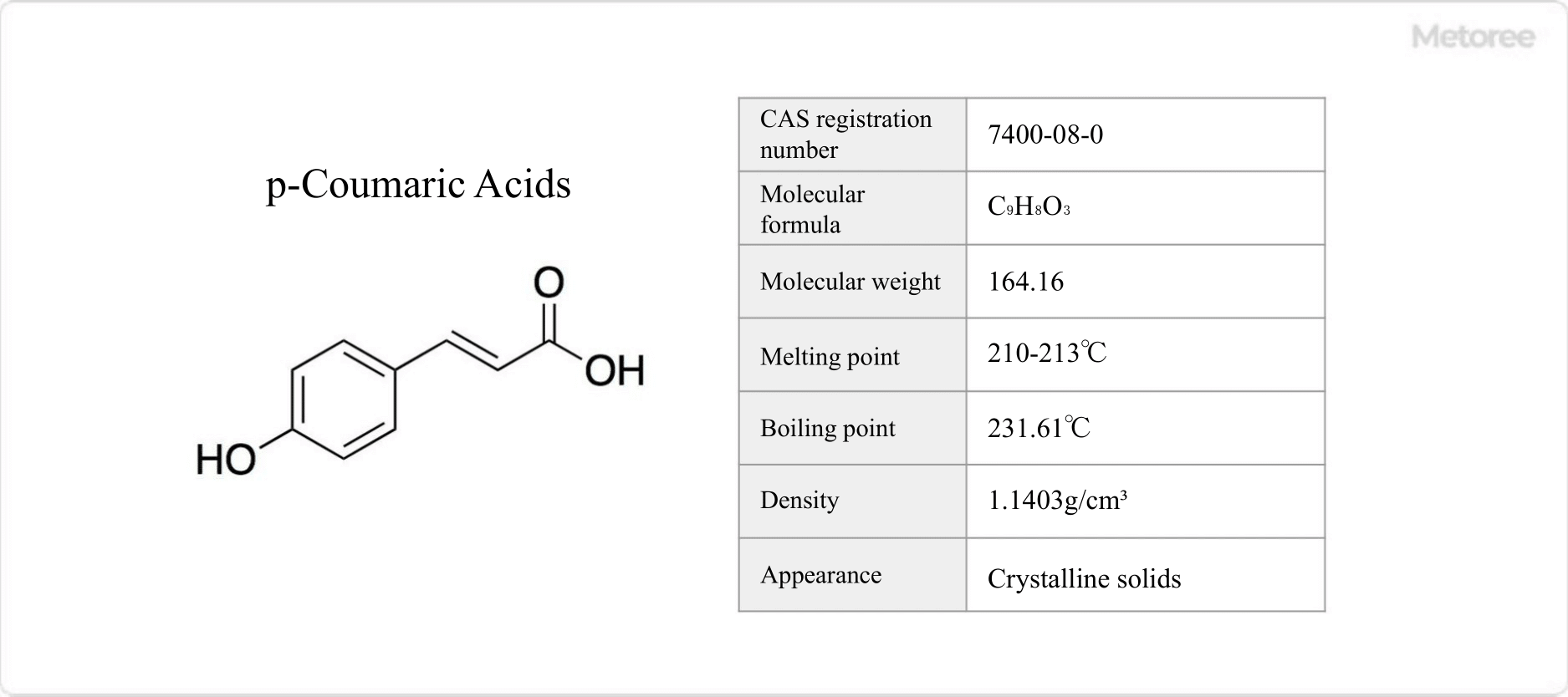
Figure 1. Basic Information on p-Coumaric Acid
Coumaric acid is a hydroxy derivative of cinnamic acid, not silicylic acid as previously mentioned. It includes three isomers: p-coumaric acid, m-coumaric acid, and o-coumaric acid, depending on the hydroxy group’s position on the phenyl group. p-Coumaric acid, the most abundant naturally occurring form among these, is found in various edible plants such as tomatoes, peanuts, garlic, and carrots. It is also referred to as 4-hydroxycinnamic acid or β-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylic acid.
Uses of Coumaric Acid
Coumaric acid is primarily used as a reagent in chemical research. It serves as a component in chemiluminescent substrates for protein detection in western blotting. Additionally, coumaric acid inhibits the formation of nitrosamines, carcinogens formed by the reaction of amines with nitrites in food additives. This inhibition is particularly relevant to reducing the risk of stomach cancer, making p-coumaric acid a subject of ongoing research.
Properties of Coumaric Acid
p-Coumaric acid is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 410-415.4°F (210-213°C) and a boiling point of 449°F (231.61°C). It is insoluble in water but dissolves well in diethyl ether and ethanol.
Structure of Coumaric Acid
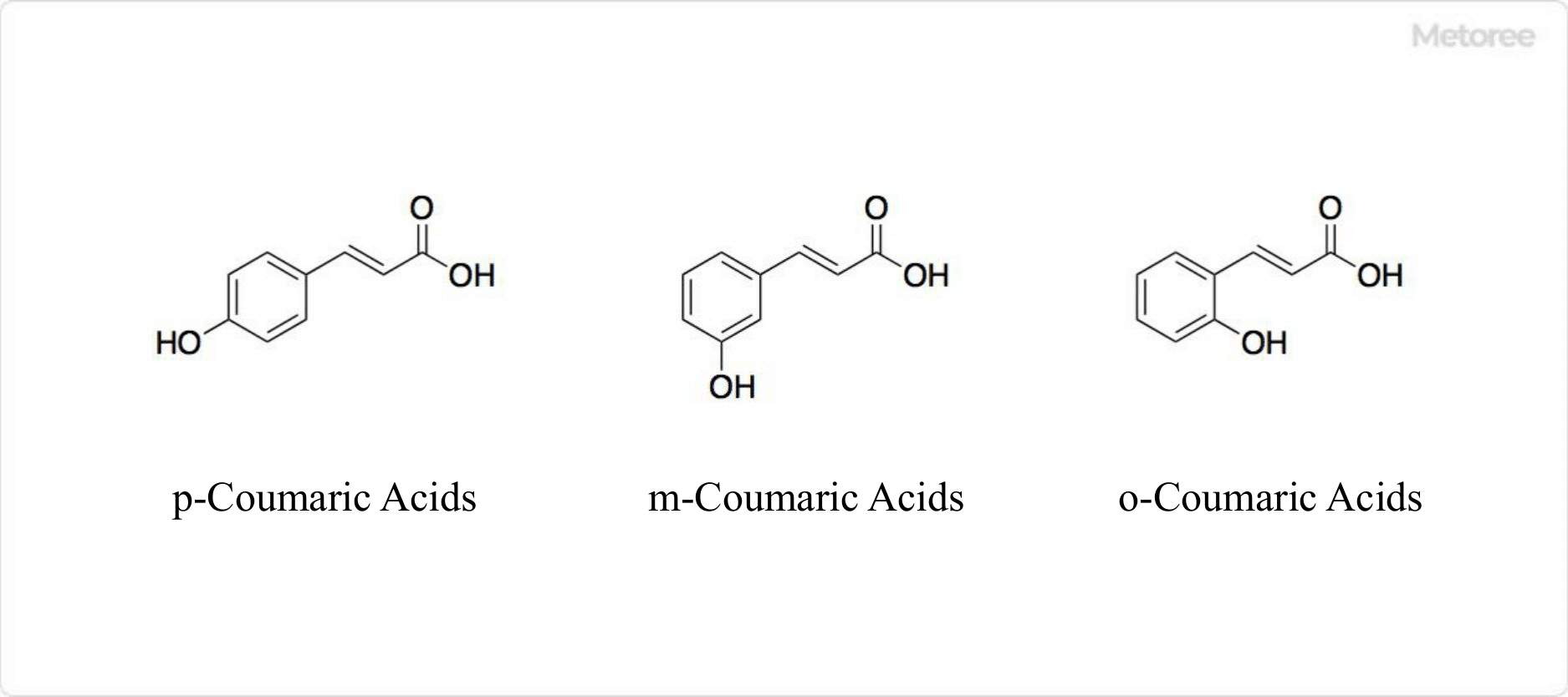
Figure 2. Structure of Coumaric Acid
The molar mass of coumaric acid is 164.16 g/mol, with a chemical formula of C9H8O3. It features a structure of a hydroxy group bonded to a phenyl group. Among its forms, trans-p-coumaric acid is a major component of lignin. p-Coumaric acid derivatives, such as p-coumaric acid glucoside, are found in various natural products, including bread containing ama seeds and carnauba wax.
Other Information on Coumaric Acid
1. Synthesis of p-Coumaric Acid
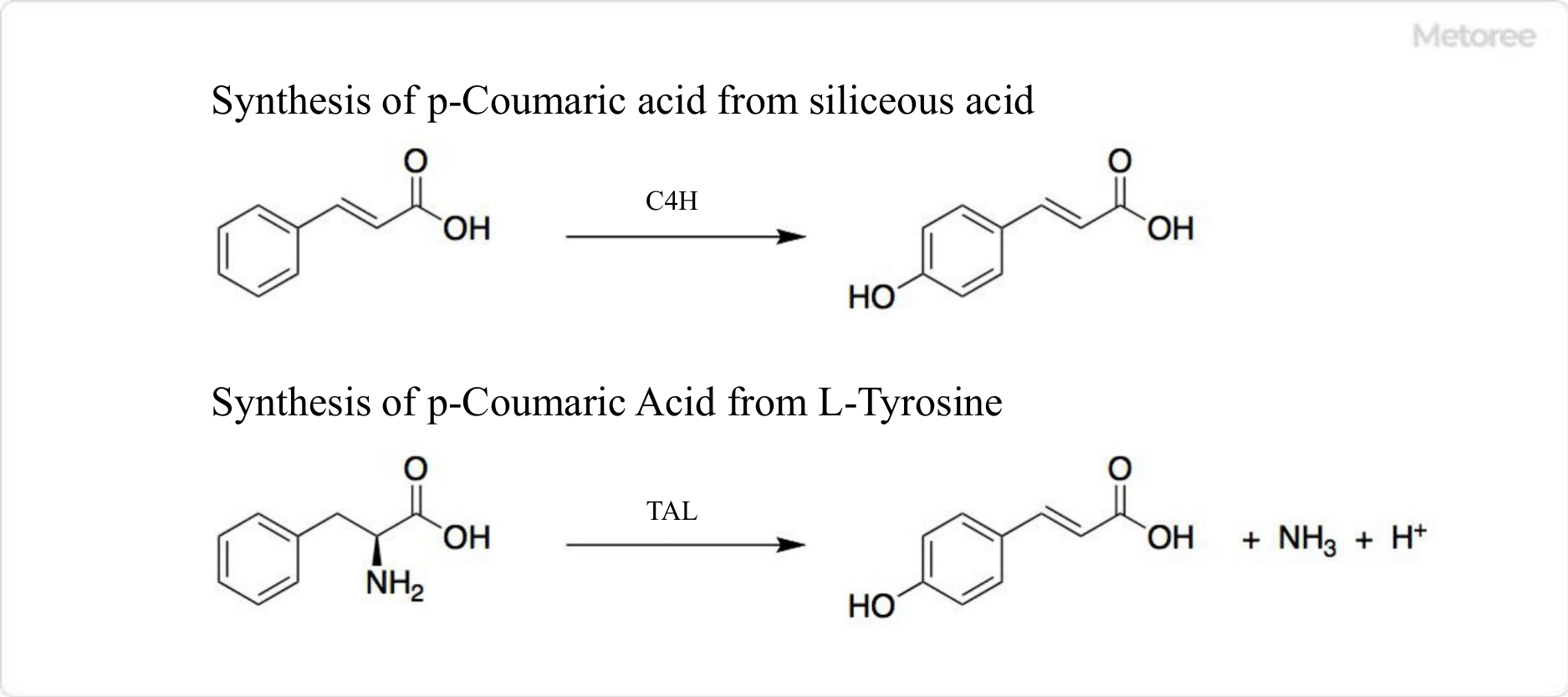
Figure 3. p-Coumaric Acid Synthesis
p-Coumaric acid is produced by the cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme trans-cinnamic acid-4-monooxygenase from cinnamic acid and from L-tyrosine by tyrosine ammonia lyase.
2. p-Coumaric Acid Reaction
p-Coumaric acid is a precursor to 4-ethylphenol in wine, produced by Brettanomyces yeast. It is converted from coumaric acid to 4-vinylphenol by 4-hydroxycinnamic acid decarboxylase and then reduced to 4-ethylphenol by vinylphenol reductase. Additionally, cis-p-coumaric acid glucosyltransferase synthesizes p-coumaric acid glucoside from cis-p-coumaric acid and UDP-glucose.
3. Characteristics of m-Coumaric Acid and o-Coumaric Acid
m-Coumaric acid and o-coumaric acid, found in vinegar, are produced through various metabolic pathways involving enzymes like 2-coumaric reductase, which is involved in phenylalanine metabolism.