What Is Plasma Processing Equipment?
 Plasma processing equipment is used to perform pretreatment, called plasma treatment, for surface treatment of metals, synthetic resins, ceramics, plastics, and all other materials used in industrial fields.
Plasma processing equipment is used to perform pretreatment, called plasma treatment, for surface treatment of metals, synthetic resins, ceramics, plastics, and all other materials used in industrial fields.
In plasma treatment, gases such as oxygen are plasmaized by electrical power, and atoms and molecules with unpaired electrons called radicals are imparted to the surface of resins and other materials. The purpose of imparting radicals is to activate the surface of the product to be treated and to increase the hydrophilic properties of adhesion and wettability.
Surface treatments for which plasma treatment is used as a pretreatment mainly include modification such as cleaning and activation, adhesion and bonding, and painting and coating. Plasma processing equipment can simplify conventional processes, improve work efficiency, and reduce costs.
Uses of Plasma Processing Equipment
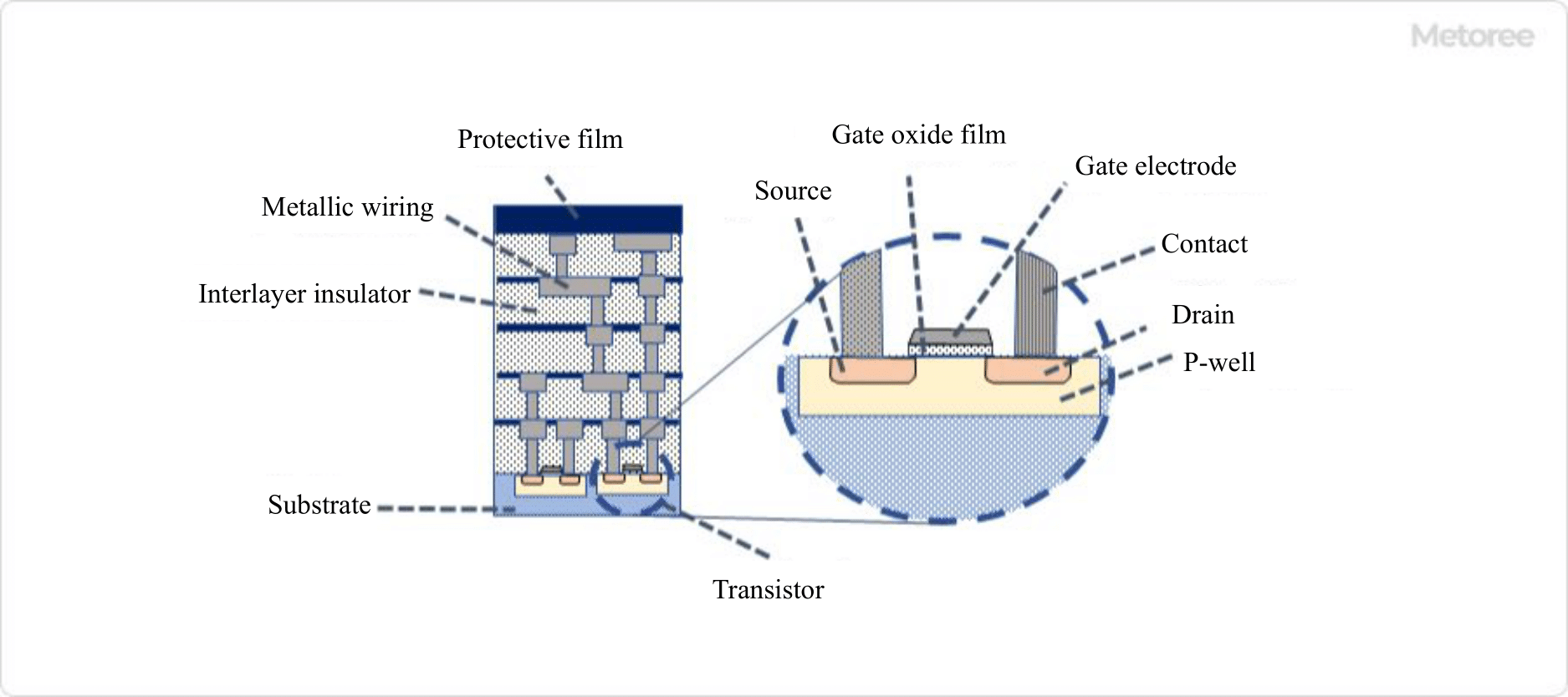
Plasma processing equipment is now widely used not only in electronics technology but also in all areas of manufacturing, from the automotive and aviation industries to packaging and everyday items. An example of their use in the electronic device industry is the anti-scratch coating of electronic components in circuits. Scratch-resistant coatings can improve the durability of substrates and make cleaning processes more efficient.
Examples in the automotive industry include bonding automotive circuit boards to epoxy resin and cleaning surface oil from metal parts for engines. In packaging and everyday products, it is used for foil stamping on plastics, surface printing, and painting. Other uses include cleaning and coating of medical equipment, etc., taking advantage of the sterilizing effect during processing.
Principle of Plasma Processing Equipment
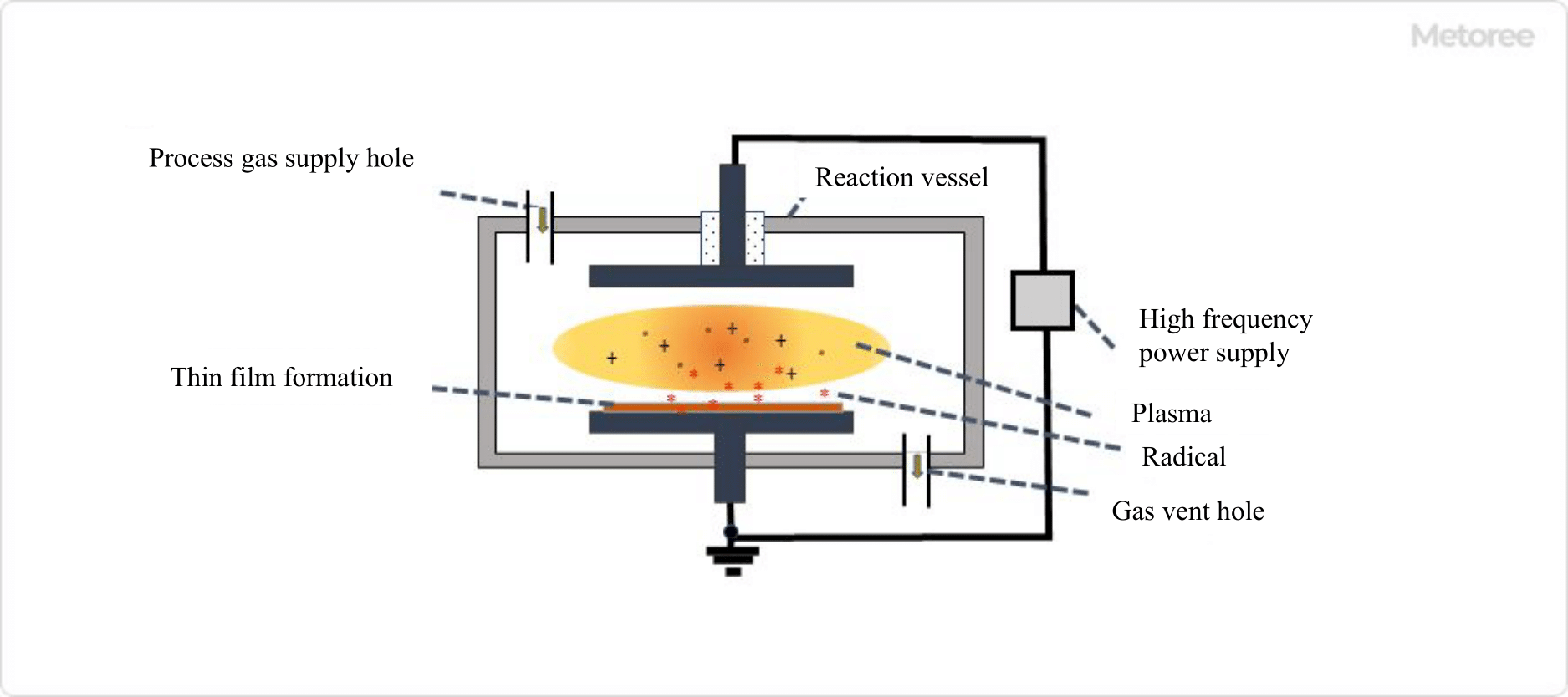
Plasma is a state in which atoms and molecules in a gas are ionized and split into positively charged positive ions and negatively charged electrons. It is called the fourth state following the individual, liquid, and gas states. The purpose of plasma processing equipment is to ionize oxygen molecules in the air by discharging them in the air, causing the oxygen atoms to be excited and generating plasma containing oxygen ions and free electrons.
The electrons, ions, and radicals of the generated plasma come into contact with the product to be treated, such as the substrate of an electronic component, and the ions and electrons in the plasma react with the molecules of the substrate material to produce hydrophilic functional groups. The formation of hydrophilic functional groups on the surface improves adhesion and wettability.
Types of Plasma Processors
There are two main types of plasma processing machines: atmospheric plasma processing machines that process at atmospheric pressure and vacuum plasma processing machines that process in a vacuum. Atmospheric pressure plasma processing equipment generates plasma at atmospheric pressure by flowing a gas, such as nitrogen or rare gas, through a pair of electrodes and applying high frequency and high voltage.
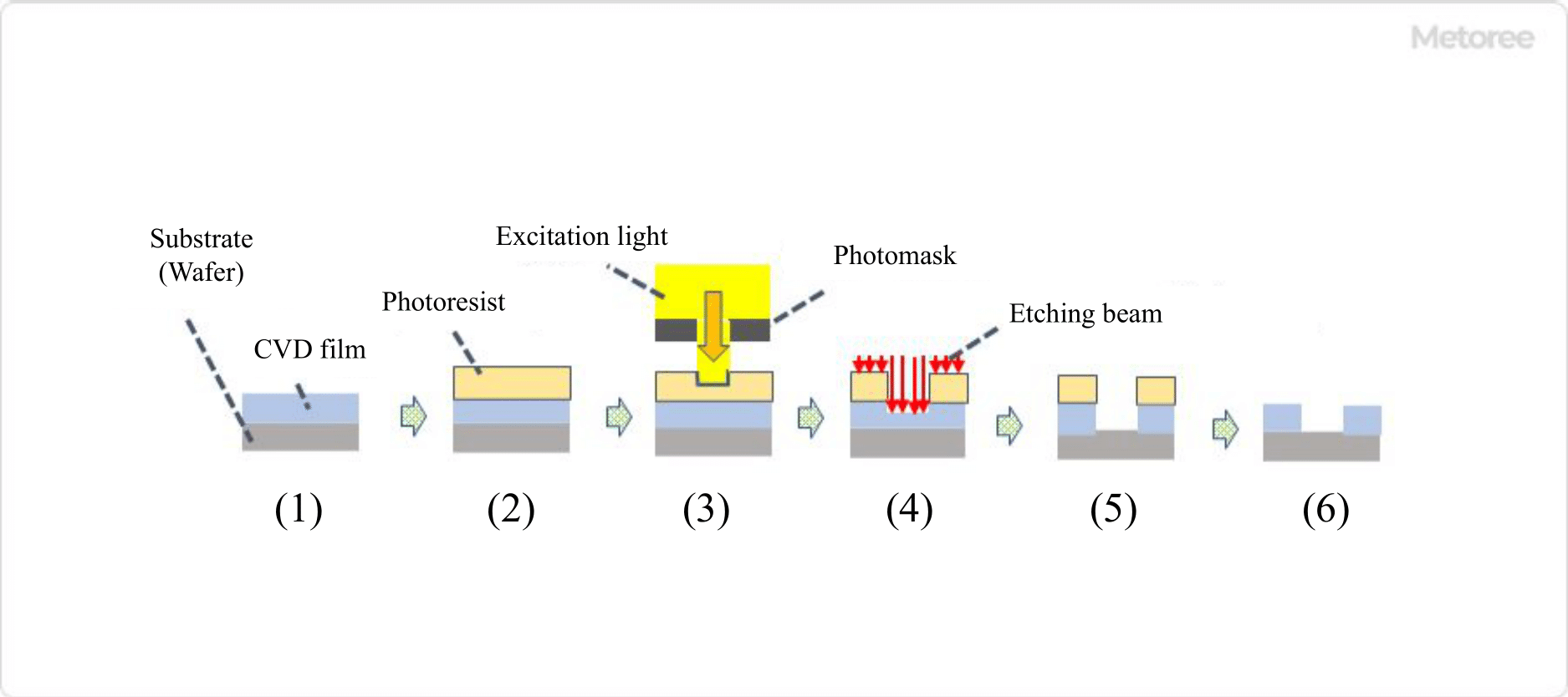
On the other hand, vacuum plasma processors place a base material in a sealed chamber and irradiate plasma evenly onto the surface of the material. They are mainly used in the manufacture of semiconductors and other electronic components, and in medical applications.
Other Information on Plasma Processing Equipment
1. Features of Plasma Processing
Plasma treatment has two main characteristics. The first is that there are multiple gases that can be plasmaized. In addition to oxygen and nitrogen, helium and other gases can be used for plasma treatment. The chemical properties of the plasma can be changed by combining gases, so the properties of the base material and the functionality to be given can be selected.
The second feature is that there is little damage to the base material. Since the plasma is in a gaseous state, it has little effect on the interior of the material and can act only on the extreme surface.
2. Effects of Plasma Treatment
There are three major effects of plasma treatment.
Hydrophilization
Hydrophilization improves wettability. It refers to the state in which the material becomes more compatible with water and less likely to form water beads. In other words, the opposite of hydrophilic is water repellent.
Improved Adhesion
Plasma treatment improves adhesion between resins and between resins and metals. Plasma treatment forms hydrophilic functional groups on the surface, which will result in a high affinity with adhesives.
Cleaning
Plasma treatment can remove organic contaminants from metal and glass surfaces. This is accomplished by plasma-generated oxygen radicals reacting with the carbon atoms of organic contaminants on the surface of the treated item and releasing them as carbon dioxide, resulting in the cleaning of the surface.

 A flexible container bag is a large-capacity, sturdy bag used to transport a single batch of powder, waste, or agricultural products.
A flexible container bag is a large-capacity, sturdy bag used to transport a single batch of powder, waste, or agricultural products.
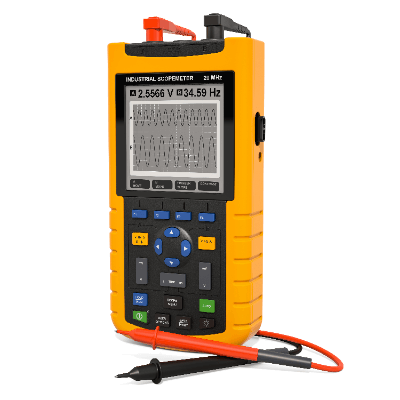 A handy oscilloscope is a small oscilloscope designed for outdoor use and can be operated by batteries.
A handy oscilloscope is a small oscilloscope designed for outdoor use and can be operated by batteries.