What Is Laser Processing?
Laser processing is, as the name implies, processing using a laser.
A laser is a beam of light with the same phase and amplitude, i.e., coherent light. Laser processing uses a powerful, light-amplified laser beam to cut, weld, engrave, mark, or punch holes in the workpiece. The types of materials processed include metals, ceramics, plastics, wood, fabric, glass, and more.
Laser processing is a non-contact processing method that does not require the use of cutting tools, and it is capable of processing without deformation or distortion of the material due to stress or pressure. It also requires fewer consumables and is easier to maintain.
The main types of lasers used are carbon dioxide gas lasers, YAG lasers, fiber lasers, and excimer lasers.
Uses of Laser Processing
1. Carbon Dioxide Laser Processing
It is capable of high output power and is used for cutting sheet metal, microscopic drilling, and welding in industrial applications. In medical applications, it is also used for surgical laser scalpels.
2. YAG Laser Processing
Mainly used for spot welding of automotive engine parts, roofs and bodies.
3. Fiber Laser Processing
Used for cutting and welding metals, welding plastic materials together, and marking.
4. Excimer Laser Processing
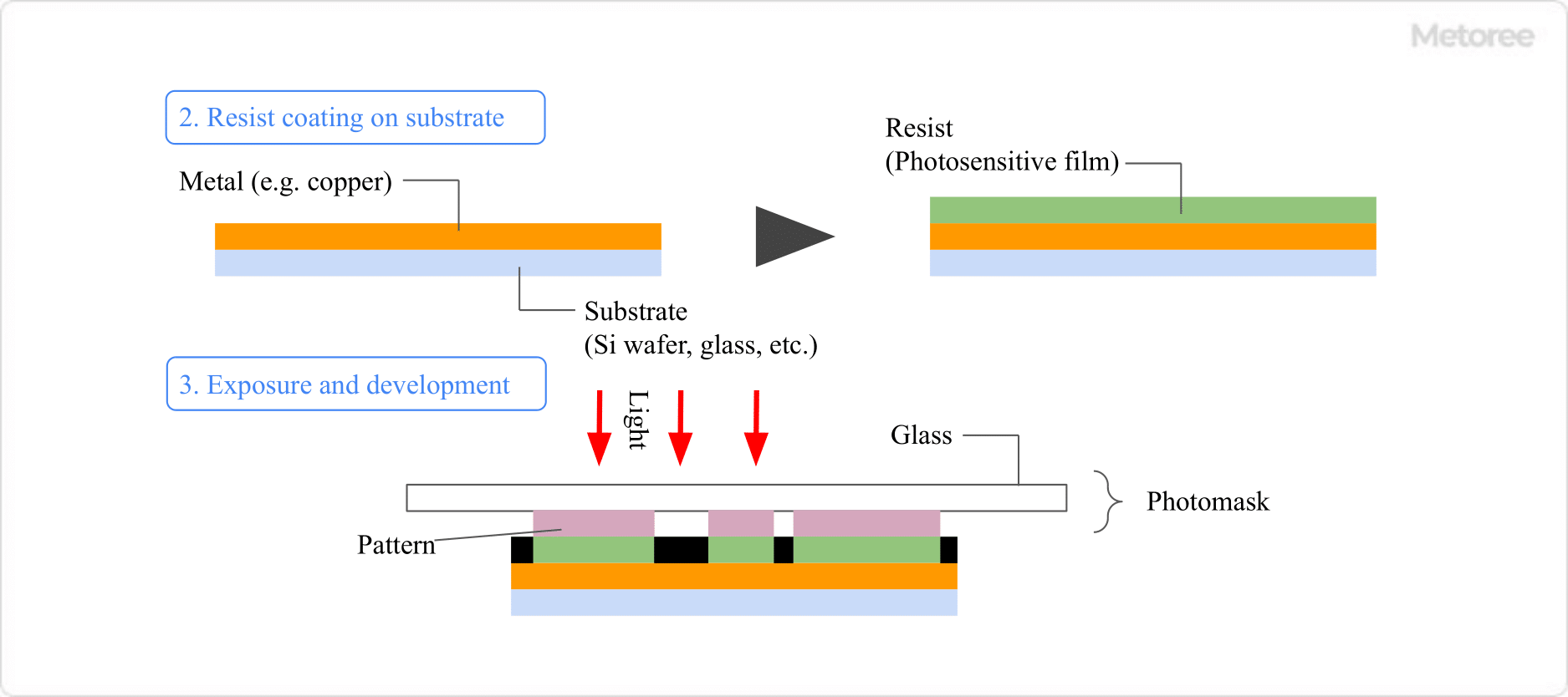
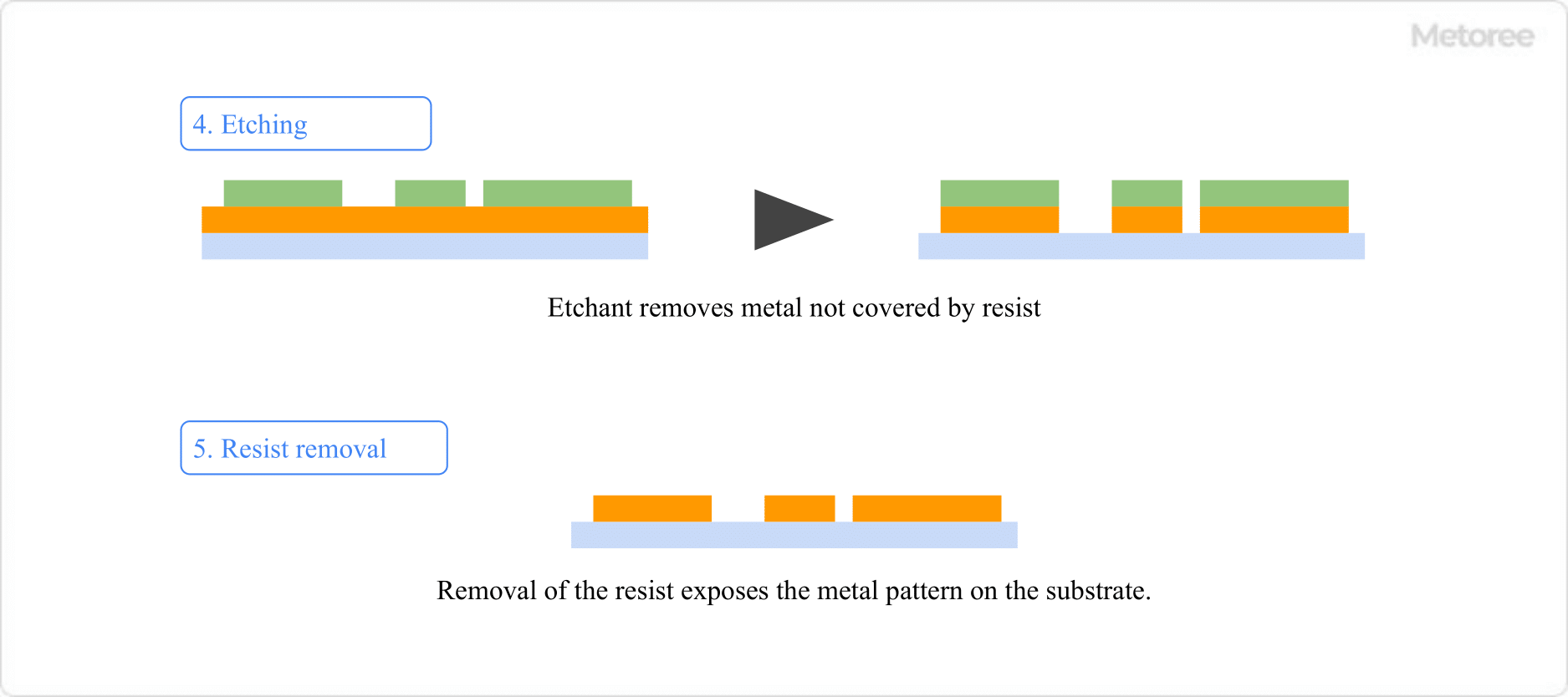
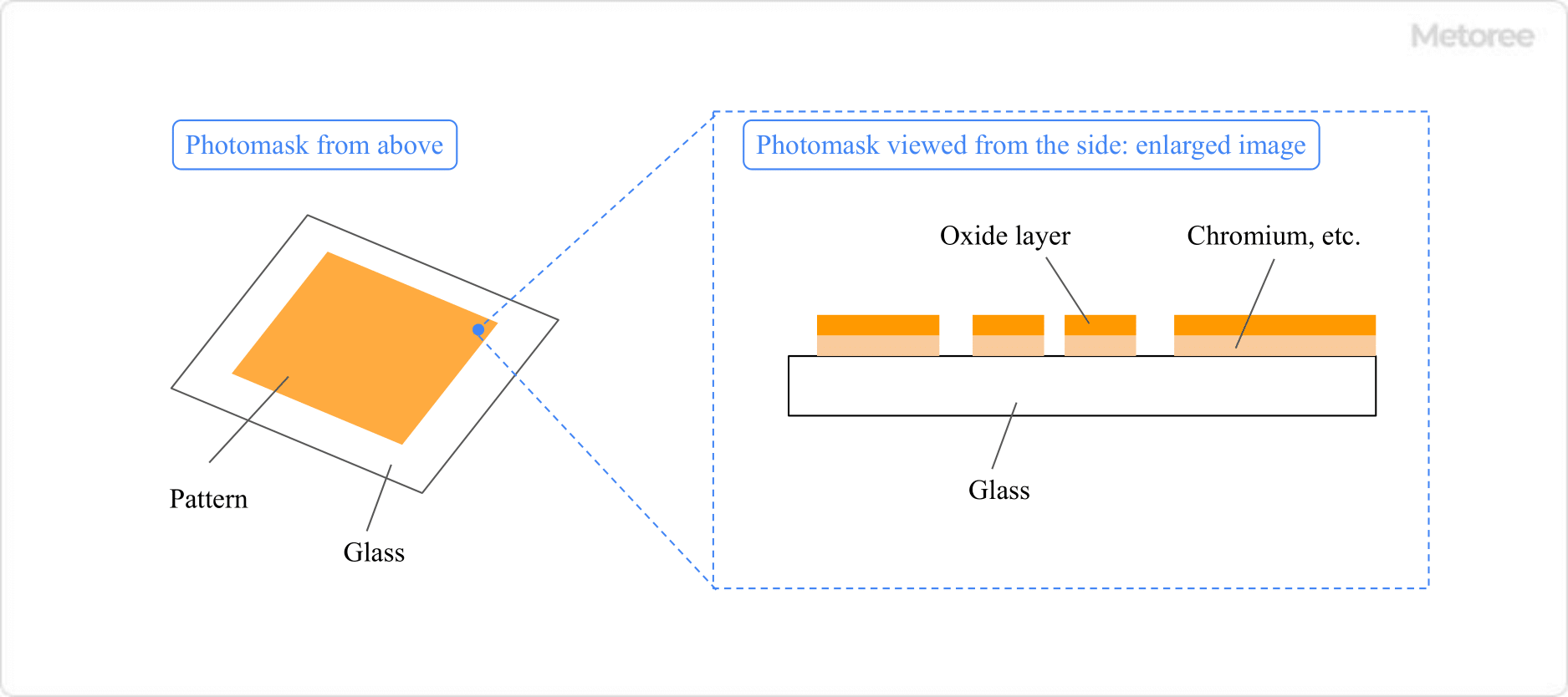
It is used as a light source for exposure in the semiconductor manufacturing process and in the low-temperature poly-silicon manufacturing process for liquid crystal displays.
Principle of Laser Processing
In general, when external energy (light, heat, etc.) is applied to atoms and molecules that make up a substance, the atoms move to a higher energy state (excited state). Then, they spontaneously emit light in an attempt to return to a lower energy state (ground state).
Especially when there are many high-energy atoms around, this spontaneous emission of light stimulates other high-energy atoms to emit light and return to the ground state. This light is called induced emission light, and its energy is amplified to twice that of the incident light.
When this induced emission light is repeatedly reflected by a mirror, it collides with electrons in other atoms, releasing light energy and producing an amplified, intense light. This is the principle of laser oscillation.
When processing a workpiece with this laser beam, a gas called a shielding gas is sprayed on the surface of the workpiece while protecting it from flying debris generated on the surface of the workpiece and preventing surface oxidation and ignition of the workpiece.
Types of Laser Processing
Laser processing is categorized by the substance that amplifies and oscillates the laser beam.
1. Carbon Dioxide Laser Processing
Uses laser light in the infrared region with a wavelength of 1.060 μm. It uses carbon dioxide-based gas as the laser medium.
2. YAG Laser Processing
It uses laser light in the infrared region with a wavelength of 1.064 μm. The laser medium is an artificial crystal composed of yttrium, aluminum, and garnet.
3. Fiber Laser Processing
The wavelength of the light is in the infrared region of 1.1 μm. This is a solid-state laser that uses an optical fiber as the laser medium. The laser light emitted from the excitation semiconductor is amplified by the optical fiber to produce a powerful laser beam for use in laser processing.
4. Excimer Laser Processing
The ultraviolet light source has a characteristic of very high optical energy. Laser beams with wavelengths in the deep ultraviolet region, such as 0.193 μm and 0.248 μm, are used. The laser medium is a mixture of inert gas (argon, krypton, xenon, etc.) and halogen gas (hydrogen chloride, fluorine).
Other Information on Laser Processing
Features of Laser Light
- Directivity
Laser light travels almost straight and true compared to natural light. - Monochromatic
It is one color because the wavelengths of light are the same. - Coherence
Since the phase and amplitude of light are the same, they can easily synthesize and strengthen each other.