What Is a Dosimeter?
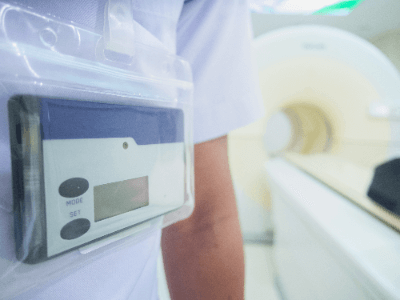
A dosimeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the amount of radiation.
Instruments used for measuring radiation are commonly referred to as dosimeters, radiation measuring instruments, survey meters, and more. Dosimeters encompass a wide range of measuring instruments, including those with and without mechanical structures.
Some dosimeters, such as glass dosimeters, thermoluminescence dosimeters, and photoluminescence dosimeters, utilize radiation-induced changes in materials. These dosimeters do not require a power source when measuring radiation. Due to their lightweight nature, they can be worn by individuals for routine monitoring of radiation exposure. Such wearable dosimeters are commonly referred to as personal dosimeters.
In contrast, semiconductor dosimeters, which require a power supply, are also used as personal dosimeters. This is because they can be manufactured to be as small as electronic thermometers.
The term “radiation measuring instrument” is often used interchangeably with “dosimeter.” However, a survey meter is a specialized instrument primarily used for measuring (surveying) radiation levels in specific areas or surfaces to assess radiation contamination.
Uses of Dosimeters
Dosimeters are employed to measure long-term radiation exposure in various aspects of daily life and in occupational settings involving potential radiation exposure.
Strict radiation control measures are mandated by law in medical facilities, research facilities, industrial sectors, and other settings where radiation is utilized. Medical facilities may encounter radiation during X-ray and CT imaging procedures, while nuclear facilities may have radiation exposure risks associated with nuclear reactor operation, nuclear fuel handling, and radioactive material management.
Given the potential health hazards of radiation exposure, workers in radiation-prone environments are required to wear personal dosimeters during tasks involving radiation.
Principles of Dosimeters
Dosimeters are measuring instruments designed to measure the “dose” of radiation.
This “dose” encompasses various indicators, including:
- Absorbed dose (measured in Gy gray), representing the energy absorbed by a material from radiation
- Effective dose (measured in Sv sievert), which expresses the overall effect of radiation on an individual’s entire body
- Irradiation dose (unit: R- Roentgen), indicating the total radiation exposure
- Effective dose equivalent (measured in Sv sievert), a practical indicator for routine radiation monitoring, among others
Dosimeters directly measure the “number” of radiation “rays.” To assess the various types of doses mentioned above, dosimeters are designed to differentiate and detect different types of radiation. By measuring the number of radiation “rays” for each type and considering their respective effects on the human body, it becomes possible to evaluate the overall impact of radiation exposure.
Personal dosimeters typically display the effective dose equivalent (unit: Sv sievert). While assessing the effective dose is ideal for evaluating radiation’s impact on the human body, it is often challenging to measure this dose in real-time. Therefore, the effective dose equivalent, a practical measure, is commonly used for actual radiation monitoring.
However, because a significant amount of radiation exposure in a short time can pose health risks, some dosimeters can also measure the dose equivalent rate (measured in Sv/h), representing the effective dose equivalent per hour. In workplaces where radiation is used, the effective dose for workers is calculated based on the measured effective dose equivalent.
Types of Dosimeters
Various types of radiation exist, including neutron, alpha, beta, gamma, and X-rays, each with distinct characteristics and varying effects on the human body. Glass, thermoluminescence, and photostimulable luminescence dosimeters are capable of detecting β-rays, γ-rays, and X-rays.
1. Glass Dosimeters
Glass dosimeters rely on the phenomenon where irradiated glass emits fluorescence when exposed to ultraviolet light.
2. Thermoluminescence Dosimeters
Thermoluminescence dosimeters leverage the thermoluminescence phenomenon of solids. This phenomenon involves the emission of light by a substance, such as a phosphor, when heated after being irradiated by an external radiation source.
3. Photostimulated Luminescence Dosimeters
Photostimulated luminescence dosimeters operate based on the photostimulated luminescence phenomenon, wherein electrons in a metastable state absorb light energy and return to their ground state after exposure to radiation.
4. Semiconductor Dosimeters
Semiconductor dosimeters function on the principle that when a material is ionized by radiation, an electric current flows through a semiconductor.
How to Select a Dosimeter
The primary consideration when selecting a dosimeter is choosing one suitable for the type of radiation to be measured. Dosimeters designed for β- and γ-rays may differ from those intended for X-rays, and product specifications for X-rays can vary based on energy levels.
1. Glass Dosimeters, Thermoluminescence Dosimeters, and Photostimulated Luminescence Dosimeters
The aforementioned three types are ideal for long-term radiation monitoring. They do not provide immediate radiation dose readings on the spot but require processing and measurement of accumulated radiation doses. This approach is known as passive radiation monitoring. In contemporary practice, specialized companies typically handle this measurement.
Although these dosimeters do not offer immediate radiation dose readings, they are highly sensitive and well-suited for radiation monitoring based on cumulative exposure over several months. Additionally, vendors can provide records of radiation doses, enhancing convenience.
2. Semiconductor Dosimeters
Semiconductor dosimeters are suitable for situations where substantial radiation exposure is anticipated within a short timeframe, and immediate radiation dose readings are required. These dosimeters provide real-time measurements and are referred to as active dosimeters. Some models display the dose equivalent, which is the dose per hour, and emit warnings when the dose equivalent exceeds predefined levels. Consider whether these functions are necessary when selecting a dosimeter.
However, certain semiconductor dosimeters have limited data storage capacity in the main unit. In such cases, consideration should be given to how dose data will be recorded. Many organizations opt for a combination of active and passive dosimeters to monitor exposure doses during work and manage long-term radiation control effectively.