What Is a Detector Tube?
 Specific Detector Tubes for Each Gas Type
Specific Detector Tubes for Each Gas Type
Detector tubes are tools for measuring gas concentrations, such as harmful hydrogen sulfide or flammable hydrogen. Each type of gas requires a dedicated detector tube.
Variety of Detector Tubes for Short and Long-Term Measurement
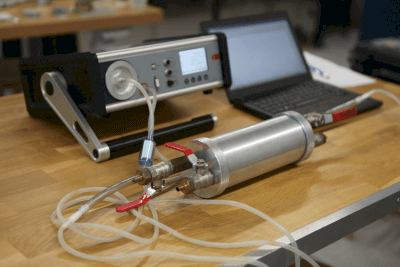
Detector tubes are available for measuring gas concentrations over short or extended periods. Their ease of use involves drawing the gas through a piston.
Applications of Detector Tubes
Environmental Monitoring in Manufacturing and Construction
Detector tubes, simple to operate, are widely used in manufacturing and construction for environment monitoring and legal compliance, especially for detecting flammable gases to prevent explosions and ignitions.
Pollution Control and Research
These tubes are also utilized for controlling pollution by measuring air contaminants and analyzing gases in chemical reactions for research purposes.
How Detector Tubes Work
Gas Concentration Measurement Through Reaction
Detector tubes contain a reactive substance that changes color upon reacting with the target gas, providing a visual quantification. Each tube type has specific quantitation and detection limits.
Applications in Hazardous Environments
In high-risk or oxygen-deficient areas, remote sampling tubes are used to measure gas concentrations safely.
Specific Tubes for Specific Compounds
Each detector tube is specific to a particular compound and has an expiration date. It’s crucial to check this before use and to sample at multiple points due to potential gas distribution variances.
Kitagawa Gas Detector Tubes
Kitagawa gas detector tubes consist of a detector and a gas sampler, used since 1947, primarily for hydrogen sulfide detection. The color change in the detector agent upon reaction indicates the gas concentration.
This method allows for rapid onsite measurement of flammable gases, preventing potential fires or explosions. The tubes are prepared with a chip cutter, inserted into the sampler, and then the discolored boundary is read for concentration assessment.
Detection Conditions for Various Gases
For ammonia gas, the measurement range is less than 30 ppm and the detection limit is about 0.2 ppm when the gas is aspirated once (100 ml). The presence of ammonia causes a neutralization reaction (2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4) with sulfuric acid, which changes the indicator from pink to yellow.
The measurement range of oxygen is 3-6%, with a detection limit of about 2% for a single aspiration (100 ml). When oxygen is present, the reaction with titanium trichloride (O2 + 4TiCl3 (black) + 6H2O → 4TiO2 (white) + 12HCl) produces titanium oxide, which causes the indicator to change from black to white.
Carbon dioxide has a measurement range of 100 to 2000 ppm with a detection limit of about 20 ppm for a single aspiration (100 ml). The presence of carbon dioxide causes a neutralization reaction (CO2 + 2KOH → K2CO3 + H2O) with potassium hydroxide, which changes the indicator from light red to orange.