What Is a Linear Guide?
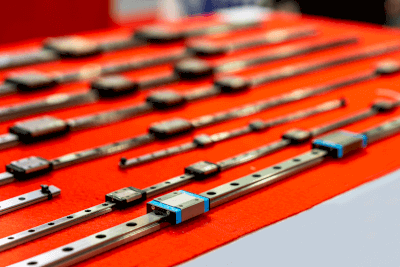 A linear guide is a mechanical component that facilitates linear motion.
A linear guide is a mechanical component that facilitates linear motion.
Similar products, such as LM guides, are also available in the market. Additionally, some linear guides come equipped with encoders, making them ideal for precision equipment like industrial robots.
Linear guides enable a block (movable base) to move back and forth along a rail with minimal resistance, ensuring consistent and smooth linear motion.
Uses of Linear Guides
Linear guides find extensive use across various industrial sectors, particularly in production facilities. Common applications include feeding workpieces in a straight line in manufacturing plants, facilitating linear movement of cylinders, and guiding workpieces for precise positioning. They are also used in automation, where mechanisms like link systems, stoppers, or reversing mechanisms are required.
Principles of Linear Guides
Linear guides typically consist of a rail, a block, and balls that facilitate movement. Most are equipped with seals to protect the moving parts from dust and other contaminants.
The interaction between the rail and block through the driving balls enables smooth linear motion. As the block moves along the rail, the balls roll on their respective surfaces, reducing friction and enhancing motion efficiency.
Integrating linear guides with encoders allows for precise position detection post-movement. When combined with feedback control and servo or stepper motors, they can achieve high-precision positioning.
Given their use in demanding applications like industrial robots, linear guides are available in various configurations. Options include guides with rollers instead of balls for increased rigidity, different sizes for diverse requirements, and guides designed for curved motion. These variations cater to specific needs and can be selected from manufacturers’ catalogs.