What Is a Rod End?
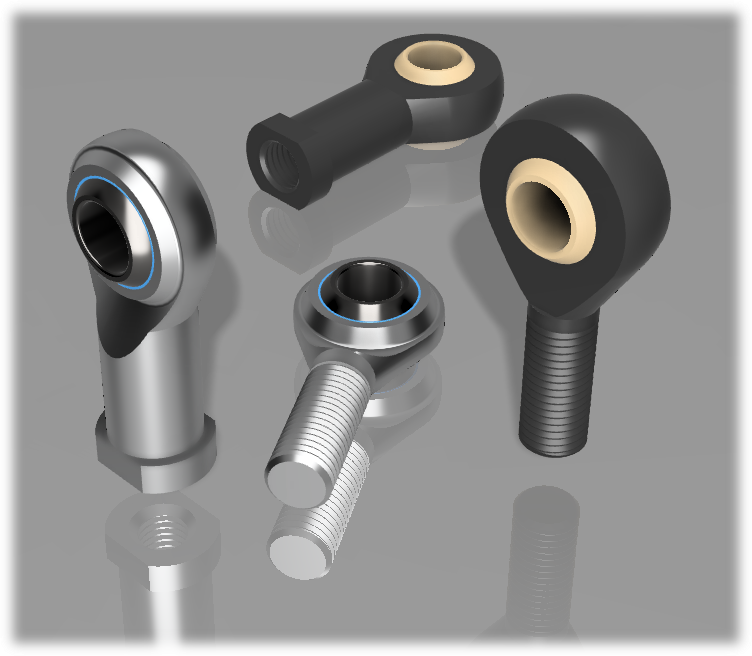 A rod end is a type of spherical plain bearing.
A rod end is a type of spherical plain bearing.
A spherical plain bearing has a spherical outer ring in a bearing housing (or the inner surface of the housing is spherically machined) and a ball-shaped inner ring with a drilled hole in it. In general, spherical plain bearings and rod-end bearings may also be treated as synonyms.
Link balls and link ball joints are also functionally treated as a type of rod end, but are not covered here.
Uses of Rod Ends
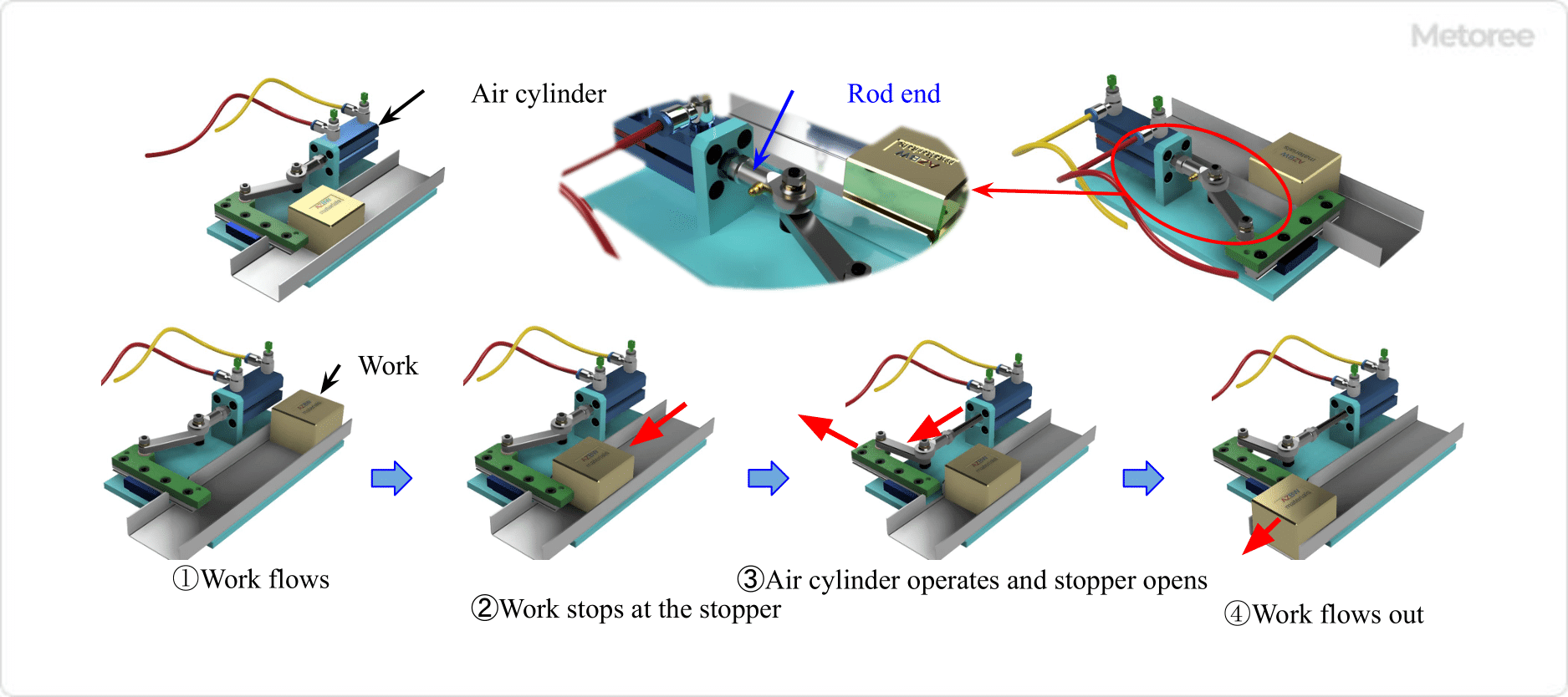
Figure 1. Example of rod end use
Rod Ends are mechanical elements that are used to fasten the housing end of a spherical plain bearing with a male or female thread to the end of a rod (shaft), such as a connecting rod, to fix or connect two parts, and allow the relative displacement of the two parts by means of their spherical plain structure.
It is mainly used to connect parts using links or to transmit linear motion to other parts. They are used in a wide range of fields, including construction machinery, industrial machinery, automobiles, and aircraft.
Rod Ends are used to connect parts by threading male threads, which are threaded at one or both ends of a shaft called a connecting rod, into the female threads of the rod end housing. A pin, shaft, bolt, or other component is inserted into the hole drilled in the center of the rod end’s ball-shaped inner ring, and the inner ring and pin or other component are fastened with a nut or other means. The distance between parts and the length of the connecting rod can be adjusted by the screwing depth of the rod end and the connecting rod.
Principle of Rod End
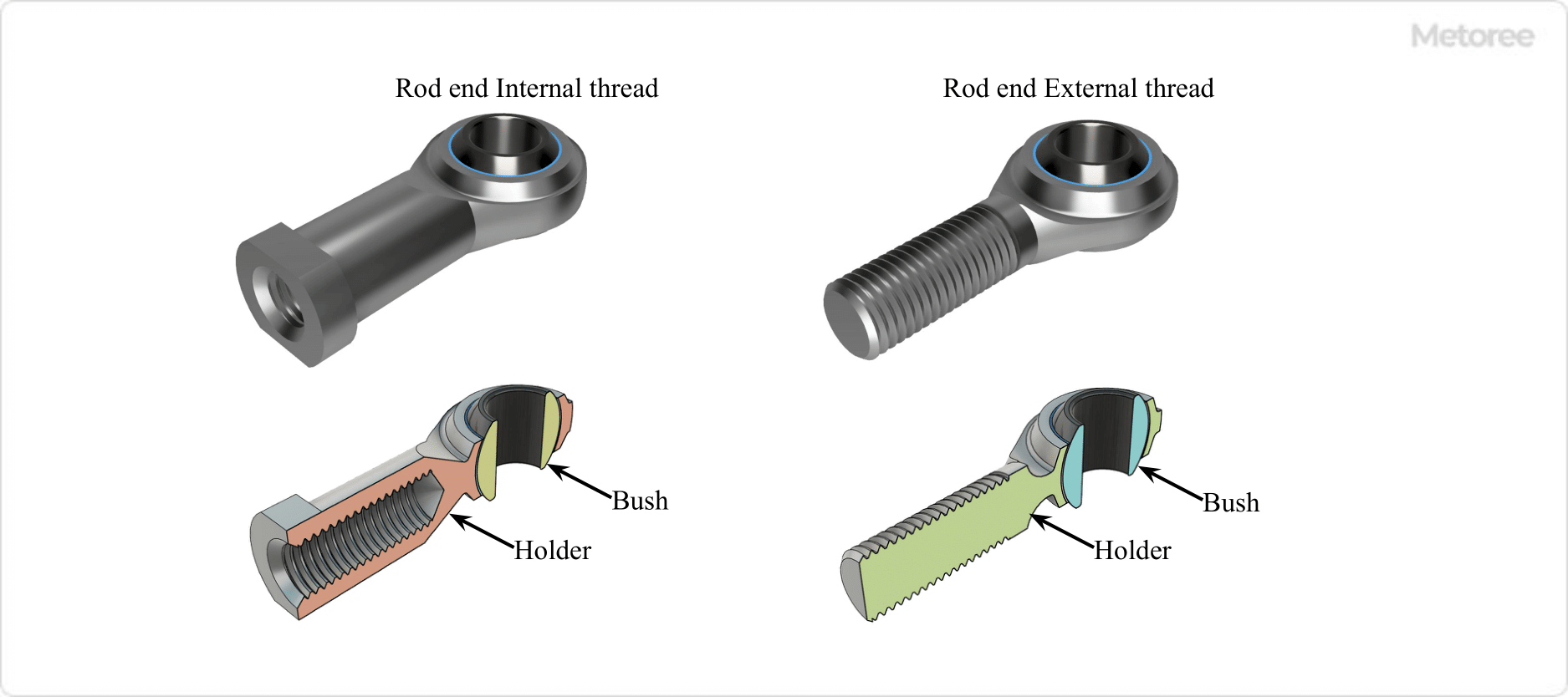
Figure 2. Configuration of rod endchol
Rod Ends consist of a bush that is the inner ring into which bolts and nuts are inserted vertically, and a “holder” that is threaded and connected to other parts such as a connecting rod.
A spherical plain bearing is incorporated. The spherical inner ring ball, which is drilled to insert a bolt or nut vertically, and the outer ring incorporated in the housing make spherical contact to enable smooth and flexible rotational motion.
It acts like a human joint, making it suitable for applications with complex movements. They can also withstand high loads, making them suitable for handling high weights.
Types of Rod Ends
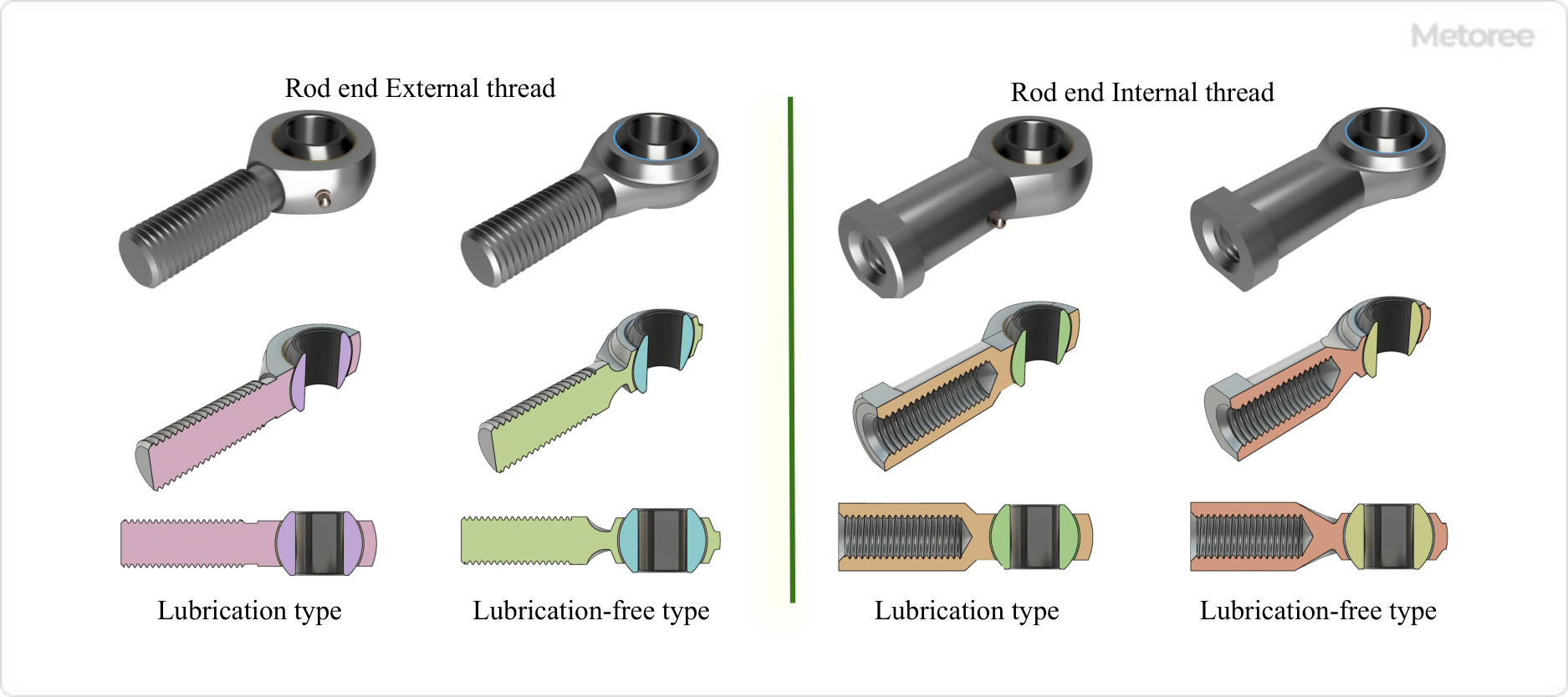
Figure 3. Types of rod ends (Steel)
The holder part of rod end has a male thread and a female thread, and is selected according to the structure of the connecting rod or other parts to be connected.
There are two types of bushings: lubricated and non-lubricated.
1. Lubricated Type
The oil-feeding type has a grease nipple attached to the housing. In the lubricated type, grease is injected through the nipple using a grease gun or the like. In the oilless type, self-lubricating synthetic resin is incorporated in the outer ring of the holder.
2. Oilless Type
Lubrication-free type does not require lubrication, and is used in confined spaces where lubrication is not possible or in maintenance-free applications.
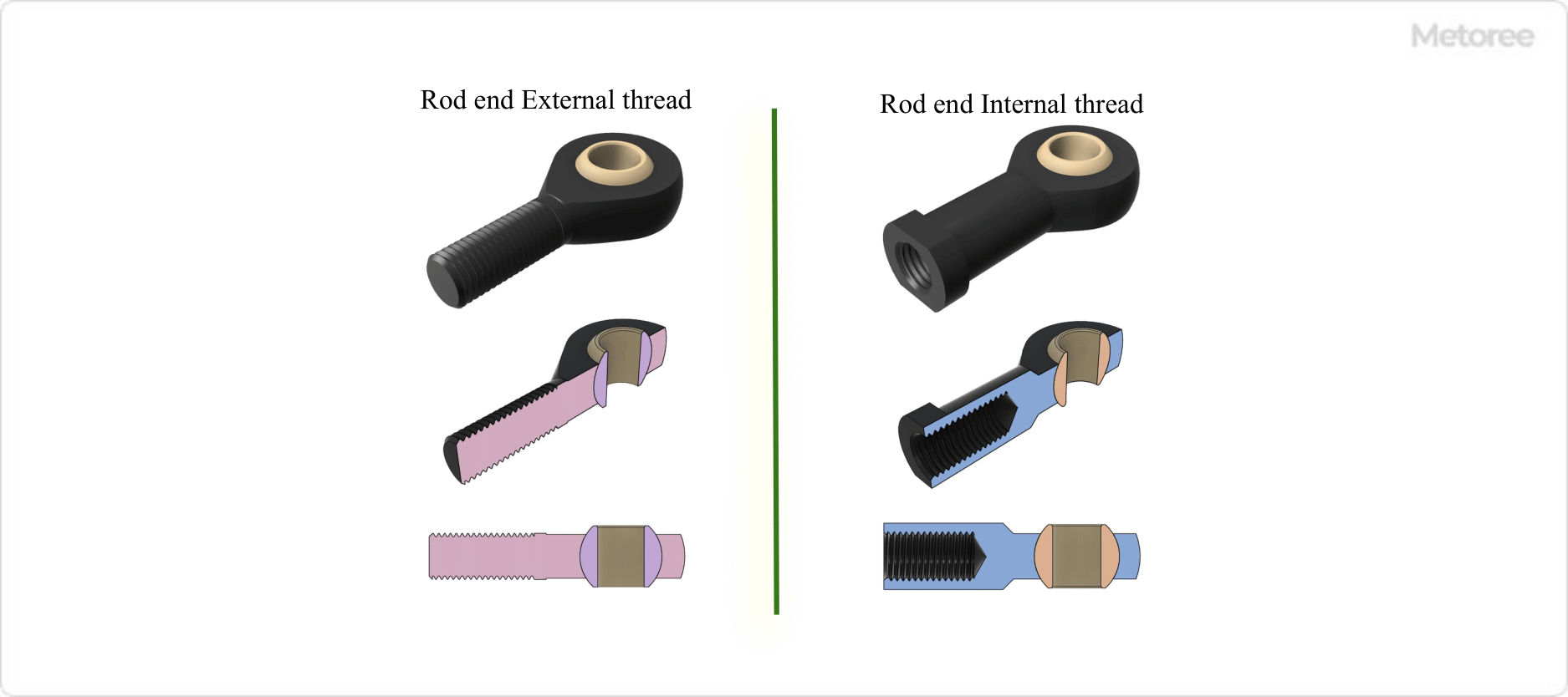
Figure 4. Types of rod ends (Plastic)
Some rod ends are made of resin. Resin contains solid lubricant and can be used without lubrication or oil supply. Compared to metal rod ends, resin rod ends are lightweight and require no oil or grease, making them suitable for use in dusty environments.
It has corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, etc. Resin can absorb vibration, so it can be applied to applications involving vibration.
How to Select Rod End
Rod End should be selected so that the following two points meet the design conditions.
1. Static Load Capacity (Radial Direction)
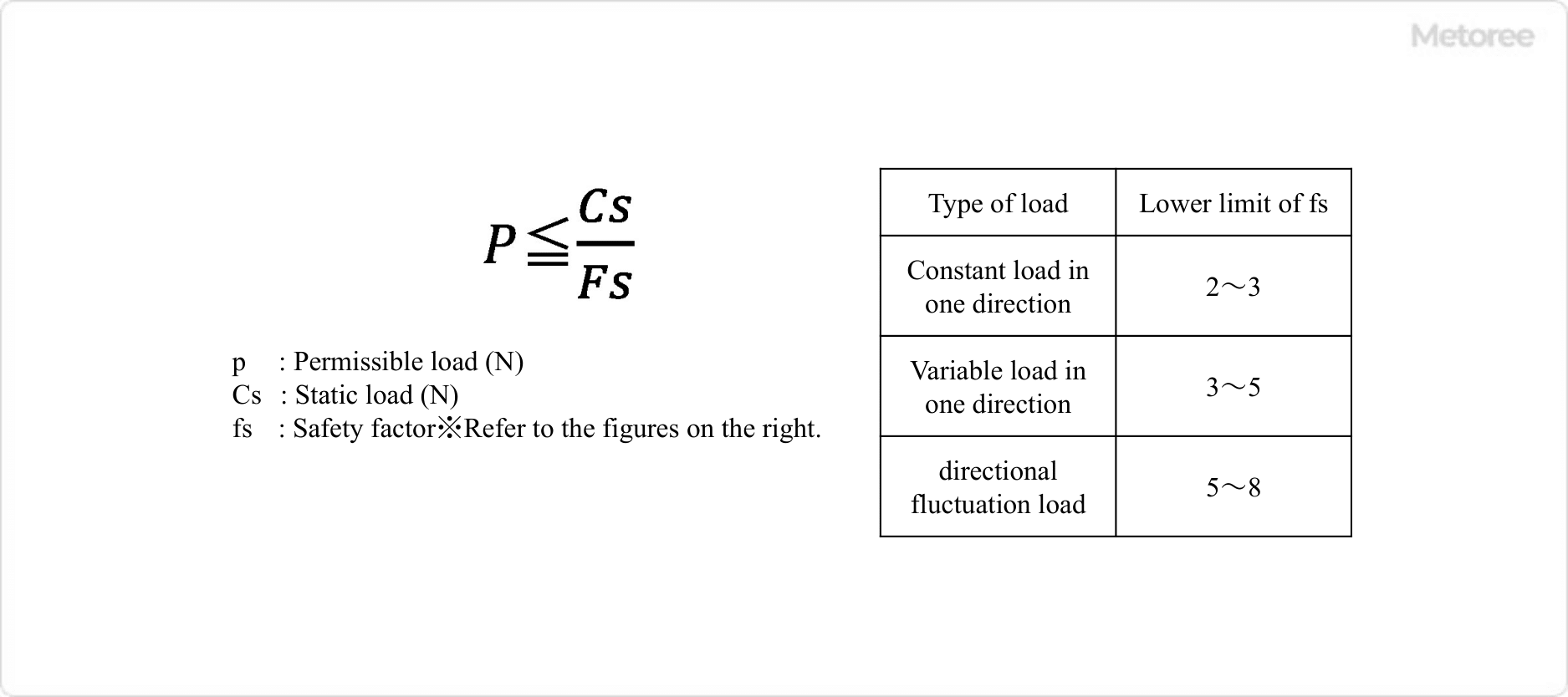
Figure 5. Allowable load calculation formula
Static load capacity is a measure of the mechanical strength of a rod end. Refer to the manufacturer’s catalog or instruction manual for details. The allowable load is calculated from the static load capacity using the above formula, and the rod end should be selected so that the load is less than the allowable load.
2. Allowable Inclination Angle
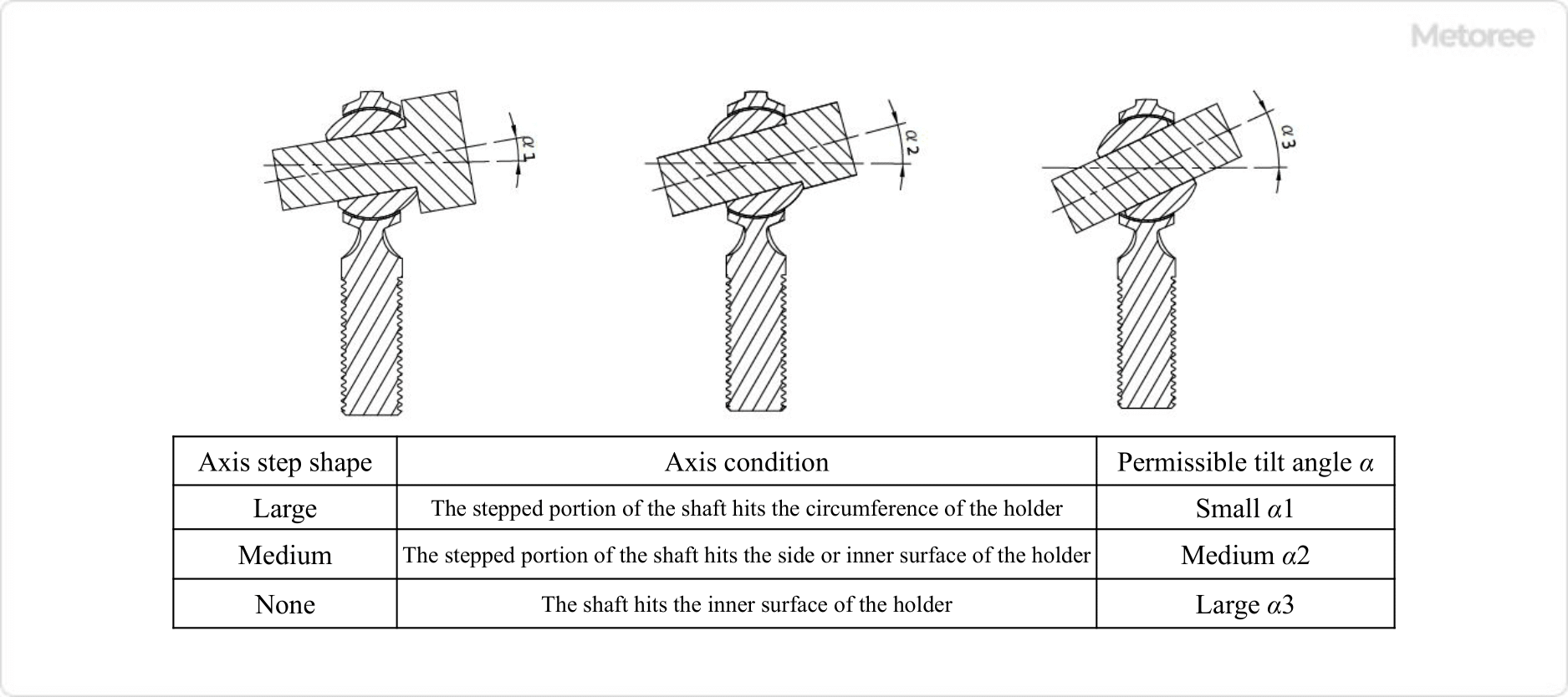
Figure6. Allowable tilt angle
The angle between the centerline of the long axis of the rod end holder and the centerline of the bushing hole is called the tilt angle, which is used within the allowable range when positioning the parts to be connected using the rod end. The allowable inclination angle is also provided by each manufacturer, so please refer to their catalogs or instruction manuals.