What Is a Nanofiber?
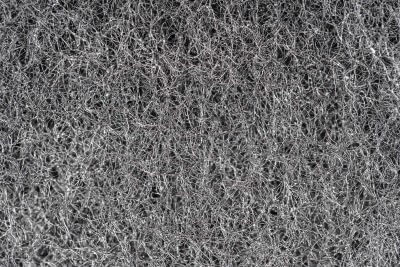
Nanofiber is a fibrous material in which each strand has a diameter of 1 to several hundred nm and a length 100 times greater than its diameter.
It is a representative of nanotechnology and one of the materials attracting attention for future application development. It has a high specific surface area and porosity, and is highly absorbent, permeable, and lightweight.
There are a wide variety of types of nanofibers, including polymeric nanofibers, plant-derived cellulose nanofibers, and carbon nanofibers with high electrical conductivity and strength.
Uses of Nanofibers
Nanofibers are still in the process of being researched and developed for use. Compared to conventional fibers, nanofibers have superior properties such as high strength, light weight, flexibility, water absorption, heat resistance, electrical conductivity, and biocompatibility.
Each material has different properties and is used in various applications.
1. Cellulose Nanofiber
Cellulose nanofibers are used in construction materials, automotive parts, and sporting goods because of their light weight and high strength. Cellulose nanofibers are also used in sanitary and medical products due to their high-water absorbency.
2. Carbon Nanofiber
Carbon nanofibers are used in the aerospace industry, automotive industry, and sporting goods because of their extremely high strength and light weight. Carbon nanofibers are also used in electronic devices and fuel cells due to their high thermal conductivity.
3. Polymeric Nanofiber
Polymeric nanofibers have a wide range of applications because their properties can be adjusted depending on the polymer used as a material. For example, they are used in filters with improved water absorbency and strength, and in electronic devices with improved thermal and electrical conductivity. Their range of applications is extremely wide, including tissue regeneration in the medical field and water purification filters in the environmental field.
Principles of Nanofibers
There are three main methods of manufacturing Nanofiber: electrospinning, composite melt spinning, and melt blowing.
1. Electrospinning Method
Nanofiber is prepared by applying high voltage to a polymer solution in a spinning nozzle. Since the applied voltage is only 10 to 40 kV, energy-saving production is possible. This method can produce nanofibers down to a few nm in diameter and can be called the current mainstream production method, but mass production requires a large number of nozzles.
2. Composite Melt Spinning Method
Nanofiber is prepared by extruding molten polymer through a special nozzle to produce fibers with a sea-island structure, and then dissolving and removing only the sea component. This method has the disadvantage of only producing nanofibers with diameters of up to 20 nm.
3. Melt-Blow Method
Molten polymer is extruded through a nozzle and simultaneously blown with hot air to produce this material. This method is also used to produce non-woven fabrics such as masks. However, since the lower limit is about 0.5 μm in diameter, the range of use is limited.
Types of Nanofibers
There are various types of nanofibers, depending on the manufacturing method and materials used.
1. Cellulose Nanofiber
Cellulose is a component of plants such as trees and grass, and is one of the most abundant organic substances in nature. Cellulose nanofibers are made from this cellulose, which is finely divided down to the nano-level and have both lightness and strength. It is also a plant-derived material, so it has a low environmental impact and can be recycled.
2. Carbon Nanofiber
Carbon nanofiber is a nanofiber composed mainly of carbon and has extremely high strength and lightness. It also conducts electricity well.
3. Polymeric Nanofiber
Polymeric Nanofibers are made from synthesized polymer compounds. Polypropylene, polyethylene, polyester, etc. can be used depending on the required properties.
Their properties vary depending on the type of polymer used, but in general they are characterized by light weight, high strength, and chemical stability.