What Is a UV Printer?
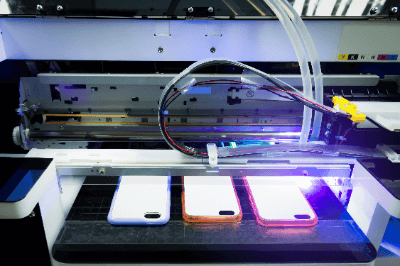
A UV printer is a printer that uses UV ink, which is cured by irradiating it with ultraviolet light.
A UV printer cures and fixes the ink, so there is no need for ink penetration. Therefore, it is possible to print on resin materials and sebum. A UV printer also has the advantage of quick-drying compared to inkjet printers.
However, a disadvantage of UV printers is that they are expensive and require special inks.
Uses of UV Printers
UV printers can print on a wide variety of materials from hard to flexible materials such as wood, general resins, and leather. Taking advantage of this feature, UV printers are used in the following applications:
- Smartphone cases
- Key holders and book covers
- Nameplates and signboards for switches
- Printing on curved surfaces such as balls
Principle of UV Printers
UV printers apply the principle of curing UV-curable resin: irradiating UV ink with UV light initiates radical polymerization, which instantly cures the ink.
While inkjet printers fix the ink by drying it after it has penetrated the ink, UV printers can be used for all kinds of materials because there is no need for the ink to penetrate. However, UV printers generate a peculiar odor when curing UV ink, so the use of a deodorizing device is recommended.
Other Information on UV Printers
1. History of UV Printers and the Market
Since 2000, UV printers have been researched and developed by various companies as the next-generation technology following inkjet printers. As a result, many UV printers have been introduced.
In the early stage of development, UV printers used metal-halide lamps to irradiate UV light, which had disadvantages such as high power consumption and short lifespan, etc. Around 2008, products using LED lamps as UV light sources appeared on the market, and their performance has dramatically improved.
The UV printers market is expected to continue to grow in the future due to the advantages of faster printing processes, diversified printing media, and environmental compatibility. In recent years, research and development of three-dimensional printing technology has also been active. Compact UV printers capable of printing on small three-dimensional media are also available.
2. Challenges of UV Printers
Comparing UV printers with inkjet printers, the following issues need to be resolved to expand the market for UV printers.
Price
Compared to water-based and solvent-based inks, UV inks are expensive, and UV-LED inks are even more expensive. UV printers are also expensive, making the introduction of UV-LED printers a financial hurdle.
Glossiness
Compared to water-based and solvent-based inks, UV printers give a matte impression without gloss. However, gloss can be expressed by printing with transparent clear ink over the original printing. The degree of gloss can be changed by changing the curing timing of the clear ink.
3. Materials That UV Printers Are Not Good At
UV printers have some conditions that make printing difficult.
Water-repellent materials
Since the ink is liquid before curing, highly water-repellent materials will repel ink when the ink is applied. Printing is difficult due to very low adhesion to the material.
Materials with high oil content or additives
The presence of oil on the material surface reduces ink adhesion. Especially with resins, plasticizers, and additives inhibit ink adhesion, so care must be taken. In most cases, de-greasing with alcohol will improve the situation.
Highly smooth materials
It is difficult to print on extremely smooth materials. The more minute irregularities there are, the more adhesion the ink will have. For this reason, unevenness may be intentionally created by sandpaper or other means.
In addition, UV printers may cause cracks in the printed area due to the nature of the ink curing process. This is especially likely to occur when printing on flexible materials, and the print may fall apart if the material is deformed.