What Is a Single Board Computer?
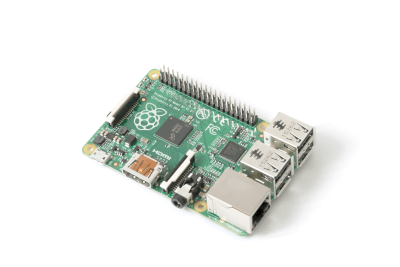
A single-board computer is a compact system that consolidates the essential components of a computer—CPU, RAM, storage, and input/output interfaces—onto a single printed circuit board.
Integrated circuits (ICs) and various electronic components are directly mounted on the board, ensuring high reliability and compactness. They find applications across a diverse range of fields, including industrial embedded systems, control devices, household appliances, robotics, and automotive technology.
They come in various shapes and sizes tailored to specific use cases, ranging from palm-sized units to large rack-mountable systems. Single-board computers offer a wide spectrum of processing capabilities.
From low-power microcontrollers to high-performance industrial computers equipped with multi-core CPUs, there exists an optimal choice for every application.
Uses of Single Board Computers
Due to their compact size and versatility, single-board computers find application in a myriad of products and systems. Here are some prominent uses:
1. Embedded Systems
Single-board computers serve as the backbone of embedded systems, which are specialized systems designed for specific tasks. Their small size and self-contained nature make them ideal for tasks such as automotive engine management systems, factory production line controls, and medical equipment operations.
2. IoT Devices
In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), single-board computers play a crucial role. Many IoT devices, including smart home devices and industrial sensor networks, leverage single-board computers at their core.
These devices can seamlessly interface with the cloud, aggregating and processing large volumes of data generated by physical devices.
3. Robotics
Single-board computers are integral to robotics, powering various types of drones, autonomous robots, and industrial robotic arms.
These robots rely on processing sensor inputs and executing appropriate actions, tasks facilitated by the advanced computational capabilities of single-board computers. This enhances the autonomy and efficiency of the robots.
These examples represent just a fraction of the applications of single-board computers. Their compactness, self-contained nature, and scalability serve as catalysts for innovation across all industries.
Principle of Single Board Computers
As the name suggests, single-board computers consolidate the core elements of a computer onto a single substrate. Here’s an overview of their core principles and operation:
1. Integrated Components
Single-board computers integrate all essential computer components onto a single board, including the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), storage (e.g., flash memory), and input/output ports. These components are highly optimized and work synergistically to provide full-fledged computer functionality.
This integration enables single-board computers to deliver the same functionality as traditional desktop or laptop computers but in a more compact and energy-efficient form factor.
2. Low Power and High Performance
Single-board computers must strike a balance between low power consumption and high performance. To achieve this balance, they utilize energy-efficient processors, low-power RAM modules, and sophisticated power management systems. These components and systems minimize power consumption and heat dissipation while delivering robust computing performance.
3. Flexible Input/Output Options
Despite their compact size, single-board computers offer a plethora of input/output options, including USB ports, HDMI connections, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, and GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins. These connectivity options enable single-board computers to interface with a wide array of peripherals, catering to diverse application requirements.
These fundamental principles and features render single-board computers as versatile and adaptable computing platforms. Their scalability and self-contained design empower a broad spectrum of applications, spanning from IoT devices to embedded systems to robotics.
Features of Single Board Computers
The primary feature of single-board computers is their affordability and versatility. By consolidating circuits onto a single substrate with only essential functions, single-board computers eliminate waste and keep costs low.
Moreover, the performance of CPUs and memory in single-board computers has been steadily improving in recent years, enabling them to handle more complex computational tasks than ever before.
Other Information on Single Board Computers
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves distributed information processing, where data from sensors attached to production equipment, for instance, undergoes processing and cleansing at the sensor side before transmitting only the relevant information to higher-level systems, rather than collecting all data in a centralized system like a cloud.
In a landscape dominated by IoT and abundant data, centralized data processing may eventually prove inadequate. Distributed processing methods, such as those employing single-board computers, are gaining traction as a means to address this challenge and achieve efficient data processing.