What Is a Spherical Plain Bearing?
A spherical plain bearing is a type of bearing that supports both radial and axial loads in both directions.
This bearing consists of a spherical outer ring and a ball-shaped inner ring with a drilled hole. It offers an alignment function that allows for misalignment between the center of rotation of the shaft and the housing.
It is utilized in parts that require oscillating and alignment movements. “Rod end” and “rod end bearing” are terms sometimes used interchangeably with spherical plain bearings.
Uses of Spherical Plain Bearings
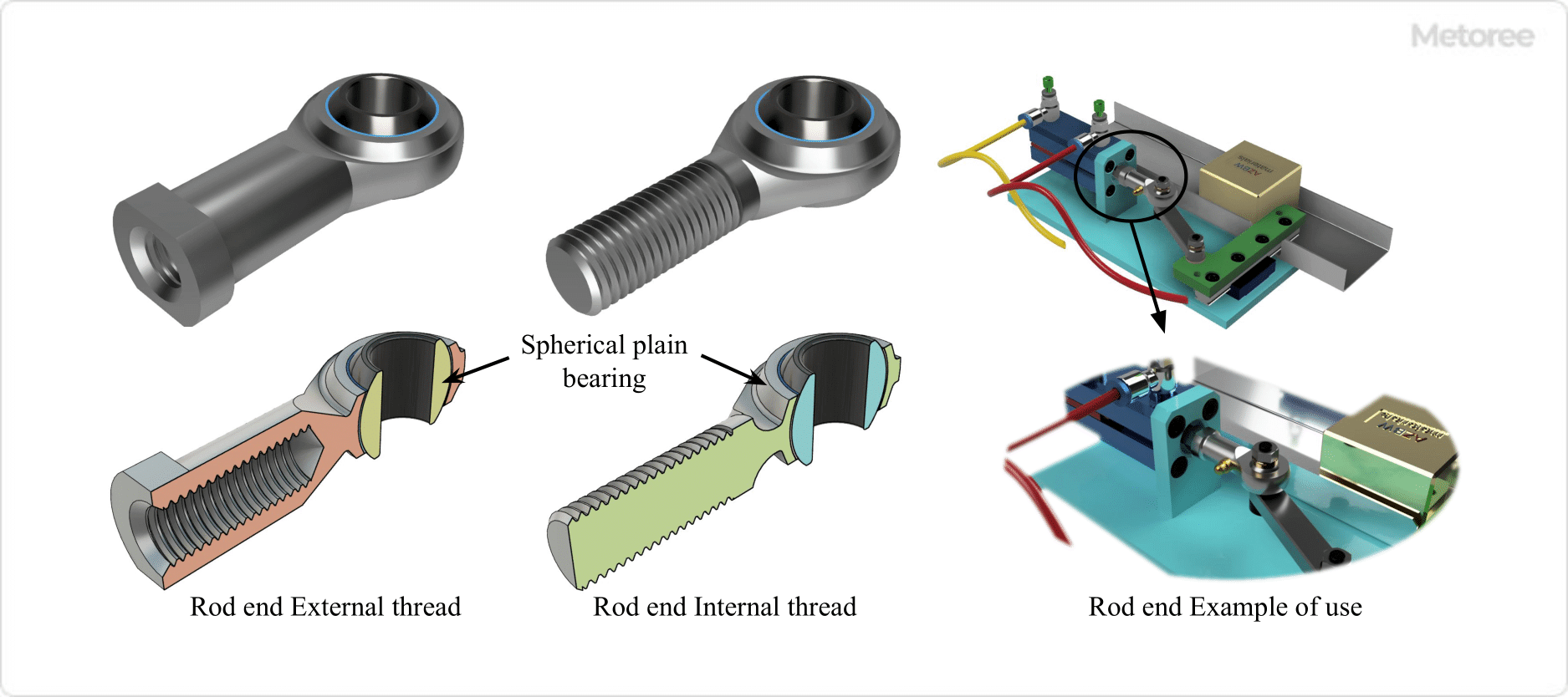
Figure 1: Applications of Spherical Plain Bearings
Spherical plain bearings are primarily used for linking parts or transmitting linear motion. They find applications in the joint motion components of construction machinery, industrial machinery, automobiles, and aircraft, supporting oscillating or alignment motions.
These bearings can withstand large radial and thrust loads in both directions. They offer high resistance to impact loads and are commonly used in cylinder clevises, hinges of construction and civil engineering machinery, and truck suspensions.
A common application for spherical plain bearings is in rod ends (or rod end bearings).
Principle of Spherical Plain Bearings
The spherical plain bearing has an outer diameter of the inner ring (sliding contact surface) that is convex and an inner diameter of the outer ring (sliding contact surface) that is concave. A small clearance between their sliding contact surfaces ensures an appropriate sliding surface while providing alignment and load-bearing capabilities.
These bearings are suitable for supporting high static and dynamic loads at relatively low rotational speeds, with the alignment function facilitating easy centering and accommodation of misalignment.
Types of Spherical Plain Bearings
1. Classification by Structure
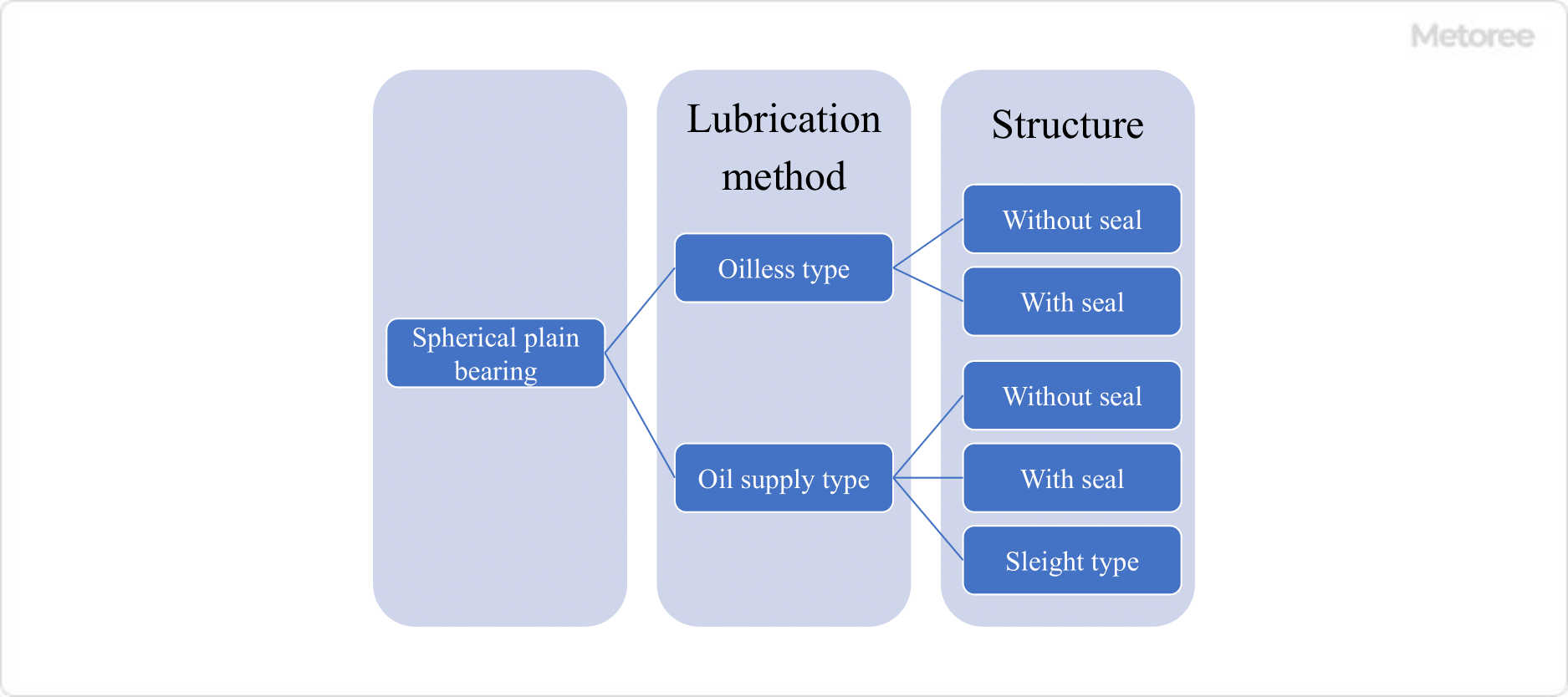
Figure 2: Types of Spherical Plain Bearings by Structure
Lubricated Type
In the lubricated type, both the outer and inner rings are greased through lubrication holes to maintain optimal lubrication. The rings are made of high-carbon chromium-bearing steel for high wear resistance.
Lubrication-Free Type
The lubrication-free type does not require lubrication. The sliding surface of the outer ring is made from a material with high self-lubricating properties and excellent wear resistance. The inner ring consists of steel balls with surface treatments such as hard chrome plating, offering maintenance-free operation and exceptional wear resistance.
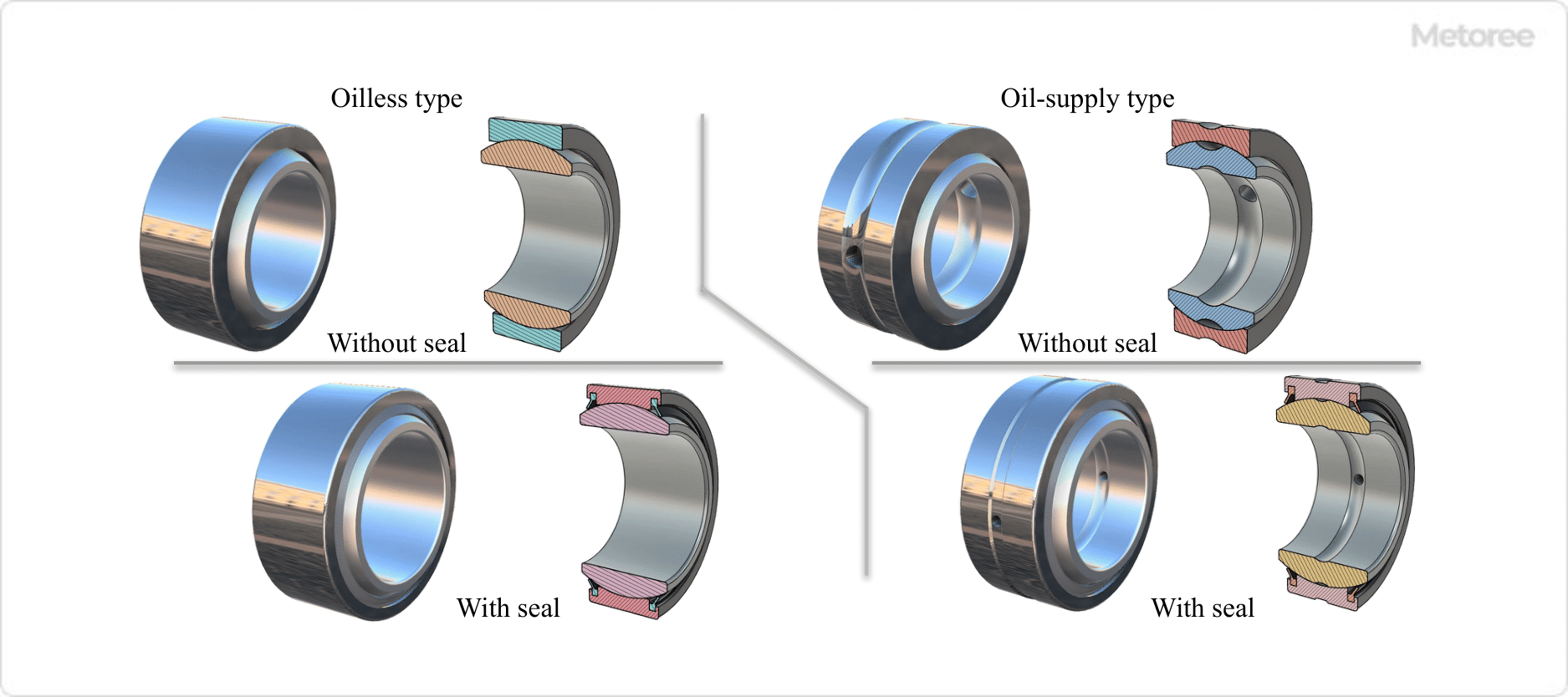
Figure 3: Spherical Plain Bearing Geometry with and without Seals
With and Without Seals
Bearings with seals have seals at both ends between the inner and outer rings to prevent grease leakage and the intrusion of foreign matter. Bearings without seals are available for applications where seals are not necessary.
2. Radial and Thrust Loads
Spherical plain bearings are categorized into two types: those that support both radial and thrust loads, and those that support only thrust loads.
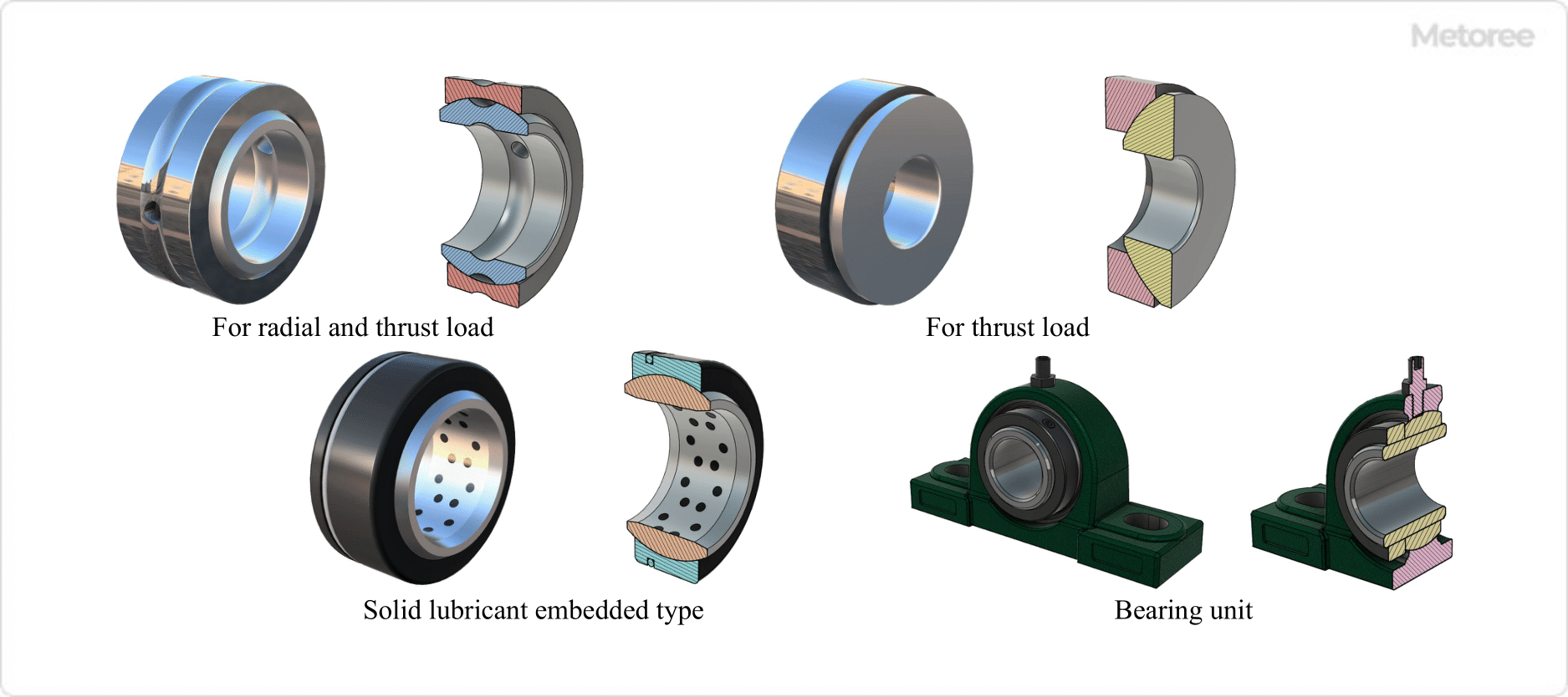
Figure 4: Other Spherical Plain Bearings
3. Solid Lubricant Embedded Type
This type features an inner ring made of a special copper alloy with a solid lubricant embedded in the sliding surface, and an outer ring with a lubricating coating on the sliding surface.
4. Bearing Unit
Spherical plain bearing units are pillow-type units incorporating spherical plain bearings.
Other Information on Spherical Plain Bearings
Spherical plain bearings are defined as “plain bearings with a spherical contact surface designed primarily for oscillating, tilting, and low-speed rotational motions.”
The motions supported are defined as:
Oscillating Motion
A rotational or tilting motion in which the direction of motion is repeatedly reversed.
Tilting Motion
A motion in which the angle of inclination between the inner and outer rings of the bearing, or between the shaft raceway and housing raceway, changes relative to each other.