What Is a CNC Lathe?
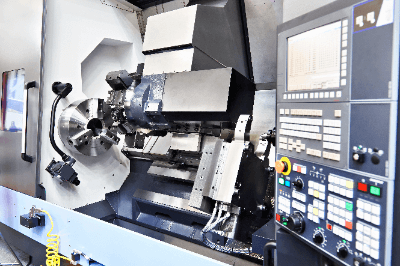
A CNC lathe is a conventional lathe equipped with a computer-controlled system that enables automated cutting operations.
The term “CNC” stands for Computerized Numerical Control.
Tool changes are also automated, either through the installation of an ATC (Automatic Tool Changer) device or by selecting the optional ATC device.
Uses of CNC Lathes
CNC lathes, often referred to as unmanned processing machines, are employed to precisely shape parts required in large quantities.
CNC lathes are primarily used for bar processing (bar work) and profile processing (chuck work).
Common processing methods include:
- Outer diameter machining
- Internal diameter machining
- Threading
- Drilling
- Grooving
CNC lathes are used for processing a wide range of parts, from precision components like those used in automobiles and aircraft to everyday items such as cookware and tools.
Principles of CNC Lathes
The operation principle of CNC lathes is explained below.
CNC lathes are computer-controlled machines and are not intended for manual operation like conventional lathes.
To perform machining operations accurately, a program must be created based on the part’s design drawings.
Various parameters and commands, such as tool movements and spindle speeds, must be specified based on the part’s design.
These command instructions include tool movement, spindle speed, and other settings.
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software can also be used to create machining programs for CNC machines.
CAM software simplifies the process by generating machine-readable data from 3D CAD models, including toolpath information.
The CNC lathe’s components include a rear spindle, feed mechanism, tool post, guide bush device, spindle (chuck, spindle head), control panel, material supply system, bed, and more.
CNC Lathes vs. Machining Centers
A machining center is a type of machining equipment where the workpiece is fixed to a base, and the cutting tool performs rotational cutting operations. While both CNC lathes and machining centers support numerical control, their machining methods differ.
Currently, “hybrid machines” combine the capabilities of CNC lathes and machining centers.