What Is a Blower?
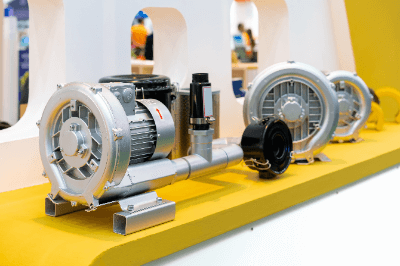
A blower, sharing a basic structure with a compressor, operates at a lower discharge pressure, typically less than 200 kPa. It finds use in industrial fields where pressure requirements are lower than those of compressors. Blowers compress and discharge air using a rotor within a container, similar to compressors, or increase pressure via a fan. The fan method is preferred in precision applications due to its low pulsation characteristics.
Uses of Blowers
Blowers find applications in production plants and industrial facilities where the required pressure is higher than what fans can provide but lower than what compressors deliver. Key considerations when selecting a blower include the air’s pressure and speed, power consumption, size, and operational stability.
Typical uses of blowers include:
- Supplying air to incinerators and heated components
- Generating jets in air jet cleaning equipment
- Enhancing oxygen supply in aquaculture oxygen systems
Principle of Blowers
Blowers function by drawing in air, increasing its pressure, and then discharging it. The main components include an inlet, an outlet, and a pressure-increasing device, such as a fan or rotor. Below are the specifics of each method:
- Fan Type: This type comprises a motor and a fan. The motor drives the fan, which propels air outwards. For higher pressures, a multi-stage fan arrangement can be employed.
- Rotor Type: In this design, a rotor attached to a motor is placed within a container. The rotor’s rotation decreases the air volume, thereby increasing the pressure, which is then expelled through the outlet.