What Is a Syringe?
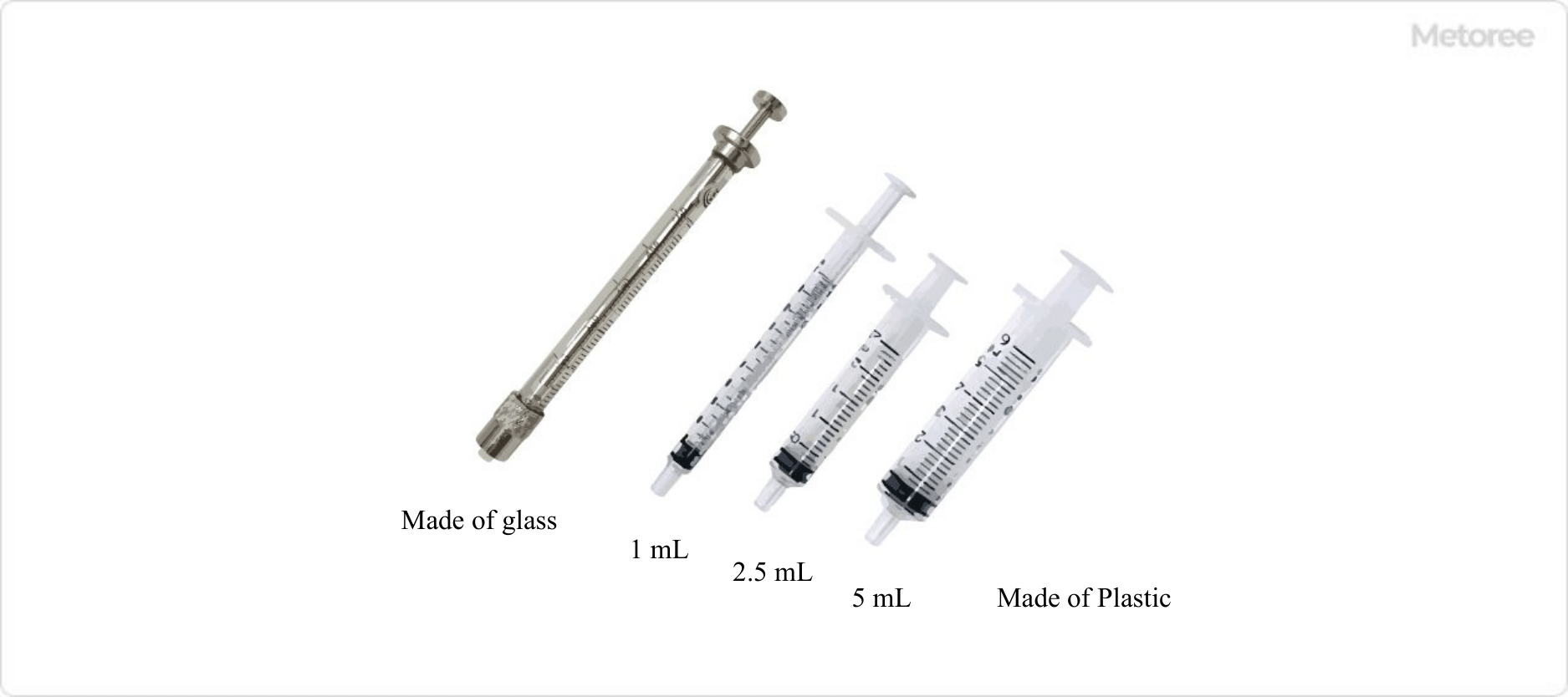

Figure 1. Image of a syringe
A syringe is the cylindrical part of a syringe, excluding the needle and plunger, used to fill the syringe with liquid. It is also called a syringe tube or outer tube. Currently, disposable plastic (polypropylene) syringes are the most common, but glass (borosilicate glass) syringes are also used as needed.
Uses of Syringes
Uses of syringes can be divided into two main categories: medical and laboratory. Plastic syringes, which are currently mainstream, are sterilized and packaged individually and are disposable. This prevents infection in the medical field and contamination in chemical experiments. Since plastic syringes cannot be heat sterilized, ethylene oxide gas sterilization or radiation (gamma ray) sterilization is used. On the other hand, glass syringes are used in the following cases. In this case, medical glass syringes are sterilized and used repeatedly for each specification.
- In the medical field, when there are concerns about drug adsorption or leakage of resin additives in plastic syringes
- When there is a risk of resin dissolving in organic solvents, such as in organic chemistry experiments.
1. Uses of Medical Syringes
In medical applications, syringes are mainly used for blood sampling, drug injection, and enemas. Pre-filled syringes may be used to inject drugs such as immunizations to prevent infection and improve work efficiency.
2. Uses of Laboratory Syringes
In addition to medical use, syringes are also used as experimental instruments in physics, chemistry, and life sciences. Their main uses include the injection of liquids and gases, volume measurement, pressurization and depressurization, dripping, and dispensing.
Principles of Syringes
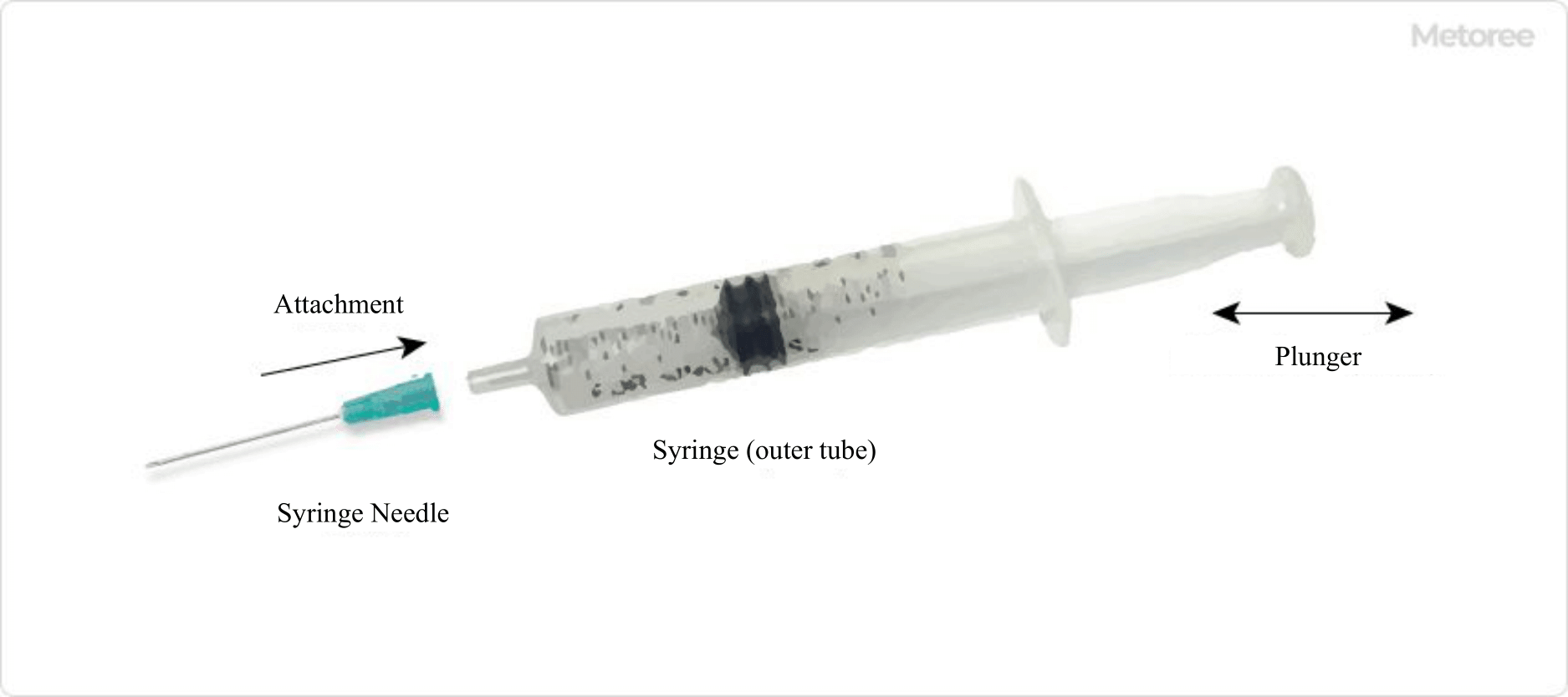
Figure 2. Image of a syringe in use
Syringes are usually used with a movable plunger (pusher) with a needle attached to the tip. Syringes come in various capacities, but the size and shape of the connection to the needle are standardized regardless of the capacity. Therefore, needles of any size and length can be attached.
Types of Syringes
Syringes can be classified according to the shape of the tip and the position of the needle connection.
1. Classification by Tip Shape
- Luer-Lock Type: The part where the needle is attached is threaded and can be secured to prevent the needle from falling out.
- Luer-Tip Type: The needle is secured in place using the taper of the needle attachment portion. The advantage is that the needle is easy to attach and detach.
- Luer Metal Type: The tip is made of metal and has high strength.
- Enema Type: This shape is found in devices such as enemas used for enema and bladder cleansing. The tip is slightly rounded for insertion into the body.
- Catheter Tip Type: The tip of a catheter syringe for connection to a catheter is thicker than the tip of a regular syringe for injection. The shapes of the catheter syringes and syringe tips are different to prevent fluid administration errors due to the mistaken use of catheter syringes and syringes for injectable syringes.
2. Classification According to the Position of the Needle Connection
- Middle-Mouth Type: The connection part is located in the center of the tube. The middle-mouth type is commonly used for small syringes with a 10 ml or less capacity.
- Side Mouth Type: The connection part is located off-center of the cylinder. Even syringes with large capacities can become punctured at a shallow angle. Also, the tip is located at the end, which makes it easier to release air.