What Is Aluminum Casting?
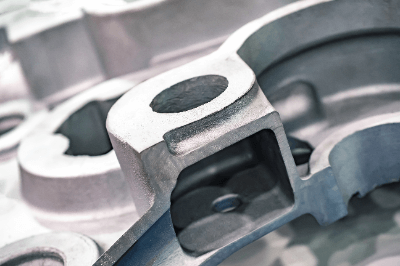 Aluminum Casting is a product made by processing aluminum alloy with a method called casting.
Aluminum Casting is a product made by processing aluminum alloy with a method called casting.
Casting refers to the process of heating an aluminum alloy at a temperature higher than its melting point, melting it, pouring it into a mold made in the desired shape, and cooling it to make a product. There are two main types of molds: sand casting and metal mold casting.
The advantages of the sand mold casting method are low cost, support for large shapes, and small-lot production. The advantages of the metal mold casting method are mass production and high dimensional accuracy. The mold casting method also includes the gravity method and die casting method.
Uses of Aluminum Casting
Aluminum Casting is often used in automobiles because of its light weight, excellent workability, electrical and thermal conductivity, recyclability, and corrosion resistance.
Parts in actual use include the following:
- Engine parts (cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, etc.)
- Body parts
- Suspension parts, etc.
Reducing the weight of automobiles leads to improved fuel efficiency and operability. In addition, the thermal conductivity is utilized to reduce cooling of parts that generate heat.
Principle of Aluminum Casting
Sand casting and Mold casting (gravity casting) are two different aluminum casting methods.
1. Sand Casting Method
- A wooden mold is used to create the shape of the product and the aluminum inlet into which the aluminum is poured.
- Sand mixed with an additive for hardening is filled into the mold.
- The sand mold is completed by removing the wooden mold (product shape and hot water outlet) from the sand mold.
- The upper and lower sand molds are made according to the above procedure.
- Align the completed sand molds top and bottom.
- Molten aluminum is poured from the hot water outlet into the top and bottom sand molds.
- After pouring, the mold is cooled and hardened.
- After hardening, the sand mold is broken and the aluminum casting is removed.
- After removing unnecessary parts and machining the surface, the casting is complete.
Mold Casting Method (Gravity Casting)
- A mold is made according to the shape of the product.
- Molten aluminum is poured into the mold by gravity*.
- After the molten aluminum is poured into the mold, it is cooled and hardened.
- After hardening, the mold is removed and the aluminum casting is taken out.
- After removing unnecessary parts and machining the surface, the product is complete.
*The method of injecting by pressure as well as gravity is called the die casting method.
Other Information on Aluminum Casting
1. Anodizing of Aluminum Casting
The surface of aluminum casting can be anodized to improve corrosion and wear resistance. Anodizing is also called anodic oxidation treatment. It is a treatment method in which aluminum is oxidized by passing an electric current through it in an electrolytic solution to produce a film that is thicker than the film produced by natural oxidation.
Aluminum casting contains a large amount of elements other than aluminum to increase its strength. Examples include silicon, copper, and magnesium. When anodizing aluminum casting, these elements may inhibit the formation of the coating. This is due to the segregation of elements other than aluminum in the casting, which changes the current-carrying conditions. To improve the situation, it is necessary to carefully remove dirt and undissolved fine particles from the casting surface, and to perform the treatment in a short time.
2. Defects in Aluminum Casting
Pinholes are one of the defects that occur in aluminum casting and are numerous fine needle-like bubbles. The size of the bubbles varies depending on the manufacturing conditions, but is about 0.1 mm. Pinholes occur when moisture in the air becomes hydrogen gas in the molten metal and is released outside the casting during the solidification process. They tend to occur in thick-walled parts of the product or parts that were difficult to cool.
Pinhole countermeasures include reducing contact between the molten aluminum alloy and air, and sufficiently drying raw materials and tools to prevent moisture contamination. It is also necessary to remove hydrogen gas from within the alloy as much as possible before solidification.
Defects other than pinholes include sinkholes, hot water borders, hot water wrinkles, seizures, and galling. These defects can be prevented mainly through maintenance such as temperature control of the mold and polishing of the mold.