What Is Aluminum Die Casting?
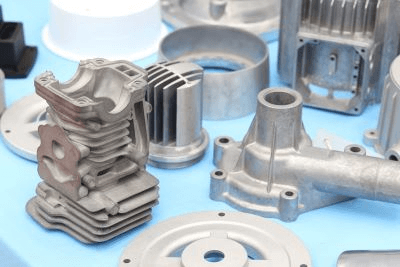 Aluminum Die Casting is a special casting method in which aluminum alloy or zinc alloy is melted and pressed into a mold. Aluminum die casting is characterized by its ability to mass-produce products of complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy and beautiful surfaces.
Aluminum Die Casting is a special casting method in which aluminum alloy or zinc alloy is melted and pressed into a mold. Aluminum die casting is characterized by its ability to mass-produce products of complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy and beautiful surfaces.
For this reason, aluminum die casting is highly regarded among metalworking methods. It is often confused with aluminum casting, however it is a different casting method from aluminum die casting because it refers to a method in which a metal such as aluminum alloy or copper is made into a liquid at a temperature higher than its melting point, poured into a mold, and cooled to harden. In addition, aluminum die casting uses metal molds, whereas sand molds are generally used for aluminum casting.
Aluminum die casting is characterized by high production costs because it requires the design and fabrication of molds from a block of metal.
Uses of Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is mainly used in automotive parts. Among them, steering related parts are in high demand in recent years. This is because aluminum die casting can manufacture products with complex shapes and high precision in large quantities and in a short time.
Aluminum die casting is not only used for automotive parts. It is also used in various products in our daily lives, such as personal computers, cell phones, digital cameras, refrigerators, and washing machines.
Aluminum die casting can also be used to produce small parts, thus contributing to product weight reduction.
Principle of Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is a casting method that uses molds. The die casting machine consists of a die clamping device that opens and closes the die, an injection device that ejects the molten metal into the die, and an extrusion device that pushes the metal out of the die.
In aluminum die casting, aluminum alloy is first melted. At this time, metals other than aluminum are also melted to produce an alloy with the desired composition, so careful adjustment and control of the composition is necessary. After the aluminum alloy is melted, the die is cleaned and the die is closed with a die clamping device. The closed mold is then filled with the molten aluminum alloy by an injection device.
Aluminum die casting is characterized by a fine surface structure because the molten metal is injected into the mold and cooled rapidly. This fine surface structure makes the surface of aluminum die casting hard and enables the production of strong products.
On the other hand, the disadvantage of aluminum die casting is that the rapid cooling process tends to create casting voids. These casting voids occur not only on the surface, but also in the center of the product where it finally solidifies. If casting cavities occur in aluminum die casting, the expected product performance will not be achieved, such as reduced strength. Therefore, aluminum die casting requires temperature control during die casting and careful consideration of the mold shape.
Other Information on Aluminum Die Casting
1. The Difference Between Aluminum Die Casting and Aluminum Casting
Aluminum die casting is formed by melting aluminum alloy or zinc alloy and press-fitting it into a die. Generally, the material is heated to approximately 500°C to 700°C to melt, poured into the mold at low speed, and then cooled under high pressure to form the mold.
Aluminum casting, on the other hand, involves melting a liquid aluminum alloy in a high-temperature furnace and pouring it into a metal or ceramic mold. Aluminum casting basically does not apply any external force, but uses the input of liquid metal by falling and subsequent flow. Aluminum die casting is sometimes referred to as gravity casting.
The advantages of aluminum die casting are its high dimensional accuracy and the ability to produce even complex shapes. This is because the molten aluminum alloy is fed into the mold under pressure, so the aluminum alloy is instantly distributed to every corner of the mold. On the other hand, aluminum casting may not achieve the desired dimensions or may cause wrinkles on the surface. This is because the high-temperature aluminum alloy has relatively low fluidity, and it takes time for it to spread to all corners of the mold by simply dropping it into the mold.
As a result, aluminum casting shrinks as it solidifies, which can result in defects such as dimensional changes and wrinkles created during flow. Aluminum die casting is also characterized by high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface roughness. Since the aluminum alloy is spread instantaneously, manufacturing time can be shortened, which has the advantage of enabling mass production of products.
Another feature that distinguishes aluminum die casting from aluminum casting is that the surface roughness remains high quality, which reduces finishing and inspection processes. One disadvantage of aluminum die casting, however, is the high cost of mold design and manufacturing. For this reason, aluminum die casting using sand molds may be more cost-effective for small-lot production.
Another disadvantage of aluminum die casting is that it is not suitable for parts that require high strength. Due to the manufacturing process, aluminum die casting involves air and evaporated mold release agent during the molding process. This creates cavities called nests, which reduce the strength of the product.
2. Materials for Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting materials include casting and elongation materials, and a large number of die casting materials are available in a series headed by ADC.
The main component systems of aluminum die casting materials are Al-Si and Al-Mg, to which elements such as Cu and Mn are added. Each material is selected according to the corrosion resistance, castability, and impact resistance required for aluminum die casting.
The metallographic structure of aluminum die casting materials is a matrix phase of Al solid solution. The matrix can be a lamellar Al-Si eutectic or precipitation strengthened by fine precipitates such as Mg2Si, Al2Cu, etc., and the properties exhibited differ accordingly.
Normally, aluminum alloys are subjected to heat treatment after casting and machining to prepare crystal grains and form micro-precipitates. However, in aluminum die casting, heat treatment is often not performed to avoid air and gas entrained in the die castings from expanding and forming defects due to heat treatment.
However, vacuum die casting and non-porous die casting methods, which have recently been increasingly applied, are characterized by the fact that these defects are less likely to occur. Therefore, in recent aluminum die casting, it is possible to bring out the characteristics of materials by adding heat treatment process.