What Is a Bi-Metal Thermometer?
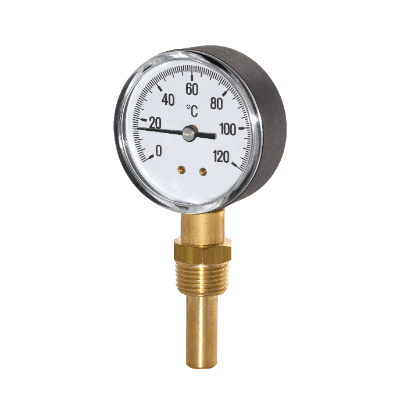 A Bi-Metal Thermometer is a measuring instrument that uses the properties of bimetal to measure temperature.
A Bi-Metal Thermometer is a measuring instrument that uses the properties of bimetal to measure temperature.
Bimetals are made by bonding two types of metal plates with different coefficients of thermal expansion, which bend as the temperature changes. This instrument uses the force of curvature to turn the axis of the needle that points to the scale on the display plate to directly read the measured temperature.
Compared to glass thermometers, it is more durable, easier to handle, and safer. Because of their simple structure and easy maintenance and inspection, bimetallic thermometers are widely used in household and industrial applications.
Uses of Bi-Metal Thermometers
Bi-Metal Thermometers are used indoors as wall-mounted or stationary thermometers. They mainly incorporate a spring-like bimetal to move the needle of a circular display plate with a printed scale.
Other applications include water thermometers, soil thermometers, and cooking thermometers.
The bimetal in the form of a spiral is incorporated in a protruding cylinder on the back side of the display plate. Furthermore, in industrial applications, bimetals are used for line temperature control in chemical plants, etc., due to their features of easy addition of waterproofness, corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, pressure resistance, etc.
Principle of Bi-Metal Thermometer
One of the bimetals is an alloy of iron and nickel, a low thermal expansion alloy whose thermal expansion coefficient is almost zero at around room temperature. The other is an alloy of manganese with chromium and copper, which has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. Bimetal is manufactured as a single metal sheet by overlapping these two metal sheets and cold rolling.
Advanced technology is required for manufacturing bimetals, as their properties may change due to heat after prolonged use. When bimetal is heated, the alloy side with a large expansion coefficient is extended, so it warps with the low-thermal-expansion alloy side inside. Bi-Metal Thermometers have a mechanism that uses the force generated at this time to move the thermometer needle.
The actual structure is that the bimetal is wound around the thermometer in the form of a spring, and the pointer is rotated by twisting caused by temperature changes. The low thermal expansion alloy is called invar in and is a registered trademark. It is an alloy containing 64% iron, 36% nickel, and a trace of manganese. It is characterized by its low thermal expansion, which causes almost no thermal expansion of the crystal as a whole as temperature rises.
How to Install Bi-Metal Thermometer
If the product is dropped or subjected to excessive impact, deviations in readings will occur.
Therefore, it is necessary to install the thermometer while paying attention to the following points:
1. Vibration
Continuous vibration of the temperature-sensitive part will cause wear and tear on the thermometer’s components. Vibration of the temperature-sensitive part is observed as a small tremor of the pointer. In this case, appropriate measures should be taken immediately without leaving it unattended.
2. Ambient Temperature
If there is a temperature difference between the ambient temperature and the object to be measured, the ambient temperature may cause measurement errors. It may be possible to improve the situation by keeping the equipment in use warm and suppressing heat dissipation and heat absorption.
3. Freezing Environment
When the temperature of the object to be measured is below the freezing point, the inside of the thermometer may freeze, resulting in damage to the product. If the product is to be used in a freezing environment, a dedicated product must be installed. In rare cases, a dedicated product may cause the inside of the product to freeze, but in many cases, this can be solved by selecting a product with special specifications, such as using a product with silicon oil.
Other Information on Bi-Metal Thermometers
1. Protective Tube for Bi-metal Thermometer
The following are cases in which a protective tube is required:
- When the object to be measured may corrode the thermosensitive part
- When high pressure is applied to the thermosensing part
- When the object to be measured is a fluid
- When the object to be measured leaks out and interferes with the thermometer when it is removed.
2. Material of the Protection Tube
If the object to be measured is subject to corrosion, select a corrosion-resistant material for the protection tube. Also, if pressure is applied to the temperature-sensitive part, use a pressure-resistant material.
3.Types of Protective Tubes
Types of protective tubes include nonferrous protective tubes, stainless steel welded protective tubes, and hollowed-out protective tubes. Selection should be made in consideration of the length of the temperature-sensitive part and other factors.