What Is an LCR Meter?
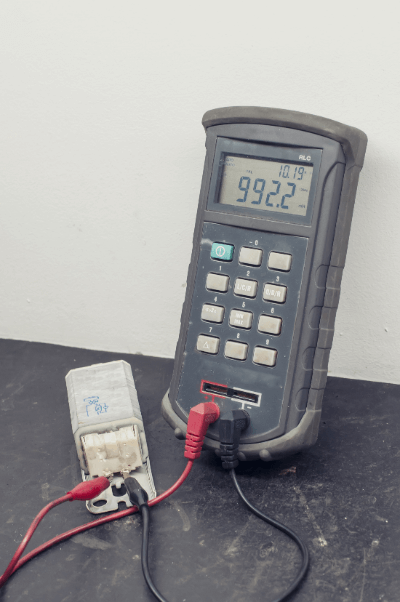 An LCR meter is a device for measuring impedance, where LCR is the symbol for L (inductance), C (capacitance), and R (resistance). Together, these three are called impedance, and an LCR Meter refers to a measuring instrument that measures impedance.
An LCR meter is a device for measuring impedance, where LCR is the symbol for L (inductance), C (capacitance), and R (resistance). Together, these three are called impedance, and an LCR Meter refers to a measuring instrument that measures impedance.
Meaning of LCR
Each component of L, C, and R has an electrical characteristic. The electrical components representing each are the coil, capacitor, and electrical resistance.
L component
The L component is called inductance. It is said that it was named L from the initial letter of Lenz’s law, which is a law concerning electromagnetic induction, but there are various theories. The unit is the Henry (H).
When the current flowing through a coil changes, it has the property of generating power in the direction that prevents the change. A circuit with a high L component will be insensitive to current changes. While it is resistant to steep noise currents, when used in AC circuits, the power factor is delayed, resulting in lower efficiency.
C Component
The C component is called capacitance. It is derived from a capacitor. The C component indicates the capacity to store electric charge, which is the source of electricity. The unit is farad (F).
A capacitor plays the opposite role of a coil in a circuit. Therefore, a circuit with a high C-component will cause a steep change in the current. In AC circuits, it advances the power factor, but there is a risk of amplifying noise currents. In DC control circuits, it plays the role of amplifying and smoothing the voltage.
R Component
The R component is called resistance. It literally means electrical resistance. The unit is ohm (Ω).
When electrical resistance is high, it is difficult for the current to flow in both AC and DC circuits. On the other hand, the maximum current at the time of a breakdown is also reduced.
Uses of LCR Meters
LCR meters are often used in the industrial field in the development and testing of electronic equipment. Specifically, they are used to test the performance of power and electronic components, such as capacitors and coils. In everyday life, LCR meters are used mainly in the medical field. A specific example is a body fat percentage measuring instrument. By measuring the impedance of the human body, body fat percentage and water content can be measured.
For the above reasons, LCR meters are also useful in medical research; they are not expensive devices like CT or NMR and have the advantage of being low cost and easy to install.
Principle of LCR Meters
Impedance measurements with an LCR meter are made by applying an alternating current to an object. The basic principle is to apply an AC voltage, measure the current and phase difference, and calculate the impedance.
The LCR meter consists of an oscillator, a vector voltmeter, and a current-to-voltage converter in a configuration called an automatic balanced bridge. This is the same configuration as an inverting amplifier circuit using an operational amplifier. The impedance calculation is done by digital conversion using an AD converter.
The most important component of the LCR meter is the vector voltmeter, which uses the lock-in amplifier principle to generate a reference signal synchronized with the input signal to detect amplitude and phase difference.
LCR meter based on an automatic balanced bridge is suitable for low-frequency measurements not exceeding 100 kHz; in the high-frequency range above 100 kHz, the effect of the impedance of the component itself, called characteristic impedance, becomes significant.