What Is a Circuit Protector?
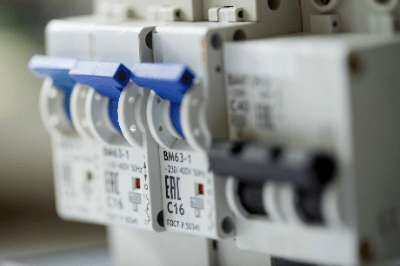 A circuit protector is a power disconnect device for instrumentation. The word “circuit” refers to an electric circuit. Therefore, the literal translation of circuit protector is “electric circuit protector,” and it is used for this purpose.
A circuit protector is a power disconnect device for instrumentation. The word “circuit” refers to an electric circuit. Therefore, the literal translation of circuit protector is “electric circuit protector,” and it is used for this purpose.
Instead of being low capacity, circuit breakers are characterized by a faster disconnection speed than general low-voltage breakers. Due to this feature, they are mostly used for protection of control circuits and instrumentation circuits. They operate before low-voltage breakers installed on the primary side to protect the upper circuits.
Uses of Circuit Protectors
Circuit protectors are used in instrumentation and control circuits. Measuring equipment for industrial applications, such as differential pressure transmitters and electromagnetic flowmeters, are called instrumentation, and the circuits used to supply power to the instrumentation and receive and transmit signals are called instrumentation circuits. Instrumentation circuits are characterized by low power consumption in spite of their high importance among industrial devices.
Circuit protectors can be used to protect the upper circuits while minimizing the effects of instrumentation circuit malfunctions. Control circuits are electrical circuits that control the power and heat sources of industrial equipment.
Large industrial motors are controlled to run and stop by electromagnetic contactors, and other drive devices. Although large motors consume oversized amounts of power, the power consumption used to control the drive device tends to be small.
However, the control circuit is of high importance because any abnormality in the control circuit will cause the industrial equipment to lose control. The use of a circuit protector minimizes the effects of a control circuit error.
Principle of Circuit Protectors
Circuit protectors in general use are divided into parts such as trip coils, contact parts, casings, and handles. The trip coil is the part that breaks the circuit by opening the contacts with the magnetic force of the electromagnetic coil in the event of an overcurrent. It is used in the disconnecting mechanism of circuit protector because it has a more immediate response than the bimetal.
The contact part is a metal part that actually conducts electricity to the circuit, and when the contact part opens, the circuit is interrupted. Copper or silver alloys are used as materials. The casing is the outer frame of the circuit protector and is made of insulating resin. It insulates the contacts from the drive spring and mounting bracket.
The handle is an interface component that allows human operation. The handle and spring turn the contacts on and off to control the conductive disconnection. Most circuit protectors are equipped with a trip-free function.
The trip-free function is a function that gives priority to overcurrent trips and opens the contacts even when the handle is locked in the “on” position. This is one of the main functions of a circuit protector and improves the reliability and safety of circuit breakage.
How to Select a Circuit Protector
Circuit protectors are used in instrumentation and control circuits; they are not often used as circuit breakers for 3-phase power motors.
The first step is to check the number of phases in the circuit. Most instrumentation and control circuits are single phase, so select a 1-phase or 2-phase circuit protector.
While a 1-phase circuit protector saves space and is more economical, it does not completely interrupt the circuit. Therefore, use the phase with 0 V to ground voltage as the common phase (common wire); if both phases do not have 0 V to ground voltage, be sure to select a 2-phase or more circuit protector.
A 3-phase circuit protector is used in circuits that indicate 3-phase voltage, such as a voltage indicator. Rarely, they are also used as circuit breakers for small 3-phase motors.
Once the number of phases has been determined, check the current rating of the equipment to be connected to the secondary side; if two or more units are connected, the total value should be used as the rated current, and a circuit breaker with a capacity greater than the rated current should be selected.
If a circuit protector is selected with less than the rated current, there is a high risk of tripping during normal use. Since control and instrumentation circuits are often of high importance and frequent tripping is uneconomical, select a circuit breaker with sufficient capacity.
Other Information on Circuit Protectors
1. Manufacturers of Circuit Protectors
Circuit protectors for industrial equipment are often manufactured by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation in Japan. Ltd. is a specialized manufacturer of FM circuit breakers, which are circuit breakers for wiring.
The company also designs and manufactures related parts such as earth leakage circuit breakers, protectors for electrical equipment protection, current limiters, various power supply devices, and, in an unusual twist, garbage disposers.
Tyco Electronics Japan also manufactures Circuit Protectors, which are sold by Asahi Giken Kogyo. Eaton Electric Japan Corp. also sells circuit protectors.
It is a wholly foreign-owned company and its birthplace is Germany, where electrical control technology was born in 1899. The former company name Muller, with over 100 years of experience since its establishment, became a member of Eaton Gr in the U.S. in 2008. Eaton Electric Japan established its Japan office in 1974, and has been providing customer support in Japan for over 45 years since then.
2. Circuit Protector Pricing
Circuit protector is available at Monotaro, an online retailer, for as low as one dollar. Many circuit breakers are made by major Japanese electronics manufacturers, such as Mitsubishi Electric and Fuji Electric, and are readily available parts unless they are special products.