What Is a Spindle Motor?
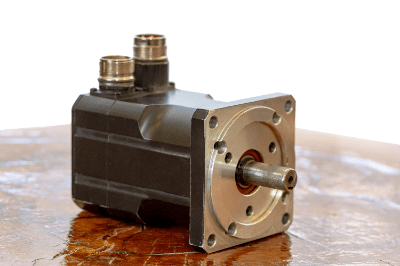 A spindle motor is a motor in which the motor part of the power source and the rotating part are integrated.
A spindle motor is a motor in which the motor part of the power source and the rotating part are integrated.
Since there is only one rotating shaft, the equipment configuration is simplified. A spindle is the rotating shaft of a rotating machine.
It is also called a spindle unit, a term used for machine tools such as lathes. Therefore, a spindle motor refers to a motor integrated with a spindle.
A typical rotation control device consisting of a motor, gears, and belts tends to be complicated to control due to the large number of parts. Spindle motors, however, make it easy to add multiple rotating shafts in parallel in a space-saving manner.
Uses of Spindle Motors
Spindle motors are widely used inside processing machines. The following are examples of spindle motor applications.
- Drilling machines and end mills
- HDD rotation for computers
- Cutting tools such as circular saws
- Drilling and grinding tools
- Arms for cooperative robots and articulated robots
A wide range of product lineup exists, from high-torque types to products capable of high-speed rotation. It is possible to select the optimum product from a variety of spindle motors according to the application.
In recent years, spindle motors have also been used in articulated robots, where the axis of rotation of the robot arm is matched with the axis of the spindle motor. Taking advantage of their space-saving characteristics, spindle motors can also be used to drive HDD rotation.
Principle of Spindle Motors
The structure of spindle motors is often very similar to the widely used servo motors. The spindle is installed coaxially with the axis of rotation. There are two types of motors used: synchronous motors and induction motors.
1. Synchronous Motor
Synchronous motors consist of a rotor made of permanent magnets fixed to a rotating shaft and multiple circular stator units installed around the periphery of the rotor. The stator consists of electric wires wound around an iron core, and when an alternating current flows through it, it acts as an electromagnet and temporarily restrains itself.
Because the phase of the AC current changes from moment to moment, the polarity of the electromagnets also changes with time. Since the polarity of the rotor’s permanent magnet is fixed, it can rotate the rotor by alternating attraction and repulsion with the stator.
2. Induction Motor
Induction motors are motors that use a conductor rotor instead of the permanent magnet rotor of synchronous motors. A cage-shaped metal part is often used for the conductor rotor.
The principle is that a rotating magnetic field generated by the stator generates an electric current in the rotor conductor, causing electromagnetic induction action that rotates the shaft. Unlike synchronous motors, this type of motor is not suitable for fine positioning because of an error called “slippage” in the rotation phase. However, they are widely used for high output products because of their low cost and small number of parts.
Other Information on Spindle Motors
Differences Between Spindle Motors and Servo Motors
Spindle refers to the rotary shaft of industrial rotating equipment used for cutting and grinding. Therefore, the main purpose of spindle motors is cutting and grinding. Motors with ultra-high speed rotation and high torque are often used.
In contrast, servo motors are widely used in precision machinery that requires strict positioning accuracy. Assembly robots and automatic packaging equipment are examples. Driving devices such as encoders are used in motors to detect the rotational position and speed of the rotor.
This detection information is communicated with a PLC or driver to implement feedback control, enabling high-speed rotation to be controlled with high precision. Both spindle motors and servo motors of all types can be applied.
However, induction motors are often used for spindle motors and large-capacity servo motors, while synchronous motors are often used for small-capacity servo motors.