What Is a Brake Disc?
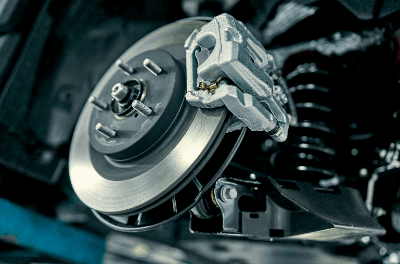
A brake disc is a disc-shaped component used in the braking system to decelerate and stop a vehicle.
There are several types of braking systems used in vehicles, and the disc brake is one of the prominent ones, alongside drum brakes. It comprises the brake disc, brake caliper, piston, and other components.
Also known as a disc rotor, it rotates along with the wheel. During braking, the brake pads inside the brake caliper, driven by force from the piston, clamp strongly on both sides of the brake disc, generating braking force.
Uses of Brake Disc
The brake disc is mounted on the axle as part of the disc brake system and is used for the vehicle’s braking. Due to the exposed nature of the brake disc in the disc brake system, the heat generated during braking can dissipate to the external environment through the brake disc.
This characteristic makes disc brakes less prone to a decrease in braking force (fade phenomenon) caused by the heat of the brake pads, which can be an issue during abrupt braking from high speeds or continuous use. Additionally, even when the brake disc surface is wet, such as in the rain, the rotating disc helps repel water droplets, minimizing the reduction in braking power in wet conditions.
Disc brakes were initially introduced in aircraft and later became widely used in automobiles, motorcycles, trains, and other vehicles. They are now employed in many automobiles.
Principles of Brake Disc
The brake disc is a crucial component of the disc brake, and it is a disc attached to the axle, rotating together with the wheel. Brake discs made of cast iron, known for their wear resistance and high heat dissipation, are predominant.
During braking, the force applied to the piston is used to sandwich the brake pads on both sides of the brake disc, creating friction between them and generating braking force. This action applies the brake to the wheel rotating as a unit.
The lever principle comes into play with the brake disc, and the larger the diameter, the greater the braking force obtained when the brake disc is sandwiched from the outer periphery. However, the brake disc and brake caliper must fit within limits to avoid interference with other components such as the wheel’s interior, suspension, and wheelhouse.
Generally, high-performance or sports vehicles tend to use larger-diameter brake discs.
Types of Brake Disc
Brake discs are classified into solid discs and vented discs based on their shape.
1. Solid Discs
Solid discs consist of a single disc-shaped plate. They are lightweight, providing the advantage of high maneuverability. However, compared to vented discs, the surface temperature of solid discs tends to rise more, making them more susceptible to the fade phenomenon. Therefore, they are used in wheels where braking loads are relatively low, such as the rear wheels of ordinary cars or the front wheels of lightweight vehicles.
2. Vented Discs
Vented discs have a structure where two disc-shaped plates with heat-dissipating cavities on the inside are overlaid with a space in between. While vented discs become heavier compared to solid discs, they offer excellent cooling effects and are less prone to the fade phenomenon, making them suitable for sports driving.
Vented discs are commonly used in vehicles with high braking loads during driving, including sports cars. Additionally, in vehicles where the braking load on the front wheels is greater than the rear wheels due to weight transfer during braking, vented discs are often used in the front wheels, with solid discs in the rear.
Other Information on Brake Discs
Material of Brake Discs
In addition to cast iron, brake discs can be made of carbon ceramic. Brake discs made of carbon ceramic are high-priced products manufactured through complex processes. However, due to their lightweight nature and resistance to performance degradation even under full-throttle driving, they have found adoption in high-priced sports cars and racing cars, among other limited automobile types.