What Is Machining?
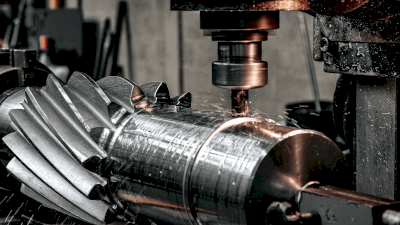
Machining is a processing method in which a blade is used to cut a material.
The product is formed by shaving off unnecessary parts of the material with a tool. Usually, machine tools are used to cut metals and plastics. The machine tools commonly used include lathes, milling machines, and machining centers, which must be selected according to the shape and size required for the process.
The machining methods include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and scraping, and the machining method must be selected according to the application. For example, drilling is selected for drilling threaded holes.
Machining is characterized by high accuracy but is time-consuming. Therefore, it is important to consider the time required for the manufacturing process when introducing this process.
Uses of Machining
Machining is used in all kinds of fields, including parts for electrical products, machinery, and automobiles. Workpieces can be made from a variety of materials, including metal, resin, and wood.
There are also various uses for processing methods. For example, lathe turning is used to cut materials to form round shapes, and drilling is used to form threaded holes. Depending on the application, a processing method should be selected.
Principle of Machining
The principle of machining consists of removing unnecessary parts of the material. For example, if you want to form a round shape, unnecessary parts are removed by lathe turning.
The following five types of machining are typical. The principle of each is as follows:
1. Lathe Turning
Lathe turning is a machining process that utilizes a machine tool called a lathe to perform grinding, drilling, and cutting services. To finish parts neatly and efficiently in lathe turning, it is necessary to adjust the speed of material rotation, the speed of blade movement, and the amount of depth of cut.
These settings will vary depending on the dimensions, shape, and material of the material, as well as the type of cutter, and cannot be determined until actual cutting is performed. Appropriate conditions must be selected by observing the noise and shavings during cutting.
2. Milling
Milling is a process to cut an object by rotating a tool. There are vertical milling machines with the rotation axis in the vertical direction and horizontal milling machines with the rotation axis in the horizontal direction.
The tool is moved in three directions, horizontally and vertically, to make a hole at the required position or cut the surface of the material. Tools called drills and end mills are used as cutting tools. End mills are cutters for flat surface machining. The automatic feed function of the milling machine can be used to produce a clean finish on the machined surface.
3. Drilling
Drilling is a process of drilling a cylindrical hole in a workpiece with a rotary tool, such as a drill. In addition to general drilling using a drill, the following drilling methods are also available.
- Boring
An additional shallow and wide hole is drilled into the screw hole to hide the screw head. - Reaming
Smoothing the inside of a drilled hole. - Tapping
Create a thread inside a hole drilled using a drill.
There are many other processing methods, in addition to those listed above. The machine used for drilling also varies, and different drilling machines, lathes, milling machines, machining centers, and turning centers must be used for different purposes depending on the intended workpiece.
4. Grinding
Grinding is a process for finishing the surface of a material with a grinding wheel. A familiar example of a grinding tool is the whetstone used to sharpen a kitchen knife. It consists of grinding the material with fine and hard abrasive grains.
5. Whittling Process
The kisage process is used to form the material into a perfectly flat surface. This process is characterized by the fact that flat surfaces are processed by hand. The material is removed by rubbing face to face.
Other Information on Machining
Other Machining Methods
In addition to machining, other machining methods include molding, joining, special machining, heat treatment, and surface treatment. Machining is characterized by higher precision than other machining methods.
However, in exchange for the higher precision, it takes more time than other processing methods because of the cutting process. When machining is used in the manufacturing process, it is necessary to manage the process to allow enough time for machining.