What Is a Multitubular Heat Exchanger?
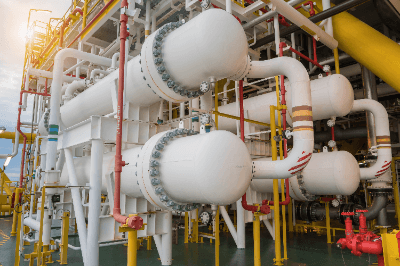 A multitubular heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger.
A multitubular heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger.
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger consists of a thick cylindrical body (shell) and a number of thin tubes to increase the installation area, and heat is exchanged between the fluid flowing on the body side and the fluid on the tube side.
Since the hot and cold fluids must not mix directly but only transfer heat, it is important that both fluids flow through a fixed wall separated by a metal or other material to ensure efficient heat transfer.
In actual use, there are various factors such as the temperature and pressure to be used, the nature of the fluid, and the location of installation, and there are a wide variety of applications. Typical examples of heat exchangers classified by structure are multitubular heat exchangers and plate heat exchangers.
Uses of Multitubular Heat Exchangers
Multitubular heat exchangers can be used for all purposes, from low pressure to high pressure, low or high temperature, super-heating, cooling, evaporation, etc. Therefore, they are not only used in air conditioning and sanitary facilities, but have also been used in various industrial fields, such as chemical plants and oil refining facilities, for many years.
Principle of Multitubular Heat Exchangers
Multitubular heat exchangers can be used in a wide range of applications from low pressure to high pressure and can accommodate high viscosity fluids because their structure allows for a small pressure drop. The simplicity of the structure allows many models to be disassembled, making maintenance relatively easy. Waste heat can also be used on the refrigerant side, leading to energy savings.
A heat exchanger with liquid or gas phase on one side is called a single-phase heat exchanger. Two-phase heat exchangers include those that heat a liquid to boiling gas (steam) (boilers) and those that cool steam to a condensing liquid (condensers), with the phase change usually occurring on the shell side.
Boilers in steam engines are usually large, cylindrical shell-and-tube heat exchangers. In large power plants with steam turbines, shell-and-tube surface condensers are used to condense the exhaust steam from the turbine into condensate, which is then turned back into steam in the steam generator.
Types of Multitubular Heat Exchangers
Among multitubular heat exchangers, they can be broadly classified into three types according to their structure.
1. Fixed Tube Plate Type
The fixed tube-plate type has a simple structure with tubes fixed to tube plates at both ends of the body. To dissipate thermal stress, expansion joints are sometimes provided in the body.
2. U-Tube Type
The U-tube has a U-shaped bend in the pipe, with the end face of the U-tube fixed to the pipe plate on one side of the body. The tube can be freely expanded and contracted.
3. Floating Head Type
The floating head has a fixed tube plate on one side and a floating tube plate on the other side, allowing free movement. The floating head can be disassembled and can be used even in harsh operating environments, but it has the disadvantage of a more complicated structure and a larger number of parts than other types of heat exchangers.
4. Plate Heat Exchanger
The plate heat exchanger has a structure in which high-temperature and low-temperature fluids flow alternately between heat-transfer plates, which are made up of a series of complex press-formed thin plates. Compared to the multi-tube type, the plate heat exchanger has higher heat exchange efficiency and is lighter and more compact than the multi-tube type with equivalent performance, but it cannot be disassembled and is difficult to maintain.
The shape of the heat-transfer plates creates a turbulent effect of fluid flow and prevents dirt from adhering to the plate surfaces, but this structure can cause clogging in the flow path.
Other Information on Multitubular Heat Exchangers
How to Select Tubing Materials
Tubes for multitubular heat exchangers are generally made of metals such as aluminum, copper alloys, stainless steel, carbon steel, and nonferrous copper alloys. Since incorrect selection of tubing material may result in leakage from the shell-and-tube sides, cross-contamination of liquids, and pressure loss, it is important to select tubing carefully by taking the following points into consideration when choosing the right tubing.
- Strength
Since heat is transferred from the hot side to the cold side through tubing, there are temperature differences in the width of the tubing. In addition, tube materials have different coefficients of thermal expansion depending on temperature, so thermal stress occurs during operation, and the fluid itself is subjected to high pressure and thermal stress. - Thermal Conductivity
For successful heat transfer in a heat exchanger, it is important that the tubing material has excellent thermal conductivity. - Corrosion Resistance
To minimize degradation, the tubing material must be compatible for long periods of time with the fluid on both the shell-and-tube sides under operating conditions (temperature, pressure, pH, etc.).